IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 8th July 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Role of international organizations; Security issues
What is CAATSA?
- CAATSA, which came into effect from January 2018; enables the U.S. government to punish entities engaging in significant transaction with the defence or intelligence sectors of Russia, Iran or North Korea.
The law is designed to punish Russian President Vladimir Putin for the
- 2014 annexation of Crimea from Ukraine
- Involvement in the Syrian civil war
- Meddling in the 2016 U.S. presidential election
In news
- Recently, we read about Defence Acquisition Council approving the procurement of 21 MiG-29 fighter jets and upgrading 59 of these Russian aircraft and the acquisition of 12 Su-30 MKI aircraft.
- India has also planned to purchase the S-400 Triumf missile defence system from Russia for about $5 billion.
- The above deals could attract CAATSA sanctions.
- CAATSA law provides for punitive action against countries purchasing defence hardware from Russia.
Species in news: Golden Birdwing
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Environment – Biodiversity and Conservation
In news:
- A Himalayan butterfly named Golden Birdwing is now India’s largest after 88 years.
- Golden Birdwing is larger than the Southern Birdwing, which was earlier considered to be the largest.
- The females (Golden Birdwing) are larger than the males.
- While the female Golden Birdwing was recorded from Didihat in Uttarakhand, the largest male was from the Wankhar Butterfly Museum in Meghalaya capital Shillong.
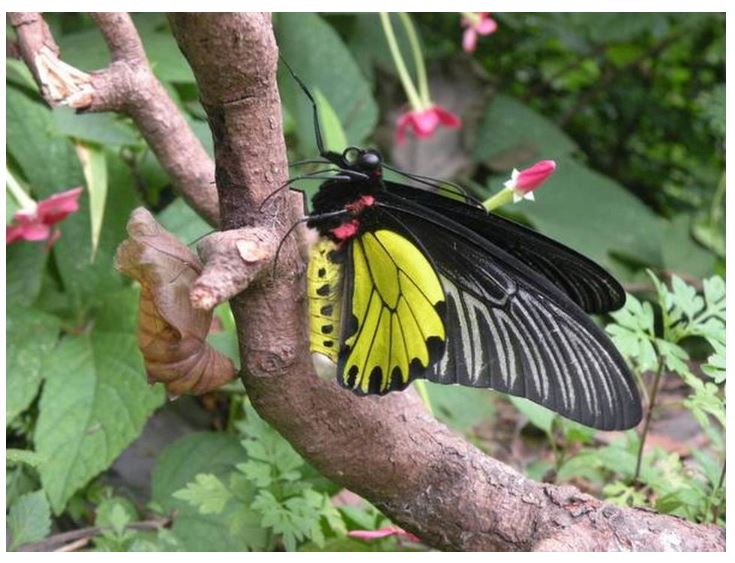

Pic: Golden Birdwing
Do you know?
- Southern Birdwing is listed as Least Concern in the IUCN Red List.
- The species is more common in the Western Ghats of south India and is the state butterfly of Karnataka, India.
Strategic Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldi (DSDBO) road
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I and III – Geography; Defence and Security issues
In news:
- Border Roads Organisation (BRO) to fast-track the work on the strategic Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldi (DSDBO) road.
- DSDBO road runs almost parallel to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) at Aksai Chin.
- China has been objecting to Indian road and infrastructure development at several points along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- DSDBO road is also objected by the Chinese.
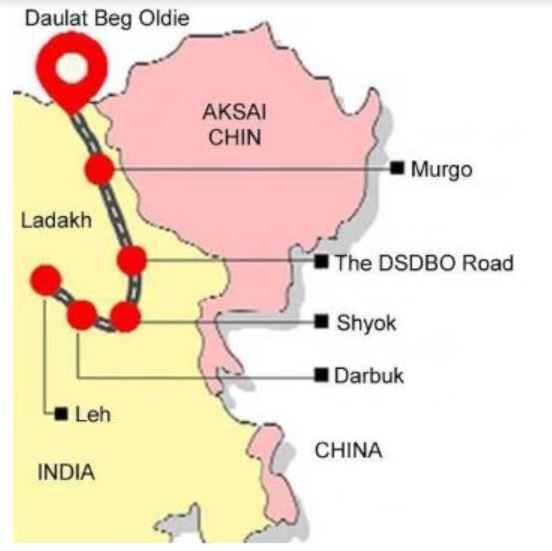
Image source: Click Here
Indo-China Border Roads
- BRO is also building the 61 strategic Indo-China Border Roads (ICBRs), measuring 3,323.57 km, under the direction of the China Study Group (CSG).
- 75% of the construction work on the 61 Indo-China Border Roads (ICBRs) is completed.
Important value additions
The Border Roads Organisation (BRO)
- It was formed in 1960 by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru.
- It was established for coordinating the speedy development of a network of roads in the North and the North Eastern border regions of the country.
- It works under the Ministry of Defence.
- It undertakes variety of construction and development works such as airfields, building projects, defence works, etc.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- India and its neighbourhood relations
- Security & challenges in border areas
Days of disengagement: On India-China LAC standoff
Context: After two months of stand-off along the LAC, India and China are moving towards a full disengagement
Why peace & tranquillity is needed now?
- This was the first time the LAC has seen such casualties in over four decades, disengagement is needed to prevent the tensions spiralling out of control that may lead to a war
- India is battling multiple battle now (COVID-19, Slowing economy, Kashmir reorganisation) and cannot afford to have prolonged border tensions with China
India-China border Clashes during May – To read more about it, Click here
What exactly is the controversy about Galwan Valley? – Click Here
Factors leading to escalation and strategic implication of dispute – Read here
Reducing border tensions & move towards disengagement
- After Diplomacy at high levels (Military & NSA), movement towards de-escalation is said to be taking place in the military build-up at the Line of Actual Control
- While the statements made in New Delhi and Beijing were not identical in language, they largely conveyed a consensus to restore peace and tranquillity at the LAC.
- The next step will be to see their agreements carried out and to ensure that Chinese troops withdraw as promised on each of the three points discussed: Galwan, Hot Springs and Gogra.
Challenges with regard to disengagement process
- Bad precedence: It was during a disengagement verification operation by the Indian troops that the Galwan clash is believed to have occurred.
- Need resolution at other points: Chinese ground units have consolidated their position in the Pangong Tso area. Therefore, similar disengagement exercises will have to be undertaken for other points along the LAC.
- Needs follow-up action: Disengagement and de-escalation must be accompanied by defined “end-points” for troops to withdraw to, to ensure they do not reoccupy positions vacated.
- Communication to Citizens: The government should inform the country about the progress & considered measures such as “buffer zones”, the patrolling-free period, and the reasons for the decision to pull back Indian troops in the areas of disengagement.
Way Ahead
- A full inquiry is needed of the build-up to the clash and the circumstances surrounding the deaths of 20 Indian soldiers.
- The government must consider whether it will continue its course of economic counter-measures against China, that includes
- Banning of apps
- Investment restrictions
- An import slowdown (increased custom duties)
- In small steps over time, India and China must return to a more balanced relationship.
Connecting the dots:
- 1962 Indo-China war
- China’s Belt & Road Initiative
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors
In stand-off, keeping an eye on the nuclear ball
Context: There is now growing evidence that the People’s Republic of China (PRC) continues to expand its nuclear arsenal
Why China is increasing its nuclear arsenal?
- Power projection: An increased nuclear arsenal means a stronger deterrence to China’s opponents
- Against USA: China is pursuing a planned modernisation of its nuclear arsenal because it fears the multi-layered missile defence capabilities of the United States.
-
- China is arming its missiles with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs) capabilities to neutralise America’s missile shield.
- China’s DF-31As, which are road mobile Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs), are equipped with MIRVs and potent penetration aids.
Expansionist mode of China vis-à-vis Nuclear arms
- Increased Tests: The PRC’s ballistic missile tests in 2019 were the highest among the designated Nuclear Weapon States (NWS).
- Increased Nuclear Arsenal: The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) observes that China’s nuclear arsenal has risen from 290 warheads in 2019 to 320 warheads in 2020.
- Tactical Nuclear Weapons: China’s Lop Nur was the site of Chinese sub-critical testing since the PRC adopted a moratorium on hot testing in 1996, enabling China to miniaturise warheads.
- Sizeable Inventory of Fissile materials: China is estimated to possess 2.9+-0.6 metric tonnes of Weapons-grade Plutonium (WGP) compared to India’s is 0.6+-0.15 tonnes of WGP
- Goal to match U.S. & Russian nuclear force levels: The Chinese state mouthpiece, Global Times, has recently called for a 1,000-warhead nuclear arsenal, underlining the motivation of the PLA
Challenges to India due to China’s nuclear expansionism
- Sophisticated nature of Chinese nuclear capabilities relative to India, give Beijing considerable coercive leverage against India which could alter the conventional military balance
- Increased nuclear arsenal could lead China to press ahead with a limited aims war.
- China is believed to base a part of its nuclear arsenal in inland territories such as in the Far-Western Xinjiang Region, which is close to Aksai Chin.
- Korla in Xinjiang is believed to host DF-26 IRBMs with a range of 4,000 kilometres, which can potentially strike targets across most of India. They can be either conventional or nuclear tipped
- China’s land-based missiles are a primarily road mobile and could play a key role in any larger conventional offensive China might mount against India along the LAC.
Way Ahead
- Conventional escalation between Chinese and Indian forces along the LAC must factor the role of nuclear weapons and their impact on military operations
- India’s Strategic Forces Command (SFC) needs to be on a heightened state of alert to ward off any Chinese nuclear threats
- India should start seriously assessing its extant nuclear doctrine and redouble efforts to get a robust triadic capability for deterrence.
Connecting the dots:
- No First Use policy of India’s nuclear doctrine
- Nuclear Suppliers Group and why India is not a part of it?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 CAATSA, which is often seen in news is associated with –
- logistics pact between India and US to build basic ground work and promote interoperability between militaries.
- foundational agreements which the U.S. signs with countries with which it has close military ties.
- punitive action against countries that engage in significant transaction with the defence or intelligence sectors of Russia, Iran or North Korea.
- mechanism instituted for Indian access to the string of U.S. facilities across the globe for logistical support.
Q.2 Consider the following statements with regard to Golden Birdwing
- It is the India’s largest butterfly species endemic to Himalayan region.
- It is the state butterfly of Uttarakhand.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements:
- Department of Border Management is under the Ministry of Defence.
- Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldi (DSDBO) road is a project of the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) in the Ladakh region.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 7th July 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
About China’s muscularity in South China Sea:
About Police violence in wake of TN Custodial deaths:
About reservations: