GS 1, Indian Geography, TLP-UPSC Mains Answer Writing
1. What are shields? How are they formed? Examine the distribution of shields in the world.
ढाल क्या हैं? वे कैसे बनते हैं? दुनिया में ढाल के वितरण की जाँच करें।
Demand of the question:
It expects students to explain about the shields and their formation process. It also expects students to present clear data about the distribution of shields in the world.
Introduction:
A shield is a large area of exposed Precambrian crystalline igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that form tectonically stable areas. These rocks are older than 570 million years and sometimes date back 2 to 3.5 billion years.
Body:
Shields have been little affected by tectonic events following the end of the Precambrian, and are relatively flat regions where mountain building, faulting, and other tectonic processes are minor, compared with the activity at their margins and between tectonic plates.
Formation of Shields:
- A shield is that part of the continental crust in which these usually Precambrian basement rocks crop out extensively at the surface.
- Shields themselves can be very complex: they consist of vast areas of granitic or granodioritic gneisses, usually of tonalitic composition, and they also contain belts of sedimentary rocks, often surrounded by low-grade volcano-sedimentary sequences, or greenstone belts.
- Shield form over the years through processes such as plate tectonics, erosion and glaciations. Plate tectonics refers to the movement and collision of the Earth’s outer crust. When these crustal plates collide they may weld together, forming larger landmasses.
- These rocks are frequently metamorphosed greenschist, amphibolite, and granulite facies. It is estimated that over 50% of Earth’s shields surface is made up of gneiss.
Distribution of shields in the world:
- Shield areas in general are regarded as continental nuclei, the observation often being made that most continental shields are bordered by belts of folded rocks of post-Precambrian age. Following figure 1 represents distribution of shields in the world.
- Shields, occur on each of the continents. One of the best known is the Canadian Shield, which extends from Lake Superior on the south to the Arctic Islands on the north, and from western Canada eastward, to include most of Greenland.
- In South America, the principal shield area is called the Amazonian Shield. It occupies much of the eastern bulge of the continent. Smaller areas of Precambrian rocks to the north and south of the Amazonian Shield are designated the Guiana and Platian shields, respectively.
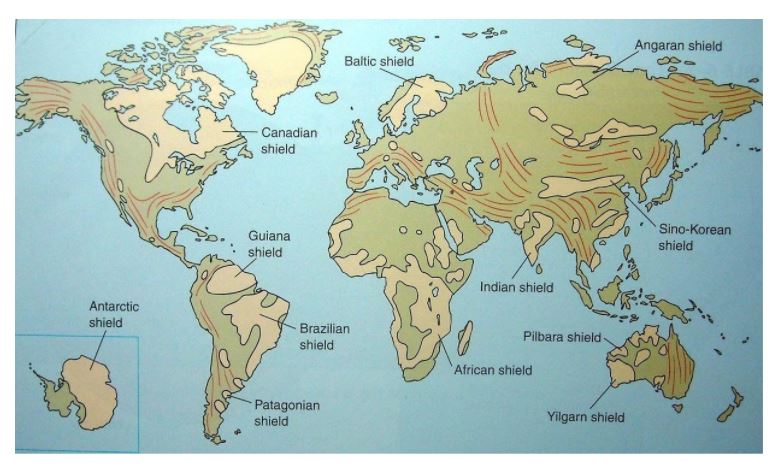
figure 1
- The Baltic, or Fennoscandian, Shield occupies most of Finland and Sweden, as well as eastern Norway. It is bordered on the west by the Caledonian Belt of younger, folded rocks.
- The African Shield, sometimes called the Ethiopian Shield, extends eastward to include western Saudi Arabia and the eastern half of Madagascar.
- The southern two-thirds of peninsular India, most of the western half of Australia, and the eastern segment of Antarctica are also areas of continental shields. These areas of Precambrian rocks are termed, appropriately, the Indian Shield, the Australian Shield, and the Antarctic Shield.
- In Asia the name Angaran Shield is applied to a large stable block bounded by the Lena and Yenisey rivers on the east and west and by the Arctic Ocean and Lake Baikal to the north and south.
Based on their location Shields are also known to provide other economic benefits like:
- Dharwad Shield with laterite soil has promoted development of building materials like bricks.
- Baltic shield: with glacier retreat shield depressions have turned into lakes supporting inland transport in Sweden and Finland.
Conclusion:
We have seen that based on their location shields have different economic significance. Hence, it becomes important to understand more about the characteristics of shields so that their true potential can be used to achieve sustainable development.











