IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
This is a part of our recently launched, NEW INITIATIVE IASbaba’s INTEGRATED REVISION PLAN (IRP) 2020 – Road Map for the next 100 Days! FREE INITIATIVE!
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about the Initiative -> CLICK HERE
SCHEDULE/DETAILED PLAN – > CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
The first hour of every parliamentary sitting is called as which of the following?
Correct
Solution (a)
The first hour of every parliamentary sitting is slotted for the Question Hour. However, in 2014 the Question Hour was shifted in the Rajya Sabha from 11 am to 12 noon.
During this one hour, Members of Parliament (MPs) ask questions to ministers and hold them accountable for the functioning of their ministries.
The questions can also be asked to the private members (MPs who are not ministers).
The presiding officers of the both Houses (Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha) are the final authority with respect to the conduct of Question Hour.
Kinds of Questions: There are three types of questions asked.
- Starred question (distinguished by an asterisk)- this requires an oral answer and hence supplementary questions can follow.
- Unstarred question- this requires a written answer and hence, supplementary questions cannot follow.
- Short notice question is one that is asked by giving a notice of less than ten days. It is answered orally.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
The first hour of every parliamentary sitting is slotted for the Question Hour. However, in 2014 the Question Hour was shifted in the Rajya Sabha from 11 am to 12 noon.
During this one hour, Members of Parliament (MPs) ask questions to ministers and hold them accountable for the functioning of their ministries.
The questions can also be asked to the private members (MPs who are not ministers).
The presiding officers of the both Houses (Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha) are the final authority with respect to the conduct of Question Hour.
Kinds of Questions: There are three types of questions asked.
- Starred question (distinguished by an asterisk)- this requires an oral answer and hence supplementary questions can follow.
- Unstarred question- this requires a written answer and hence, supplementary questions cannot follow.
- Short notice question is one that is asked by giving a notice of less than ten days. It is answered orally.
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Which of the following does not have postal ballot service?
Correct
Solution (d)
Ballot papers are distributed electronically to electors and are returned to the election officers via post.
Currently, only the following voters are allowed to cast their votes through postal ballot:
- Service voters (armed forces, the armed police force of a state and government servants posted abroad),
- Voters on election duty.
- Voters above 80 years of age or Persons with Disabilities (PwD).
- Voters under preventive detention.
The exception to the above-mentioned category of voters is provided under Section 60 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Ballot papers are distributed electronically to electors and are returned to the election officers via post.
Currently, only the following voters are allowed to cast their votes through postal ballot:
- Service voters (armed forces, the armed police force of a state and government servants posted abroad),
- Voters on election duty.
- Voters above 80 years of age or Persons with Disabilities (PwD).
- Voters under preventive detention.
The exception to the above-mentioned category of voters is provided under Section 60 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Mass Spectrometry:
- It is based on ionization and fragmentation of sample molecules in the gaseous phase.
- The instrument operates on the principle that moving ions may be deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
Which of the above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Mass Spectrometry (MS):
- It is an analytical technique used for determining the elemental composition of samples, quantifying the mass of particles and molecules, and elucidating their chemical structure.
- MS is based on ionization and fragmentation of sample molecules in the gaseous phase.
- The instruments used in this technique are called mass spectrometers and mass spectrographs, and they operate on the principle that moving ions may be deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
- Clinical laboratories use the MS technology for disease screening, diagnosis of disease and metabolic disorders, monitoring of drug therapy, identifying drug toxicity and poisoning, and discovering new biomarkers.
- Biomarker is short for biological marker, and is used as an indication that a biological process in the body has happened or is ongoing.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Mass Spectrometry (MS):
- It is an analytical technique used for determining the elemental composition of samples, quantifying the mass of particles and molecules, and elucidating their chemical structure.
- MS is based on ionization and fragmentation of sample molecules in the gaseous phase.
- The instruments used in this technique are called mass spectrometers and mass spectrographs, and they operate on the principle that moving ions may be deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
- Clinical laboratories use the MS technology for disease screening, diagnosis of disease and metabolic disorders, monitoring of drug therapy, identifying drug toxicity and poisoning, and discovering new biomarkers.
- Biomarker is short for biological marker, and is used as an indication that a biological process in the body has happened or is ongoing.
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
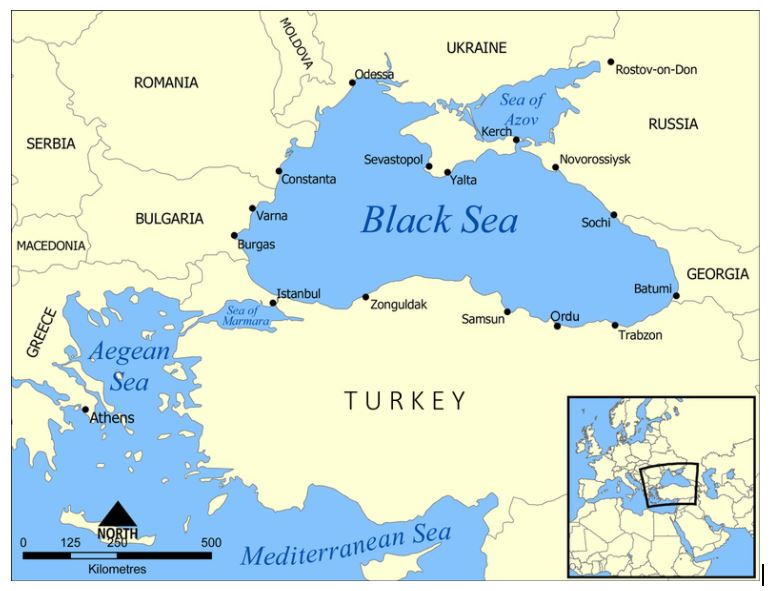
Which of the following country share border with both Black sea and Mediterranean Sea?
Correct
Solution (a)
Turkey is the only county which shares borders with both Black sea and Mediterranean Sea
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Turkey is the only county which shares borders with both Black sea and Mediterranean Sea

-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
which part of the Indian constitution deals with the official languages?
Correct
Solution (a)
Part XVII of the Indian Constitution deals with the official languages in Articles 343 to 351.
- Article 350A (Facilities for instruction in mother-tongue at primary stage) provides that it shall be the endeavour of every State and of every local authority within the State to provide adequate facilities for instruction in the mother-tongue at the primary stage of education to children belonging to linguistic minority groups.
- Article 345: Official language or languages of a State subject to the provisions of Article 346 and 347.
- Article 351 (Directive for development of the Hindi language) provides that it shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Part XVII of the Indian Constitution deals with the official languages in Articles 343 to 351.
- Article 350A (Facilities for instruction in mother-tongue at primary stage) provides that it shall be the endeavour of every State and of every local authority within the State to provide adequate facilities for instruction in the mother-tongue at the primary stage of education to children belonging to linguistic minority groups.
- Article 345: Official language or languages of a State subject to the provisions of Article 346 and 347.
- Article 351 (Directive for development of the Hindi language) provides that it shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language.











