UPSC Articles
ENVIRONMENT/ INTERNATIONAL
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation
US and Paris Agreement
Context: US formally left the Paris Climate Agreement on 4th Nov 2020, three years after President Donald Trump announced his intention to undo what had been seen as a key achievement of his predecessor Barack Obama.
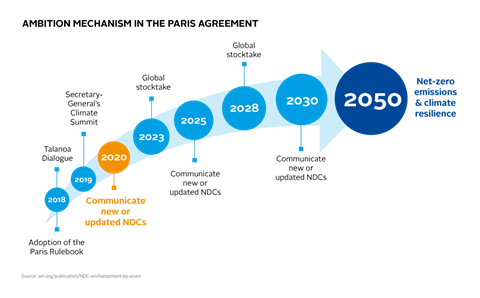
What is the Paris Agreement?
- In December 2015, 195 countries signed an agreement (came into force on Nov 2016) within the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change(UNFCCC), dealing with greenhouse-gas-emissions mitigation, adaptation, and finance
- Objective: To slow the process of global warming by limiting a global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- Another crucial point in this agreement was attaining “net zero emissions” between 2050 and 2100. Nations have pledged “to achieve a balance between anthropogenic emissions by sources and removals by sinks of greenhouse gases in the second half of this century”.
- Developed countries were also told to provide financial resources to help developing countries in dealing with climate change and for adaptation measures.
- As part of a review mechanism, developed countries were also asked to communicate every two years the “indicative” amount of money they would be able to raise over the next two years, and information on how much of it would come from public financial sources.
- In contrast, developing countries have only been “encouraged” to provide such information every two years on a voluntary basis.
- The agreement also includes a mechanism to address financial losses faced by less developed nations due to climate change impacts like droughts, floods etc. However, developed nations won’t face financial claims since it “does not involve or provide a basis for any liability or compensation”.
So, why did the US leave the Paris agreement?
- During his 2016 presidential campaign, Donald Trump had described the Paris Agreement as “unfair” to US interests, and had promised to pull out of the agreement if elected.
- So in June 2017, months after his inauguration, Trump announced his government’s decision to quit the accord
- The US could not immediately exit the Paris Agreement, however, as United Nations rules permitted a country to apply for leaving three years after the accord came into force, i.e. November 4, 2019.
- The US formally applied to leave on that day, and the departure automatically came into effect on November 4, 2020, at the end of a mandatory year-long waiting period
Trend of US retreating from Global leadership role
Since Trump Presidency (2016 onwards), US has
- Quit the U.N. Human Rights Council and U.N. cultural agency UNESCO
- Pulled out of Paris accord and Iran nuclear deal
- Cut funding for the U.N. Population Fund (UNFPA) and U.N. agency that helps Palestinian refugees (UNRWA)
- Opposed a U.N. migration pact
What were the criticisms of US’s withdrawal from Paris accord?
- The step is against the principle of common responsibility.
- The GHGs emissions done is past puts a moral obligation on US to take strict measures to cut it down in future.
- The step take by US may result into domino effect, with other nations too withdrawing from the deal. This would bring to standstill one of the most comprehensive deal for climate change.
- It also provides China an opportunity to show environmental leadership especially with its Climate Commitments made during UN General Assembly in Sep 2020.
- While US is out of Paris deal, many of the US states and companies still consider themselves party to the deal.
Is there any possibility of US joining back the Paris Accord?
- Democratic presidential nominee Joe Biden has long maintained that the US would rejoin if he wins the 2020 US Presidential Elections.
- Thirty days after formally applying to the UNFCCC, the US would again become a part of the Paris framework, and would be required to submit its emission-reduction targets for 2030.
- Joe Biden, who might possibly replace Trump as US President from 2021, has proposed a $2 trillion spending plan that includes promoting clean energy and climate-friendly infrastructure.
India and Climate Emission
- Despite the accelerated economic growth of recent decades India’s annual emissions, at 0.5 tonnes per capita, are well below the global average of 1.3 tonnes.
- China’s total C02 emission is 29.51% of the world and per capita emission is 7.7 whereas USA’s total C02 emission is 14.34% of the world and per capita emission is 16.1.
- In terms of cumulative emissions, India’s contribution by 2017 was only 4% for a population of 1.3 billion, whereas the European Union, with a population of only 448 million, was responsible for 20%.
- India is one of the few countries which is currently on track to fulfilling their Paris Agreement commitments.
Connecting the dots:
- International Solar Alliance
- US to withdraw from WHO











