International Relations
Why in News: India and 12 countries led by the US launched the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- The framework aims to strengthen economic partnership among participating countries to enhance resilience, sustainability, inclusiveness, economic growth, fairness, and competitiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Indian Prime Minister said “The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework is a declaration of our collective will to make the region an engine of global economic growth.”
- Leaders and officials joined in virtually from Australia, Brunei, Indonesia, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- A joint statement said that the countries share a commitment to a free, open, fair, inclusive, interconnected, resilient, secure, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region that has the potential to achieve sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
- The joint statement said that they are launching collective discussions toward future negotiations, and identified four pillars under the IPEF.
- Trade: To build high-standard, inclusive, free, and fair trade commitments and develop new and creative approaches in trade and technology policy that advance a broad set of objectives that fuels economic activity and investment, promotes sustainable and inclusive economic growth, and benefits workers and consumers
- Supply Chains: Committed to improving transparency, diversity, security, and sustainability in supply chains to make them more resilient and well-integrated.
- Clean Energy, Decarbonization, and Infrastructure: In line with Paris Agreement goals and efforts to support the livelihood of peoples and workers, the framework plan to accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy technologies to decarbonize economies and build resilience to climate impacts.
- Tax and Anti-Corruption: Committed to promoting fair competition by enacting and enforcing effective and robust tax, anti-money laundering, and anti-bribery regimes in line with existing multilateral obligations, standards, and agreements to curb tax evasion and corruption in the Indo-Pacific region.
Indo Pacific
- The Indo-Pacific is a geopolitical construct that has emerged as a substitute to the long-prevalent “Asia-Pacific”, which represented the eastwards shift of global developments from Euro-Atlantic dimension
- It is an integrated theatre that combines the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, and the land masses that surround them.
- One of the reasons behind the popularity of this term is an understanding that the Indian Ocean and the Pacific are a linked strategic theater.
- Also, the centre of gravity has shifted to Asia. The reason being maritime routes, the Indian Ocean and the Pacific provide the sea lanes.
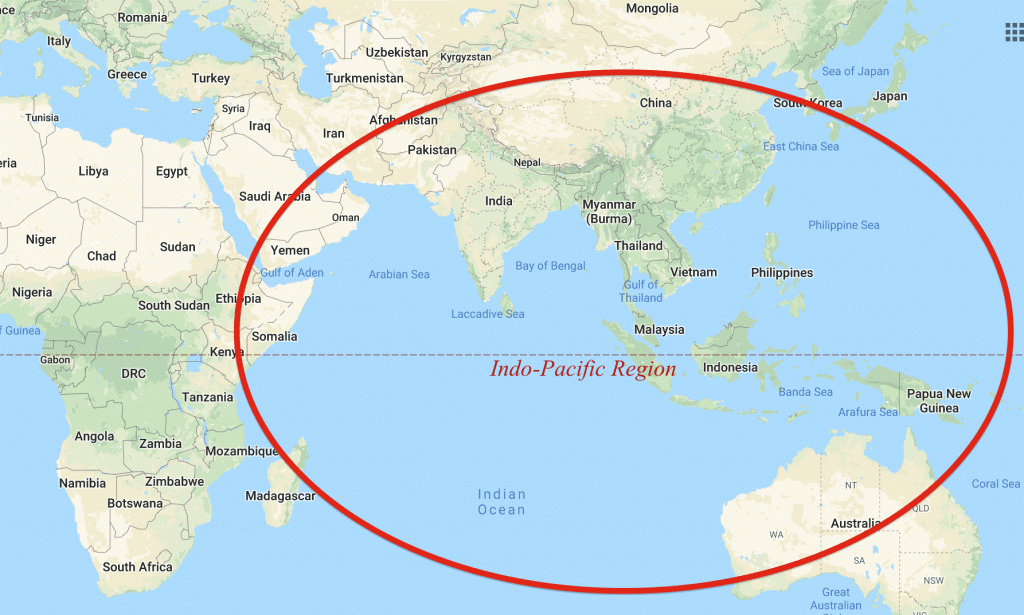
The term ‘Indo-Pacific’ is interpreted differently by different stakeholders.
- India considers the region as an inclusive, open, integrated and balanced space. India continuously emphasizes on strategic inter-connections, common challenges and opportunities between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific.
- The S. considers it to be a free and open Indo-Pacific, highlighting the importance of rules or norms of conduct in the region, thus trying to contain the role of China in the region.
- The ASEAN countries look at Indo-Pacific as a consociational model, thus bringing in China not only for the sake of giving it some stakeholdership but looking for ways to cooperate with it in the region.
Factors driving the global shift towards the Indo-pacific
- Important Sea Lines of Communication – presence of key choke points, from the Mozambique Channel and Bab-el-Mandeb in the west to Lombok Strait in the east
- Flourishing Trade and Economy – The Indo-Pacific Region shares 44% of the world surface area; includes 65% of the world population; accounts for 62% of the world GDP
- Natural resources: The expanse of Indian and Pacific Ocean combined has vast reserves of marine resources including- Offshore Hydrocarbons, Methane hydrates, Sea Bed minerals, Rare earth metals, fisheries etc
- China factor – China’s aggressive foreign policy, rapid economic expansion, military modernization and power projection has raised several red flags among regional and extra-regional countries
- Increasing Militarization of Indian Ocean Region (IOR) – China has established commercial ports across the Indo Pacific, such as Gwadar port (Pakistan), port in Hambantota (Sri Lanka) etc., in addition to its overseas naval base in Djibouti.
India’s interest in the region
- Peace and security in the Indian Ocean: Nearly 50% of India’s trade is centered in the Indo-Pacific Region and the Indian Ocean carries 90% of India’s trade and its energy sources. India wants to assure freedom of navigation, secure choke points, resolve conflicts peacefully and address non-traditional security threats in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Geo-political aspirations: To expand its own presence in the region
- Countering China: Ensuring that China does not gain a significant strategic foothold in the region
- Enhancing Trade and Investment Cooperation: by encouraging greater flow of goods, services, investment and technology between India and other countries in the region.
- Promoting sustainable development in the region, combating marine pollution, Regulating illegal fishing etc
Challenges faced by India in the region
- Limited Naval Capacity and Lack of military bases
- Poor infrastructure connectivity
- Countering China – China has established commercial ports across the Indo Pacific, such as Gwadar port (Pakistan), port in Hambantota (Sri Lanka) etc – India lacks resources for such major projects
Way forward
- It is important to establish connectivity in the region based on respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity, consultation, good governance, transparency, viability and sustainability.
- The countries in the region should have equal access as a right under international law to the use of common spaces on sea and in the air that would require freedom of navigation, unimpeded commerce and peaceful settlement of disputes in accordance with international law.
- Strong naval capabilities, multilateral diplomacy, economic integration in the region is the need of the hour
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1) With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’,
Consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’
- Argentina, Mexico, South Africa, and Turkey
- Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Source: Indian Express & PIB











