Science and Technology
Context: The Indian government asked the smartphone makers to enable support for its NavIC navigation system in new devices sold in the country from next year.
Global standards body 3GPP has approved India’s regional NavIC:
- Earlier, Global standards body 3GPP, which develops protocols for mobile telephony, approved India’s regional navigation system NavIC, developed by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- The specification approval will boost commercial use of NaVIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) by international and domestic mobile device makers, which means such manufacturers can now mass-produce navigation devices compatible with NaVIC so that users of these devices can easily access desi GPS or NaVIC signals.
- The implications of NavIC acceptance by 3GPP would bring NavIC technology to the commercial market for its use in 4G, 5G and Internet of Things (IoT).
- Indian companies and startups will have an opportunity to design integrated circuits (ICs) and products based on NavIC
What is 3GPP:
- It comprises seven telecommunications standard development organisations (ARIB, ATIS, CCSA, ETSI, TSDSI, TTA, TTC) from across the world and provides their members with a stable environment to produce specifications that define 3GPP technologies.
- 3GPP currently has global navigation satellite system support from BDS (Chinese), Galileo (European), GLONASS (Russian) & GPS (US) for cellular positioning system.
About NavIC:
- The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, with an operational name of NavIC, is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system that provides accurate real-time positioning and timing services. It covers India and a region extending 1,500 km around it, with plans for further extension
- NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation, is an independent stand-alone navigation satellite system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It became operational in 2018.
- Three satellites in geostationary orbit and five satellites in geosynchronous orbit. Currently one at stand by.
- Currently, NavIC’s use is limited. It is being used in public vehicle tracking in India, for providing emergency warning alerts to fishermen venturing into the deep sea where there is no terrestrial network connectivity, and for tracking and providing information related to natural disasters.
- Enabling it in smartphones is the next step India is pushing for.
- At full functioning , IRNSS will provide two types of services, namely, Standard Positioning Service (SPS) which is provided to all the users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
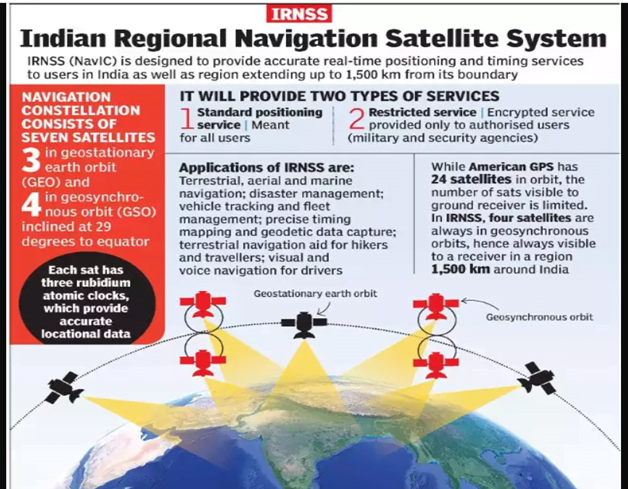
Applications of IRNSS:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation
- Disaster Management
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Integration with mobile phones
- Precise Timing
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements :
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2018)
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Q.2) In which of the following areas can GPS technology be used? (2018)
- Mobile phone operations
- Banking operations
- Controlling the power grids
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3











