Governance
Context: Recently, President Droupadi Murmu while addressing the delegates of a National Workshop on ‘Janjatiya Anusandhan – Asmita, Astitva evam Vikas’ said that the Indian Knowledge System (IKS) that the National Education Policy is currently emphasizing needs to incorporate the knowledge of indigenous tribes.
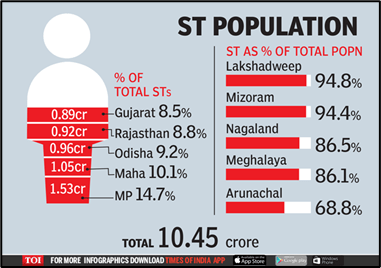
- According to the 2011 Census, the Scheduled Tribes account for 104 million representing 8.6% of the country’s population. The essential characteristics of these communities are:
- Primitive Traits; Geographical isolation; Distinct culture; Shy of contact with community at large; Economically backwards.
About Integrating tribal knowledge systems:
- Tribal knowledge systems represent inter-generational wisdom in band societies passed on to the present times through centuries of experience and learnings.
- Tribal societies have contemporary knowledge of nature due to continued closeness to forests, flora and fauna.
- Tribal methods are based on conservation of knowledge.
- For example, the awareness among tribals of Andaman & Nicobar about a wall of sea helped them against Tsunami in 2004.
Significance of Tribal Knowledge Systems:
- Tribal societies have contemporary knowledge of nature due to continued closeness to forests, flora and fauna. Mainstream societies have moved on to agricultural basis of society, and their cultural knowledge represents impressions of their tribal past, which no longer exists.
- While mainstream knowledge systems are based on rigorous refining and questioning of ideas through discussions and scientific verification, tribal methods are based on conservation of knowledge.
- Tribal knowledge systems are stored in songs and stories, while mainstream knowledge is preserved in books and recordings.
- Tribal knowledge systems promote integrated learning for the community. In mainstream society, knowledge and traditions have bifurcated, with traditions becoming a subject of study instead of mode of studying.
- Tribal knowledge systems are non-exclusionary and marked by equity.
- Mainstreams knowledge systems are mired in barriers like cost of education, patent protections, social exclusion etc.
Government of India Initiatives for Tribal welfare:
Eklavya Model Residential Schools
- The objective of EMRS is to provide quality middle and high-level education to Scheduled Tribe (ST) students in remote areas, not only to enable them to avail of reservation in high and professional education courses and as jobs in government and public and private sectors but also to have access to the best opportunities in education at par with the non-ST population.
Tribes India E-Marketplace:
- Tribes India E-Marketplace is India’s largest handicraft and organic products marketplace.
- The initiative aims to onboard 5 lakh tribal producers for sourcing various handicraft, handloom, and natural food products across the country and brings to you the best of tribal produce.
- The suppliers comprise individual tribal artisans, tribal SHGs, and Organisations/ Agencies/ NGOs working with tribals.
Vanabandhu Kalyan Yojana
- The Government of India, Ministry of Tribal Affairs has launched the Vanabandhu Kalyan Yojana (VKY) for the welfare of Tribals.
- KY aims at creating enabling environment for need-based and outcome-oriented holistic development of the tribal people.
Minor Forest Produce
- Minor Forest Produce (MFP) is more often than not determined by the traders instead of the self-sustained process of demand and supply.
- Implementing a scheme to ensure that such forest dwellers are not deprived of their due.
- Under the scheme maximum selling price for MFP is being implemented in schedule V States initially.
- A web-based portal has also been developed which indicates the current price of MFPs on a real-time basis across different mandis of States.
Van Dhan Scheme:
- The Van Dhan Scheme is an initiative of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and TRIFED. It was launched on 14th April 2018 and seeks to improve tribal incomes through the value addition of tribal products.
- The scheme will be implemented through the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and TRIFED as Nodal Agency at the National Level.
- At the State level, the State Nodal Agency for MFPs and the District collectors are envisaged to play a pivot role in scheme implementation at the grassroots level.
Tribal museums:
- There are records of over 200 tribal freedom fighters across India who participated in about 85 instances of revolts and uprisings against colonial rule.
- To recognise this, 10 tribal freedom fighter museums are being set up in the States of Andhra Pradesh (Lambasingi), Chhattisgarh (Raipur), Goa (Ponda), Gujarat (Rajpipla), Jharkhand (Ranchi), Kerala (Kozhikode), Madhya Pradesh (Chhindwara), Manipur (Taminglong), Mizoram (Kelsey) and Telangana (Hyderabad) will showcase the contribution of tribal freedom fighters.
Way Forward:
- While mutual interaction is visible among tribal and mainstream culture, it is necessary to preserve tribal knowledge by appropriate documentation, including them in disaster management, policy making, thus making India truly inclusive in nature and spirit.
- As India celebrates its 75th year of Independence with ‘Azadi ka Amrit Mahostav’, Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas would be a thoughtful gift for our tribal community and a recall to Ram Rajya where the likes of Guha are given due respect, their cultural diversity is respected, and their contributions celebrated.
Additional Information:
Indian Knowledge System (IKS)
- Indian Knowledge System (IKS) is an innovative cell under Ministry of Education (MoE) at AICTE, New Delhi.
- It is established to promote interdisciplinary research on all aspects of IKS, preserve and disseminate IKS for further research and societal applications.
- It will actively engage in spreading the rich heritage of our country and traditional knowledge in the field of Arts and literature, Agriculture, Basic Sciences, Engineering & Technology, Architecture, Management, Economics, etc.
Functions of IKS:
- Facilitate and coordinate IKS based/related inter and transdisciplinary work done by various institutions in India and abroad including universities, institutions of national importance, R&D laboratories and different ministries and inspire private sector organisations to engage with it.
- Facilitate funding of various projects and develop mechanisms to undertake research.
- Establish, guide and monitor subject-wise interdisciplinary research groups of researchers from institutes, centres and individuals.
- Create and promote popularisation schemes.
- Make Policy recommendations wherever required for the promotion of IKS.
About National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes was established by amending Article 338 and inserting a new Article 338A in the Indian Constitution through 89th Amendment Act, 2003.
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes is a constitutional body.
- Its role is to safeguard the interests of the scheduled tribes or under any other order to the Government and to evaluate the working of such safeguards.
- The Union and every State Government shall consult the Commission on all major policy matters affecting Scheduled Tribes.
- The Commission and its officers participate in formulation of policies and in the developmental programmes for Scheduled Tribes including Tribal Sub-Plan.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
- This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
- This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
- This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
- The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Q.2) At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006? (2021)
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climatic change.
- Ministry of Panchayat Raj
- Ministry of Rural Development
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs











