Environment & Ecology
Context: Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates has invested in an Australian climate technology start-up that aims to curtail the methane emissions of cow burps, according to a report in the BBC.
About Methane:
- Methane (CH4) is a hydrocarbon that is a primary component of natural gas.
- Methane is also a greenhouse gas (GHG), so its presence in the atmosphere affects the earth’s temperature and climate system.
- Methane (CH4) is a colourless, odourless and highly flammable gas.
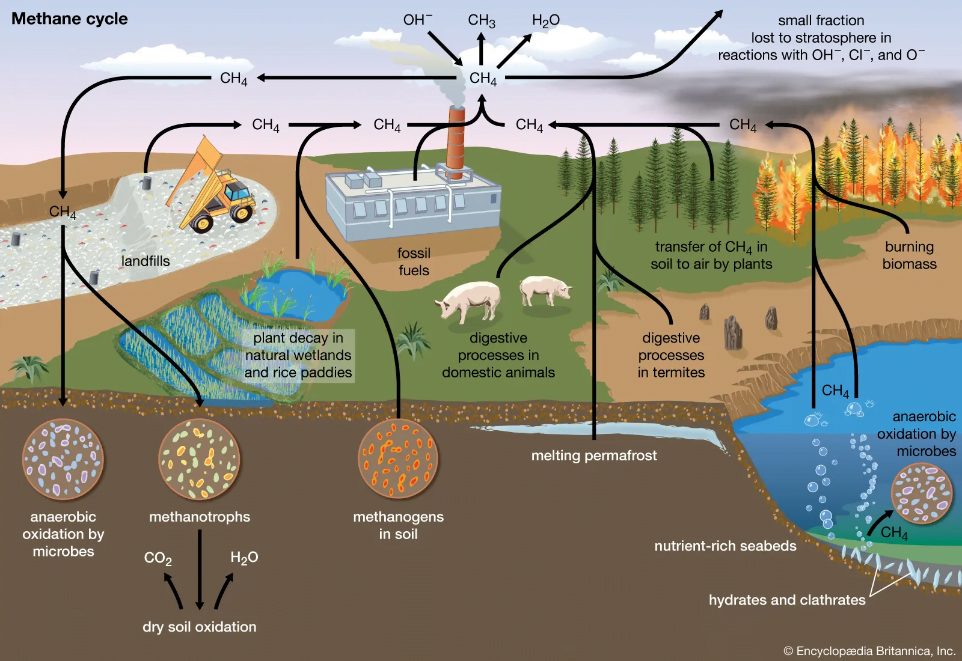
- Methane is the second most abundant anthropogenic GHG after carbon dioxide (CO2), accounting for about 20 percent of global emissions.
- China, the United States, Russia, India, Brazil, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Mexico are estimated to be responsible for nearly half of all anthropogenic methane emissions.
- Because methane is both a powerful greenhouse gas and short-lived compared to carbon dioxide, achieving significant reductions would have a rapid and significant effect on atmospheric warming potential.
Sources of Methane:
- Globally, 50 to 65% of total methane emissions come from the following human-caused activities:
- Raising livestock: Ruminants such as cows, sheep, goats, and buffaloes have a special type of digestive system that allows them to break down and digest food that non-ruminant species would be unable to digest.
- Livestock emissions (from manure and gastroenteric releases) account for roughly 32 per cent of human-caused methane emissions.
- Leaks from natural gas systems
- Landfills and waste from homes and businesses
- Agriculture is the predominant source.
- Paddy rice cultivation in which flooded fields prevent oxygen from penetrating the soil, creating ideal conditions for methane-emitting bacteria – accounts for another 8 per cent of human-linked emission.
Consequences of Methane:
- Potency: Methane is about 80 times more powerful at warming the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period.
- Ozone formation: Methane also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone a hazardous air pollutant and greenhouse gas.
- Global warming: Methane has accounted for roughly 30 per cent of global warming since pre-industrial times and is proliferating faster than at any other time since record keeping began in the 1980s.
Global and Indian Initiatives to tackle Methane Emissions
India Greenhouse Gas Program:
- This Program is an industry-led voluntary framework aiming to help Indian companies monitor progress towards measurement and management of GHG emissions using tools and methodologies from WRI’s (World Resources Institute) GHG Protocol.
Harit Dhara:
- The Harit Dhara is an anti-methanogenic feed supplement prepared from the Natural Phyto-sources.
- It is found very effective in reducing the enteric methane emission upto 17% to 20% when incorporated in the livestock feed.
Methane Alert and Response System:
- UNEP’s International Methane Emissions Observatory launched the Methane Alert and Response System (MARS) at COP27, a new initiative to accelerate implementation of the Global Methane Pledge by transparently scaling up global efforts to detect and act on major methane emissions sources.
Global Methane Initiative:
- It was launched in 2004.
- It is an international public-private initiative that advances cost-effective, near-term methane abatement and recovery and use of methane as a valuable energy source in three sectors: biogas (including agriculture, municipal solid waste, and wastewater), coal mines, and oil and gas systems.
- It focuses on collective efforts and a cost-effective approach to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and increase energy security, enhance economic growth, improve air quality and improve worker safety.
- GMI includes 46 Partner Countries, which together represent approximately 75 percent of the world’s estimated man-made methane emissions.
- Active involvement by private sector entities, financial institutions, and other non-governmental organizations is essential to build capacity, transfer technology, and promote private investment.
Global Methane Pledge:
- The Global Methane Pledge was launched at COP26 in November 2021 to catalyse action to reduce methane emissions.
- Led by the United States and the European Union, the Pledge now has 111 country participants who together are responsible for 45% of global human-caused methane emissions.
- By joining the Pledge, countries commit to work together in order to collectively reduce methane emissions by at least 30% below 2020 levels by 2030.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Among the following crops, which one is the most important anthropogenic source of both methane and nitrous oxide ? (2022)
- Cotton
- Rice
- Sugarcane
- Wheat
Q.2) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a : (2022)
- Database created by coalition of research organisations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank











