IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS2
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Mauritius (March 11-12), will be a celebration of the deep and long-standing ties between the two countries.
Background: –
- Newly elected Prime Minister Navinchandra Ramgoolam (Labour Party) shares a historic connection with India. His father, Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam, led Mauritius to independence and worked with Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose.
Key takeaways
People to people ties
- Nearly 70% of Mauritius population is of Indian origin, mainly descendants of indentured laborers brought by colonial rulers. About 50% trace their ancestry to Bihar and Uttar Pradesh and still speak the Bhojpuri dialect.
- There are smaller communities of Tamil, Telugu-, and Marathi-speaking communities.
- In 1976, India inaugurated the Mahatma Gandhi Institute as a premier institution for promoting Indian languages and culture.
- The Indian Cultural Centre in Mauritius is the largest of anywhere in the world. The island hosts the World Hindi Secretariat that is supported by India.
Economic and Trade Cooperation
- Bilateral trade reached $554 million in 2022-23.
- Mauritius serves as a business gateway to Africa, being part of the African Union.
- Due to a favourable Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) with India, Mauritius is also a major channel for foreign investment into India.
- Mauritius has emerged as a successful international financial centre.
Maritime Security Cooperation
- Mauritius is strategically located in the western Indian Ocean.
- The Colombo Security Conclave brings together India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, Mauritius and Bangladesh to ensure regional maritime security.
- Mauritius has a vast EEZ of 2.3 million sq. km, making surveillance vital.
- India has set up a chain of coastal radar stations, redeveloped the Mauritian island of Agaléga to serve as a joint surveillance facility and given Mauritius access to the Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) in Gurugram, to significantly advance domain awareness in its vast EEZ.
- India’s oceanographic survey ship, INS Sarvekshak, has completed the survey of 25,000 sq.km of Mauritius’ ocean territory.
- At a time when China’s footprint in the Indian Ocean is expanding, India-Mauritius maritime security cooperation has assumed special importance.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: The Centre declared the Madhav National Park in Madhya Pradesh as the country’s 58th tiger reserve on Sunday (March 9, 2025).
Background: –
- Three tigers, including two females, were introduced to the Madhav National Park in 2023 as part of the tiger reintroduction project in the State.
- Madhav National Park is country’s 58th tiger reserve and also the ninth from the State of Madhya Pradesh.
- Notably, on December 2, 2024 India got its 57th tiger reserve in the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary of Madhya Pradesh.
Key takeaways
- Madhav National Park is a protected area located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, India.
- Established in 1959, Madhav National Park was originally a hunting ground for the erstwhile Scindia royal family. the park was named after Madho Rao Scindia, the Maharaja of Gwalior.
- Madhav National Park is situated in the northern part of Madhya Pradesh. It lies on the northern fringe of the Central Highlands of India, forming part of the Upper Vindhyan Hills intermixed with plateaus and valley sections.
- Notable lakes within the park include Sakhya Sagar and Madhav Sagar, both created by damming the Manihar River.
- Fauna: Madhav National Park hosts a variety of wildlife, including:
- Mammals: Species such as the Indian gazelle (Chinkara), Chital (Spotted deer), Nilgai (Blue bull), Sambar deer, Four-horned antelope (Chousingha), Sloth bear, Leopard, Indian wolf, Jackal, Bengal fox, Dhole (Wild dog), Wild boar, and Porcupine.
- Reptiles: The park is home to reptiles like the Mugger crocodile, various turtle species, and snakes.
- Birds: The lakes attract numerous migratory birds during winter, including species of geese, ducks, and waders.
Historical Significance:
- George Castle: At the park’s highest point (484 meters), George Castle was built in 1911 by Madho Rao Scindia for an anticipated visit by King George V, although the king never stayed there.
Conservation Efforts:
- Ramsar Site: In January 2022, a 248-hectare area around Sakhya Sagar Lake within the park was designated as a Ramsar site, recognizing its importance as a wetland of international significance.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: India is set to roll out its first domestically manufactured semiconductor chip in 2025.
Background:
- This initiative aims to reduce India’s dependency on semiconductor imports, which have risen significantly over the past decade.
Key takeaways
Semicon India Programme
- The Semicon India Programme, launched in 2021, aims to develop the semiconductor and display manufacturing ecosystem.
- Key Initiatives: Five manufacturing facilities are under construction for the manufacturing and assembly of semiconductor chips, backed by the Semicon India Programme.
- Notable projects:
- Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test Facility – Morigaon, Assam.
- Dholera Semiconductor Fabrication (Fab) Facility – Tata Electronics in collaboration with Taiwan’s Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation.
- However, the actual spending under the Semicon India Programme has consistently fallen short of budgeted allocations.
India’s Semiconductor Import Dependency
- India heavily relies on semiconductor imports, with key imports including:
- Monolithic Integrated Circuits (ICs) – Used in CPUs, smartphones, automobiles, medical devices, and industrial automation.
- Memory Chips – Includes volatile (RAM) and non-volatile (NAND flash).
- Amplifiers – Used in wireless communication and audio equipment.
- Import trends (FY16-FY24):
- Monolithic IC imports increased by 2,000%.
- Memory chip imports surged by 4,500%.
- Amplifier imports rose by 4,800%.
- Semiconductor imports now constitute a higher share of total imports, with monolithic ICs forming 2.09% of total imports in FY25, up from 0.19% in FY16.
- Major Semiconductor Suppliers to India
- Top Supplier: China (except FY19).
- Other key sources: Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Taiwan.
Challenges in India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem
- With the new facilities, India will be able to add value in the assembly, testing, and packaging, and fab segments of the global value chain for semiconductors, but it is yet to make major strides in –
- EDA (Electronic Design Automation) software – Critical for chip design.
- Core IP (Intellectual Property) – Patents for semiconductor technology.
- Wafers – Key raw material for chip fabrication.
- Fab tools and ATP (Assembly, Testing, and Packaging) tools – Machinery required for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Chip design capabilities – India needs to invest more in R&D to develop indigenous chip designs.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims- CURRENT EVENT
Context: After receiving a nod from the State Wildlife Board of Karnataka in January, the controversial Sharavathi pumped-storage project has now secured final approval from the state government.
Background: –
- The project has encountered environmental concerns, particularly due to its location within the Sharavathi Lion Tailed Macaque Sanctuary.
Key takeaways
- The project is situated on the Sharavathi River in Karnataka, India. The Sharavathi River is a vital source of hydroelectric power in the region and is known for the Jog Falls, one of the highest waterfalls in India.
Key Features:
- Capacity: The project is designed to generate 2,000 megawatts (MW) of power, utilizing eight units of 250 MW each.
- It leverages existing water bodies—the Talakalale and Gerusoppa reservoirs—as the upper and lower reservoirs, respectively. The Talakalale dam, standing at 62.48 meters, and the 64-meter high Gerusoppa dam are integral to the project’s infrastructure.
- During periods of low electricity demand, water will be pumped from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir using grid power. When electricity demand is high, water from the upper reservoir will be released to generate electricity.
Additional Information – Sharavathi River
- The Sharavathi River is a west-flowing river in Karnataka.
- It originates in the Western Ghats and flows into the Arabian Sea, making it an important river for Karnataka’s water resources and biodiversity.
Source: Bangalore Mirror
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
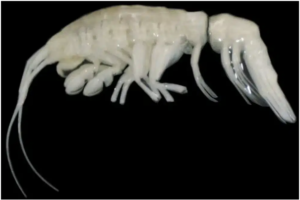
Context: Marine biologists have discovered a new species of amphipod, named Dulcibella camanchaca, hidden in the extreme depths of the Atacama Trench.
Background: –
- The discovery of this species highlights the incredible diversity of life forms that have evolved to survive in the most extreme conditions on our planet.
Key takeaways
- Dulcibella camanchaca is a species of amphipod crustacean discovered in the Atacama Trench, one of the deepest parts of the ocean.
- This species was found at depths of nearly 8,000 meters (26,000 feet) in the South Pacific Ocean near Chile. The Atacama Trench is known for its extreme conditions, including crushing pressure, frigid temperatures, and complete darkness.
Physical Characteristics
- Size: Dulcibella camanchaca measures approximately 4 centimeters (1.6 inches) in length, making it larger than most amphipods found at similar depths.
- Appearance: This amphipod has specialized appendages designed for capturing and consuming smaller crustaceans, indicating its predatory nature.
Ecological Role
- Predatory Behavior: Unlike many deep-sea amphipods that scavenge for food, Dulcibella camanchaca is an active predator. It uses its specialized appendages to capture and consume smaller crustaceans.
- Adaptations: This species is adapted to the extreme conditions of the hadal zone, making it one of the deepest-living predators identified to date. The hadal zone encompasses ocean depths between 6,000 and 11,000 meters.
Source: Times of India
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to Madhav National Park, consider the following statements:
- It is located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh.
- The park was originally a hunting ground for the Scindia royal family.
- Sakhya Sagar Lake within the park has been designated as a Ramsar site.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) With reference to the Sharavathi Pumped Storage Project, consider the following statements:
- It is located on the Sharavathi River in Karnataka.
- The project uses the Talakalale and Gerusoppa reservoirs for energy storage.
- It is located outside any ecologically sensitive zone and does not impact wildlife.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Dulcibella camanchaca, recently discovered in the Atacama Trench, belongs to which of the following groups of marine organisms?
(a) Mollusks
(b) Amphipods
(c) Echinoderms
(d) Cnidarians
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 8th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b














