Ethics Theory, TLP-UPSC Mains Answer Writing
Q. 2. Differentiate between tropical and temperate cyclones in terms of formation, structure, and impact. Explain their relevance to India. (150 words, 10 marks)
Introduction
Cyclones are large-scale air masses that rotate around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure. They are classified into tropical and temperate types based on their origin, characteristics, and geographical occurrence.
Body
Differences Between Tropical and Temperate Cyclones
| Feature Tropical Cyclones Temperate Cyclones | ||
| Formation
Region: |
Originate over warm tropical oceans (5°–30° latitudes) | Originate over mid-latitudes (35°–65°) mostly over land-ocean boundaries |
| Energy Source: | Latent heat from warm ocean water | Temperature contrast between warm and cold air masses |
| Structure: | Symmetrical, circular, tightly packed isobars | Asymmetrical, comma-shaped, with frontal systems |
| Vertical Extent: | Extend vertically up to the tropopause (~12–14 km) | Extend from surface to tropopause, more slanted |
| Fronts: | No fronts; warm-core system | Possess warm and cold fronts; cold core system |
| Wind Speed: | Very high (can exceed 200 km/h) | Moderate (typically 100–150 km/h) |
| Rainfall Pattern: | Heavy and concentrated around the eye wall | Moderate to heavy, spread over larger area |
| Duration &
Movement: |
Last several days; relatively slow movement | Last 5–7 days; faster movement |
Relevance to India
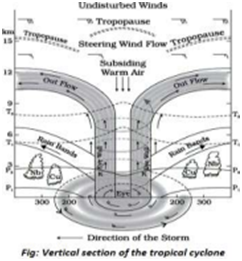
- Tropical Cyclones
- Affect India’s east coast (Bay of Bengal) and to a lesser extent, west coast (Arabian Sea), especially between May–June and October– November.
- Cause heavy rainfall, flooding, storm surges, and crop damage. Example: Cyclone Amphan (2020) and Cyclone Biparjoy (2023).
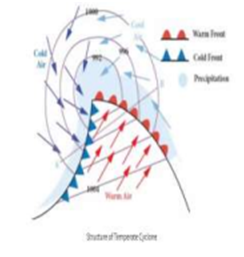
- Temperate Cyclones (Western Disturbances)
- Influence northern India during winter, bringing rain and snow to the Western Himalayas and northern plains.
- Vital for rabi crops like wheat and mustard. Example: January 2024 Western Disturbance caused widespread snow in Kashmir.
Conclusion











