भारत में जैव-उपचार /बायोरेमेडिएशन: आवश्यकता, प्रकार, सरकारी प्रयास और चुनौतियां (Bioremediation in India: Need, Types, Government Efforts & Challenges)
(यूपीएससी जीएस पेपर III — “पर्यावरण; प्रदूषण नियंत्रण; जैव प्रौद्योगिकी; सरकारी नीतियां और हस्तक्षेप”)
संदर्भ (परिचय)
भारत के तीव्र औद्योगिकीकरण ने मिट्टी, पानी और वायु प्रदूषण को तेज कर दिया है। पारंपरिक उपचार विधियों के महंगे और अस्थिर साबित होने के साथ, बायोरेमेडिएशन एक कम लागत वाला, मापनीय और पर्यावरण के अनुकूल विकल्प प्रदान करता है, विशेष रूप से प्रदूषित नदियों, भूमि और औद्योगिक स्थलों की सफाई के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
मुख्य तर्क
- औद्योगिक प्रदूषण संकट: गंगा और यमुना जैसी नदियों को रोजाना अविरलित सीवेज और औद्योगिक अपशिष्ट मिलते हैं, जिससे कम लागत वाला जैविक सफाई आवश्यक हो जाता है।
- सतत विकल्प: पारंपरिक उपचार विधियां ऊर्जा-गहन, महंगी होती हैं और कभी-कभी द्वितीयक प्रदूषण उत्पन्न करती हैं; बायोरेमेडिएशन प्रकृति-संचालित और कम संसाधन-गहन है।
- पारिस्थितिक बहाली: बायोरेमेडिएशन तेल रिसाव, कीटनाशक अवशेष और भारी धातु प्रदूषण को संबोधित कर सकता है जो पारिस्थितिक तंत्र और सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य को प्रभावित करते हैं।
- जैव विविधता लाभ: भारत के विविध देशज सूक्ष्मजीवी उपभेद, स्थानीय जलवायु के अनुकूल, आयातित प्रजातियों की तुलना में उच्च दक्षता प्रदान करते हैं।
- आर्थिक व्यवहार्यता: बायोरेमेडिएशन संसाधन-विवश स्थानीय निकायों के लिए उपयुक्त है और स्वच्छ भारत, नमामि गंगे, और हरित प्रौद्योगिकी मिशनों के तहत समकालीन लक्ष्यों का समर्थन करता है।
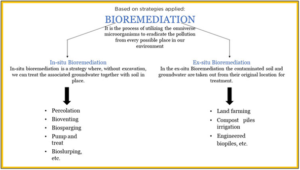
बायोरेमेडिएशन के प्रकार
- इन सीटू बायोरेमेडिएशन: प्रदूषण स्थल पर उपचार – उदाहरण के लिए, तेल खाने वाले बैक्टीरिया को सीधे रिसाव पर छिड़कना।
- एक्स सीटू बायोरेमेडिएशन: प्रदूषित मिट्टी या पानी को हटाकर नियंत्रित सुविधाओं में उपचार किया जाता है और विषमुक्ति के बाद वापस लौटाया जाता है।
कैसे पारंपरिक सूक्ष्म जीव विज्ञान अत्याधुनिक जैव प्रौद्योगिकी के साथ जुड़ता है
- उन्नत सूक्ष्मजीवी पहचान: आधुनिक जीनोमिक्स प्रदूषक-निम्नीकरण गुणों वाले सूक्ष्मजीवों की पहचान करने में मदद करता है।
- आनुवंशिक रूप से संशोधित सूक्ष्मजीव: जीएम बैक्टीरिया प्लास्टिक, तेल अवशेषों या लगातार रसायनों को निम्नीकृत कर सकते हैं जो प्राकृतिक प्रजातियां नहीं कर सकतीं।
- बायोअणुओं का प्रतिकृतिकरण: जैव प्रौद्योगिकी उपकरण सीवेज उपचार और कृषि में उपयोग के लिए उपयोगी सूक्ष्मजीवी एंजाइमों की प्रतिकृति बनाना संभव बनाते हैं।
- नैनोबायोटेक्नोलॉजी: आईआईटी शोधकर्ताओं ने तेल रिसाव को सोखने के लिए सूती आधारित नैनोकम्पोजिट विकसित किए हैं।
- लक्षित अनुप्रयोग: इंजीनियर एंजाइम और सूक्ष्मजीवी कंसोर्टिया को साइट-विशिष्ट विषाक्त पदार्थों को निम्नीकृत करने के लिए अनुकूलित किया जाता है।
बायोरेमेडिएशन का समर्थन करने वाली सरकारी पहलें
- डीबीटी स्वच्छ प्रौद्योगिकी कार्यक्रम: बायोरेमेडिएशन समाधानों पर शिक्षाविदों, अनुसंधान प्रयोगशालाओं और उद्योग को जोड़ने वाली परियोजनाओं को निधि देता है।
- सीएसआईआर-नीरी जनादेश: भारत भर में प्रदूषित स्थलों के लिए बायोरेमेडिएशन ढांचे विकसित और तैनात करता है।
- स्टार्ट-अप इकोसिस्टम समर्थन: बीसीआईएल और इकोनिर्मल बायोटेक जैसे संगठन मिट्टी और अपशिष्ट जल के लिए सूक्ष्मजीवी समाधान प्रदान करते हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय मिशनों के साथ एकीकरण: स्वच्छ भारत मिशन, नमामि गंगे, शहरी अपशिष्ट जल प्रबंधन सुधार और आगामी हरित प्रौद्योगिकी पहलों के साथ संभावित संबंध।
भारत में अपनाने की चुनौतियां
- स्थल-विशिष्ट ज्ञान की कमी: विभिन्न प्रदूषक और मिट्टी/पानी की स्थितियों के लिए अनुकूलित सूक्ष्मजीवी समाधानों की आवश्यकता होती है, जो अक्सर उपलब्ध नहीं होते।
- जटिल प्रदूषक: मिश्रित रसायन, माइक्रोप्लास्टिक और भारी धातुओं जैसे औद्योगिक प्रदूषकों के लिए बहु-उपभेद या उन्नत जैव प्रौद्योगिकी समाधानों की आवश्यकता होती है।
- कमजोर मानक: भारत में सूक्ष्मजीवी अनुप्रयोगों और बायोरेमेडिएशन प्रोटोकॉल के लिए एकीकृत राष्ट्रीय मानकों की कमी है।
- जैव सुरक्षा जोखिम: जीएम सूक्ष्मजीवों को पारिस्थितिक असंतुलन या अनपेक्षित प्रसार को रोकने के लिए सख्त निगरानी की आवश्यकता होती है।
- क्षमता अंतराल: सीमित प्रशिक्षित कर्मियों, कमजोर जागरूकता और अपर्याप्त स्थानीय बुनियादी ढांचे से बड़े पैमाने पर विस्तार बाधित होता है।
निष्कर्ष
बायोरेमेडिएशन भारत को देशज जैविक संसाधनों का उपयोग करके प्रदूषित पारिस्थितिक तंत्र को बहाल करने का एक शक्तिशाली मार्ग प्रदान करता है। हालांकि, जिम्मेदार विस्तार के लिए राष्ट्रीय मानकों, जैव सुरक्षा ढांचों, स्थानीयकृत अनुसंधान केंद्रों और सार्वजनिक जुड़ाव की आवश्यकता है ताकि यह सुनिश्चित किया जा सके कि जैव प्रौद्योगिकी पारिस्थितिक बहाली को मजबूत करती है , न कि खतरे में डालती है।
मुख्य प्रश्न
प्र. बायोरेमेडिएशन/ जैव-उपचार क्या है? उपयुक्त उदाहरणों के साथ शामिल तंत्रों की व्याख्या करें। भारत की अपशिष्ट प्रबंधन रणनीति में इसकी भूमिका की जांच करें और इसके अपनाने को बढ़ावा देने वाली प्रमुख सरकारी पहलों की रूपरेखा तैयार करें। (250 शब्द, 15 अंक)
स्रोत: द हिंदू