IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs July 2015, National, UPSC
Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs- 11th July, 2015
NATIONAL
PSLV C-28 launches five UK satellites
In the heaviest commercial launch since its inception, the Indian Space Research Organisation’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) launched five satellites, weighing 1,440 kg for a United Kingdom-based company.

What are the Must Know facts about PSLV-C28?
- This is the 30th flight of the PSLV since it became operational in 1995, with one early failure
- It is launching 5 UK satellites
- The satellites totally weigh 1,440 kg, the heaviest paid PSLV service to date
- Launch site Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota is in Andhra Pradesh and about 70 km from Chennai
- Also its ninth flight in the modified `extended’ configuration, called XL
- ISRO has so far launched about 40 small to medium size foreign satellites for a fee
- Of today’s payloads, 3 are identical mini satellites, weighing 447 kg each
- They are DMC-3 1, 2 and 3 optical earth observation satellites; 91-kg CBNT-1 micro-satellite; and the 7 kg De-orbitSail
- DMC-3 satellites are each 3m high. ISRO designed a circular launcher adaptor and a triangular deck to fit them in
- The late-night flight helps the UK operator to get control over them in orbit at suitable time
- Nearly 63-hour countdown began on July 8 at 7.28 a.m.
Why are all satellites and missiles launched from the east coast?
- The surface velocity of rotation varies from point to point on the Earth. It is about 1600 km per hour or about 460 meters in a second near the equator.
- The velocity gradually reduces as we move to the poles and it is practically zero there. A satellite launched from the sites near the equator towards the east direction will get an initial boost equal to the velocity of Earth surface. This is similar to an athlete circling round and round before throwing a discus or a shot put.
- The initial boost helps in cutting down the cost of rockets used to launch the satellites.
- This is the major reason for launching satellites in the east ward direction.
What is the difference between GSLV and PSLV?
- Both PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) and GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) are the satellite-launch vehicles (rockets) developed by ISRO.
- PSLV is designed mainly to deliver the “earth-observation” or “remote-sensing” satellites with lift-off mass of up to about 1750 Kg to Sun-Synchronous circular polar orbits of 600-900 Km altitude.
- The GSLV is designed mainly to deliver the communication-satellites to the highly elliptical (typically 250 x 36000 Km) Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- The satellite in GTO is further raised to its final destination, viz., Geo-synchronous Earth orbit (GEO) of about 36000 Km altitude (and zero deg inclination on equatorial plane) by firing its in-built on-board engines.
Connecting the dots:
- Why is PSLV-C28 accounted as heaviest commercial vehicle so far?
- What are the Major Applications of PSLV-C28?
SCO decides to include India as full-time member
- Beijing-based SCO currently has China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan as members.
- India, which has an Observer status for the past 10 years, will technically become the member by next year after completion of certain procedures.
What and who of SCO
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation or SCO or Shanghai Pact is a Eurasian political, economic and military Organisation which was founded in 2001 in Shanghai by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- These countries, except for India, Pakistan and Uzbekistan had been members of the Shanghai Five, founded in 1996; after the inclusion of Uzbekistan in 2001, the members renamed the Organisation.
- After over a decade, on July 2015, SCO decided to include India and Pakistan as full-time members.
What are the activities of SCO?
- Cooperation on security
- Military activities
- Economic cooperation
- Cultural cooperation
How are the relations of SCO and the WEST?
- While the SCO (together with the BRICS) is described by Western analysts as a way for Russia and China to cooperate with each other in creating stability in Central Asia as well as challenging the current, Western-dominated global order, the organisation’s lack of resources are seen as a sign of weakness.
- The United States applied for observer status in the SCO, but was rejected in 2005.
- The SCO has made no direct comments against the U.S. or its military presence in the region; however, some indirect statements at the past summits have been viewed by the western media as “thinly veiled swipes at Washington”
Connecting the Dots:
- Why the International Federation has for Human Rights has called SCO a “vehicle” for human rights violations?
- What are the Geo Political Advantages and Disadvantages of Permanent Member status of India in SCO?
Gujarat and Tamil Nadu lead in project clearance in coastal areas
- The State Coastal Zone Management Authorities (SCZMA) of Gujarat and Tamil
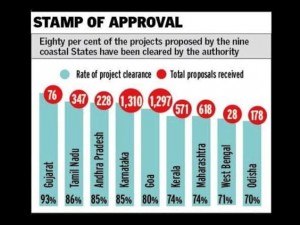 Nadu have topped in granting clearances to proposed projects in last two decades.
Nadu have topped in granting clearances to proposed projects in last two decades. - A recent report by the Centre for Policy Research (CPR) and Namati, titled “Coastal Zone Management Authorities (CZMAs) and Costal Environments: Two decades of regulating land use change on India’s coastline” shows that Gujarat topped the list with 93% rate of project clearance, with only one project was rejected out of 76 proposals.
What is the role of The State Coastal Zone Management Authorities (SCZMA)?
- To take measures for protecting and improving the quality of the coastal environment
- Examination of proposals for changes or modification in classification of Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) areas
- Enquiry into cases of alleged violation of the provisions of the CRZ Notification, 1991 and take appropriate decision under Section-5, 10 & 19 of Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- To examine all projects proposed in CRZ areas and give their recommendations
- To identify ecologically, economically and highly vulnerable areas of the coastal zone and formulate area specific management plans.
Why there are many rejections in other states?
- The Report relies on 39 interviews with sitting and ex-members of the CZMAs and staff, consultants and officers of the MoEFCC in charge of implementation of the CRZ Notification and analyses the functioning of CZMAs on their key tasks – project appraisals, coastal zone mapping, action against violations and conservation of coastal areas.
- If one blames the environmental laws and authorities to delay the approval of projects along India’s coastline, the report challenges the apprehensions.
Connecting the Dots:
- Write a note on structure, functioning and performance of Coastal Zone Management Authorities (CZMAs).
- Explain the role of Coastal Regulatory Zone/Authorities (CRZ) in protecting Environment.
Did you know?
|








