Polity Strategy
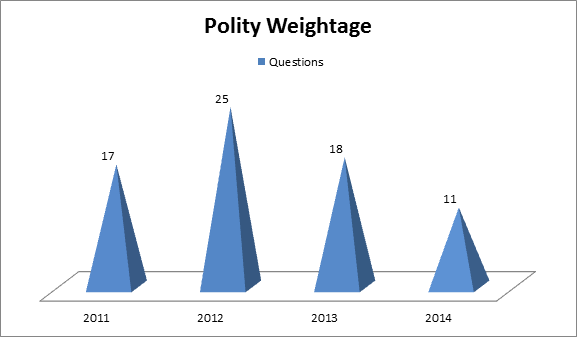
Weightage given to Indian Polity (since 2011)
So on an average 15%-18% of the questions come from Indian Polity. Because of the significance of weightage given in the exam, Polity as a subject becomes even more important in the preparation process.
How to Prepare
Polity is an important topic at all the three stages of exam, be it Prelims, Mains or Interview. The significance of the subject is carried forward, even when you get into the service. It forms an important part of administration. The topics under Polity range from –
Everything about Constitution, individual’s rights, duties and responsibilities to structure, power, functions and responsibilities of various institutions of administration. It also discusses about various policies of the Government, rights-based issues of the vulnerable groups.
So, one has to be abreast with the local happenings in and around you. A sense of awareness is created in the mind of the common man – about one’s rights, duties, responsibilities and help him/her to take an informed decision. It also helps in holding the Government accountable for failing to serve its people.
This is what makes Polity interesting and enjoyable. Henceforth, we recommend Polity to be read, not only as a civil service aspirant, but every Indian !!
Now, coming to the exam scenario
Questions from Polity cover both static (basic) as well as the dynamic (current events) part. For example in 2014, Judicial Appointment Bill was in news very frequently.
So, one must know the basics of Judiciary – its mode of appointment, powers and its autonomy granted by the Constitution of India.’ Issue’ related to Judiciary’s autonomy comes under the dynamic part whereas the mode of appointment and powers of Judiciary comes under the static part.
This is the best way to go about reading Polity. If you can read this way, then many myths about Polity (like mugging-up all the articles, everything and anything about Constitution) can be dealt with easily.
In 2014, two questions had come from Judiciary, based on the current issues. These were of static nature-
| The power to increase the number of judges in the Supreme Court of India is vested in
a) The President of India
b) The Parliament
c) The Chief Justice of India
d) The Law Commission
Solution (b) |
| The power of the Supreme Court of India to decide disputes between the Centre and the States falls under its
a) Advisory jurisdiction
b) Appellate jurisdiction.
c) Original jurisdiction
d) Writ jurisdiction
Solution (c) |
Similarly when Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) was in news (in 2012) with regard to exposing 2G Scam and Coal Scam), one has to go back to basics (static part) in understanding the powers and functions of CAG, mode of appointment and removal. Current events should always be prepared along with its basics.
For example:
|
In India, other than ensuring that public funds are used efficiently and for intended purpose, what is the importance of the office of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)?(2012)
1. CAG exercises exchequer control on behalf of the Parliament when the President of India declares national emergency/financial emergency.
2. CAG reports on the execution of projects or programmes by the ministries are discussed by the Public Accounts Committee.
3. Information from CAG reports can be used by investigating agencies to press charges against those who have violated the law while managing public finances.
4. While dealing with the audit and accounting of government companies, CAG has certain judicial powers for prosecuting those who violate the law.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 3 and 4 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Solution (c) |
Current events related to new Bills, Acts, Policies and related provisions should be noted down. One should try to relate current happenings with provisions of Indian Constitution.
For example
| The National Green Tribunal Act, 2010 was enacted in consonance with which of the following provisions of the Constitution of India?(2012)
1. Right to healthy environment, construed as a part of Right to life under Article21
2. Provision of grants for raising the level of administration in the Scheduled Areas for the welfare of Scheduled Tribes under Article 275(1)
3. Powers and functions of Gram Sabha as mentioned under Article 243(A)
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Solution (a) |
Polity is the easiest of all the subjects to score, because of the following reasons:
- The syllabus is concise and factual
- Straight forward questions are asked (not much analytical) and if you have revised Polity thoroughly then, you can get most of the answers right if not for 100% accuracy
- The questions are generally easy to moderate
- Not many Books to read apart from the two omnipresent and most referred books of Polity – By DD Basu and Laxmikanth)
Note: ‘Indian Polity by M. Laxmikant’ alone can fetch you close to 100% marks in Polity section in the Prelims stage. This is based on the experience of all the Toppers. The language used is lucid and very easy to understand, even for a beginner who is reading Polity for the first time. However, because of its factual nature, one must revise more.
You can read ‘Introduction to the Constitution of India by D.D.Basu’ (if you still have time and patience J) after you have finished reading Laxmikant. This book is important from the MAINS perspective and gives you an in-depth analysis of the subject. The language of the book is quite complex with legal terms, and hence it will be difficult to understand for anyone who is studying Indian Polity for the first time.
Note: However, questions at times are tricky, as the options given in the questions are very close to the correct choice. This creates ambiguity in the mind of the aspirant often leaving them confused.
For example:
| Which of the following are associated with ‘Planning’ in India? (2013)
1. The Finance Commission
2. The National Development Council
3. The Union Ministry of Rural Development
4. The Union Ministry of Urban Development
5. The Parliament
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1, 2 and 5 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 5 Only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Solution (c) |
Here, though Finance Commission is involved in devolution of money it is not involved in Planning process. Many would have chosen (a) as the answer. Neither are the Ministries of Rural or Urban Development involved.
|
‘Economic Justice’ the objectives of Constitution has been as one of the Indian provided in: (2013)
(a) the Preamble and Fundamental Rights
(b) the Preamble and the Directive Principles of State Policy
(c) the Fundamental Rights and the Directive Principles of State Policy
(d) None of the above
Solution (b) |
Prima-facie all the options look similar and may lead to confusion.
So, one should be more focused and attentive while attempting these questions. Having clarity in the powers and functioning of various institutions of administration and provisions of the Constitution, is very important. This comes by revising and regular practice of the MCQ’s (Multiple choice Questions). This will not only strengthen your basic concepts/understanding of the subject, but will also boost your confidence. Going through previous year Prelims Question papers and solving them will help you in understanding the nature of questions and prepare accordingly.
Common Myths about polity
Do I have to remember the entire list of Articles from 1 to 395?
No, you don’t have to. Try to understand the basics, when you revise it many a times, it will automatically be ingrained in your memory. Trust us J it is based on our own personal experiences. And also you don’t have to remember all the 450 articles. Only a few important articles like Article 72, 110, 249, 266, 267, 312 etc are important.
Next Page



