IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Jan 2017, Science and Technology, UPSC
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 13th January 2017
Archives
GEOGRAPHY
TOPIC: General Studies 1
- Urbanization, their problems and their remedies
Restructuring India’s Urban Strategy
Introduction
The present government in India has urbanisation and development of cities on top of its agenda. The same is visible from the policies focussing on the same such as Smart Cities Mission, mass rapid transit systems such as the metro services being developed and waste management etc.
However, the policy makers also need to understand that urban areas are not all about concrete structures but more about the kind of lifestyle that is given to the people and the objective should be to make the lives of people better. The culture of cities should emerge out of local desires and needs of the local population. Commercial, cultural and professional attributes should define the nature of the development of cities.
Challenges for Urbanisation in India
In contemporary times, India is faced with a few challenges that it needs to overcome for achieving sustainable urbanisation. These challenges are:
- In the recent past, even though funds have been available, cities have been unable to expand road networks and metro lines as per growing demand.
- Uncontrolled growth of population has made plans for public facilities ineffective. For example: Delhi Metro has increased the number of coaches, the frequency of trains, the size of stations and the length of platforms but still it struggles to accommodate the rising population.
- Increased vehicular pressure has led to congestion on roads and clogged networks.
- Migration is on a continuous rise with a Mumbai witnessing an influx of 4,000 families per week.
- Real estate businesses are building high-end luxury homes but cities still lack basic infrastructure for the public.
- A majority share of some cities are not recognised or do not qualify for being eligible to be a part of the planning process.
- Populist measure and bureaucratic tendencies are another hurdle in the way to urbanisation as per citizen needs.
Re-thinking for India
No doubt Indian government is aptly focussing on cities and urban infrastructure in the light of increasing pressure and migration still certain things need to be kept in mind while we rethink our strategy with respect to the cities.
- Indian cities are highly heterogeneous so the conventional approaches to their mega size may not work as in case of world cities such as Rome and Shanghai.
- Small towns such as Meerut which are part rural, part cantonment and are also essential to maintaining commercial links to surrounding villages are the cities which need most of the attention from government policies.
- India needs to devise a development strategy for smaller towns. This will be a shift from the conventional approach.
- Policies for these towns must take into account new forms of public housing, regulate bye-laws that restrict commuting and delineate public space over private commerce.
- So as the focus on smaller towns grows, simultaneously larger towns need to be relieved of the burden of new citizens.
- Instead of long distance connectivity steps should be taken to include pedestrianisation, conversion to mixed-use streets, reduction of commercial activity and an eradication of gated neighbourhoods.
- Residential areas should be promoted where all people live together and encourage a sense of community and inclusion. This will also help in eroding differences of ethnicity, profession, caste, social and economic position.
- Behavioural and attitudinal changes have to be brought about amongst the citizens for all the above non conventional methods to be successful. The Western model of urbanisation is not the best one that India should be following.
Way Forward
The new cities are going to witness a new kind of population group which will not be restricted to one place. The mobility of the people will be very high. Bureaucracy will have an enabling role to play in terms of migration but will not be defining the strategies for urbanisation.
In this contemporary set up, traditional structures of justice and legislature not hold prime importance and people with private needs will take up an important role in the society.
India will definitely need to work towards smart cities and include digitisation as a part of urban policies like Stockholm and Berlin but it will not be the only and the most comprehensive solution for India. Considering the high number of migratory citizens and pedestrians, India should follow cities such as Lagos or Cairo rather than European or Chinese cities.
Connecting the dots
- India needs to rethink on its strategy towards urbanisation. Give reasons for the need to restructure the strategy and suggest a non conventional strategy best suited for India based on international examples.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
TOPIC: General Studies 3
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
New digital reigns in human life
2017 will be the coming of age of the tech-enhanced human. Though it is difficult to predict a profound new trend in a one-year time frame, but this evolution promises to bring a fundamental shift with long-term implications for organisations, individuals and economies.
- Tech enhancement should be seen through a framework of three ‘A’s — assistance, augmentation and automation.
- These have been quietly gaining momentum over the last couple of years which are now expected to go mainstream in 2017.
- For example, the digital assistants powered by artificial intelligence have been in vogue for quite a time. From SIRI in iPhones and iPADs to Cortana in Microsoft Windows 10 devices, artificial intelligence has made inroads into everyday lives of human beings in a subtle but significant manner.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)- an area of computer science that emphasises the creation of intelligent machines that work and react like humans such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages.
The three A’s
Assistance
- The automated software applications or platforms, from the basic Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) to the sophisticated virtual assistants of today, assisting human users with search and retrieval related intelligence are getting better.
- With the enhancement in their capabilities, their demand and usage will also spike.
- According to a research organisation, there will be 1.8 billion consumer users of virtual assistants worldwide by 2021 and 843 million enterprise users.
- Whether it is google assistance or Amazon’s Alexa, they work alongside humans and complement their skills, thereby easing the tasks quietly.
Augmentation
- It enhances the human core capabilities by providing specifically contextual support that is required to do a task.
- The way doctors are working with IBM Watson is a great example of augmentation.
- IBM Watson- it has deep cognitive computing skills which assimilates vast amounts of patient information and interprets them reducing time for doctors to make their diagnoses.
Automation
- By taking a step forward from assistance and augmentation, automation all together removes the need for human effort.
- It is not complimentary to human skills but is a substitute bringing in agility to tasks which is very necessary today.
- But automation need not necessarily always mean job losses, especially in areas where significant judgement calls are needed. For example, self-driving cars.
There are different approaches taken by industry in tech enhancement. In retail, consumer decisions are becoming more assisted, the supply chains are becoming more augmented. In healthcare sector, at the patient end there is assistance in the form of chatbots and virtual platforms, while at the provider end there is augmentation (diagnosis) as well as automation (surgery).
India and Artificial intelligence
- Policymakers in India have to take into account the growing opportunities related to artificial intelligence.
- PM’s flagship initiatives — Make in India, Skill India, Digital India — will be impacted by the recent advances in artificial intelligence, making it imperative for Indian policymakers to take both an immediate and a long-term view.
- The private sector has been working rigorously in this field to provide maximum support to human beings. The government should also propel more and more research in this area. The AI can be used in many ways:
- The farmer’s smartphone will not only track weather forecast but also perhaps advise him on the next best action to take if the weather turns inclement.
- A smart fishing app will learn from the past performance of fishing trips on the high seas to guide Indian fishermen on improving their catch.
- A clever tax collection app will help the government detect sophisticated methods of tax evasion while a subsidy app will better target benefits to those who need them the most thereby helping plug leakages.
- Even for national security strategy, India can use the machine intelligence in the ways Pentagon’s DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) model uses which collaborates defence research with private sector and universities in order to create dual-purpose technologies.
- The proposed National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) platform, which would link citizen databases, might be a good start for creating a machine intelligence-based platform with both national security and civilian benefits.
- For this, there is a need to make radical recommendations through National Education Policy on alternative models of education that would be suitable to an AI-powered economy of future.
- Though, the issue of job creation will arise as technology will work with humans, but job prospects depends on the kind of technology used. Augmentation will not lead to job losses while automation might replace human labour.
- Also, there might be economic impact of tech enhancement on individuals and institutions as labour cost advantage will slowly vanish, particularly in emerging economies. Hence, India may see losses in job creation or provision if not adapting the emerging trends.
Conclusion
It is difficult for India to replicate China’s manufacturing strategy from the 1980s, hence, India has no option but to develop a new economic strategy that relies on technological innovation. The ‘fourth industrial revolution’ offers new possibilities to deal with the twin national security challenges — cross-border terrorism from Pakistan and the growing gap in conventional military capabilities with China. Flagship initiatives like Make In India, Skill India should become simulators for research and innovation in artificial intelligence. Thus, the recent advances in AI are a wake up call to Indian policymakers to spur AI-based innovation and AI-ready infrastructure in preparing India’s jobs and skills markets.
Connecting the dots:
- The manufacturing export driven economy is now a passé. India should augment its scientific capacities in artificial intelligence for a robust growth. Do you agree? Critically examine.
MUST READ
Strategic partnership. Really?
Niti Aayog calls for review of RTE Act
No pass marks
Project Of Defiance
Give credit
Improving India’s scientific capabilities
India’s job challenge requires collective action
No debate on healthcare in India
Tax policy in the time of demonetisation
No frills please, focus on the core
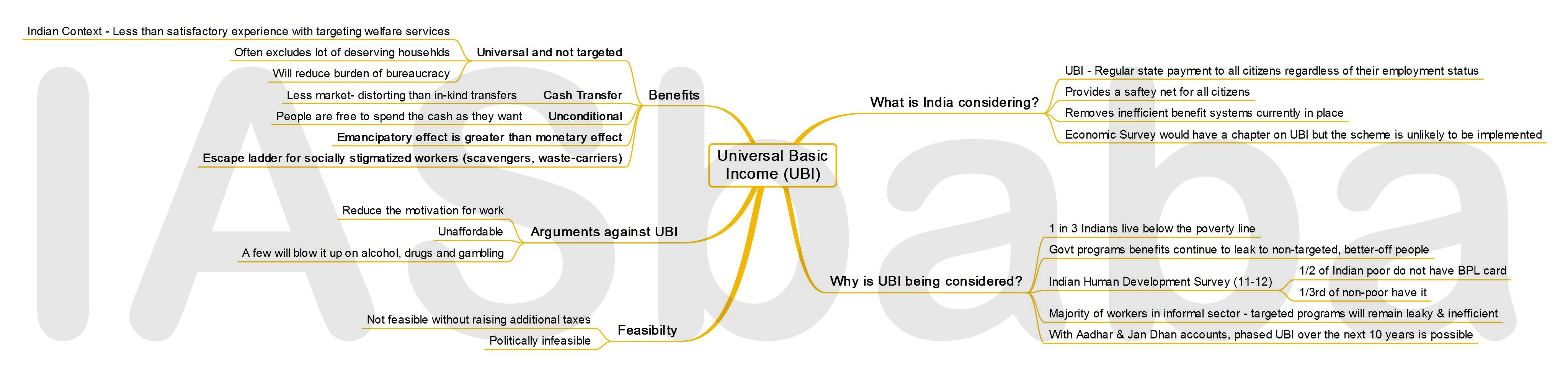
MINDMAP
Universal Basic Income