IASbaba's Think Learn and Perform 2017, UPSC Mains Answer Writing
SYNOPSIS- IASbaba’s TLP 2017 [20th March] – Day 45
ARCHIVES
1. What is the difference between honesty and probity? Explain by taking suitable examples.
• Introduction:
Write a brief introduction.
• Body:
Probity: The quality of having strong moral principles, honesty and rectitude. It brings the objectivity in the concept of Ethics and Morality because it lets a person to take an extra step to confer to what they feel right. It is the high action part of ethics and morality.
It is the quality of showing unwavering honesty especially in monetary matters. Probity gives a person strong character in public sphere as well as personal capacity.
Example: A public servant whose probity is not threatened by any temptation or greed offered by his supervisors.
Integrity is the quality of having strong moral character which encompasses honesty and truthfulness. Integrity is the inner sense of upholding the ethical values in every situation. Integrity exudes courage to speak up truth, it encourages to be honest in every circumstances.
Example: the life of Mahatma Gandhi.
Probity is situation specific whereas the integrity encompasses all the activities that a person undertakes
E.g: A person may be a very good administrator, who never takes bribes, help everyone who comes to his office, and has an impeccable service record. But if the person practices domestic violence at home, beast his wife for very minor reasons then that person has high standard of probity but his integrity is questionable.
Integrity espouse the conduct of a person both in his public as well as private life, whereas probity is limited to the public life.
• Conclusion:
Write a brief conclusion.
Best answer: PBN
2. Indian literary works on administration and statecraft have elaborate discussions on the philosophy of governance. Discuss.
• Introduction:
Write a brief introduction.
• Body:
The Arthashastra explores issues of social welfare, the collective ethics that hold a society together, advising the king that in times and in areas devastated by famine, epidemic and such acts of nature, or by war, he should initiate public projects such as creating irrigation waterways and building forts around major strategic holdings and towns and exempt taxes on those affected
In Mahabharata, Bhisma gave a discourse on the ethics of governance, duties of the king. Krishna in his sermon to Arjuna emphasizes the importance of duty towards the people, and ow king has to discharge his duties first even at great personal cost.
In Ramayana, the duties and obligations of the king towards the people are elaborately discussed.
The Vedas and the Dharmashstras have dealt in great detail about the duties of the kings, the intellectuals and the priests. They provide a code of ethics for all those classes that possess authority.
• Conclusion:
Write a brief conclusion.
Best answer: Nature
3. The sense of service associated with the job of a bureaucrat makes him more responsive and responsible. Comment.
This is a pretty straight forward question which asks you to tell why bureaucracy is a service and not a job.
To add more impact to your answer, you can put some quotes of Indian and foreign thinkers.
The sense of service should come as a part of work ethics. Once a person get to that position of responsibility and get to work in the field, he meet new people and face several challenges. This makes him more responsive to the need of people and he can actually empathise with them.
The best answer here has covered all the aspects of this question very nicely, so there is nothing much to mention now in the synopsis.
Best Answer: Arthanari
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/a66c0b3388b2bcf7be9add34d59858611d3049e3ad3b0716846c7d532089232b.jpg
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/427d080a678e8a13aab04eee67b59901844b2b7b45dd49fd4682e35aa5e9f5ba.jpg
4. Fake currencies have started to creep into the economy even after demonetization. This clearly depicts the inadequacy of the move to root out fake currency. Critically examine the problem and suggest ways to address it.
Steps taken to prevent fake currency: 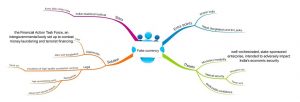
• It has been decided by the government that it would require multiple agencies to coordinate with each other in a bid to curb this menace. On this issue the Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Home Affairs, Reserve Bank of India, Security and Intelligence Agencies to the Centre and States are working in tandem.
• A Special FICN coordination (FCORD) Group has been formed by the MHA to share intelligence among the different security agencies.
• The CBI and National Investigation Agency are the Central Agencies for investigation of FICN cases. The Government has also constituted a Terror Funding & Fake Currency Cell (TFFC) in NIA to investigate Terror Funding and Fake currency cases.
• Further the government has made amendments to the Unlawful Activities (Prevention Act, 1967 (UAPA) wherein damage to the monetary stability of India by way of production or smuggling or circulation of High Quality Fake Indian Paper currency, coin or any other material has been declared as a “Terrorist” act.
• A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) has been signed between India and Bangladesh to prevent and counter smuggling and circulation of Fake Currency Notes. The objective of this MOU is to promote bilateral cooperation in the field of preventing and combating, production, smuggling and circulation of fake currency notes, taking into account the applicable laws and legal provisions of the two countries.
• The RBI conducts awareness programmes to make the public aware of the features of Indian Bank notes and to identify genuine Indian bank notes. The RBI regularly conducts training programmes on detection of counterfeit notes for employees/officers of banks and other organizations handling large amount of cash.
• To prevent smuggling of fake currency notes in India, staff posted at airports, Railway Stations and border posts have been sensitized from time to time, which has resulted in significant hauls of FICN in these locations.
Best Answer: Arjun
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/c722610344c362741cc
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/e717922505e229d3cbea2b63f075cb42bd557fcd0c779833c501f5d400242529.jpg
5. Discuss the status of tiger population in India. What are the most severe threats to tigers in India?
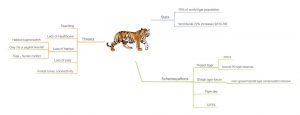
Best Answer: Axi Tak
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/b8ccec57499280795ef7e3c2be0f715642c1f1d69fedaafcec177b6f0774c39f.jpg
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/d9e40562cce7d3bb35ac8c2e8f3dacce4133e84cf4c3130331105a4ea9e4f3d4.jpg














