IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 9th May 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
Iran says it will not honour nuclear curbs
Part of: GS Mains II – International affairs; Security issues
In news:
- Iran said it had stopped respecting limits on its nuclear activities agreed under a 2015 deal with major powers until they find a way to bypass renewed U.S. sanctions.
- The announcement came as the US imposed sweeping unilateral sanctions against Iran.
- Iran’s Supreme National Security Council said that it no longer considered itself bound by the agreed restrictions on stocks of enriched uranium and heavy water.
Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES)
Part of: GS Mains III – Environment and Ecology; Human impact on biodiversity and ecosystem
In news:
According to global assessment report of the (IPBES) –
- Human beings have aggressively exploited nature.
- Species belonging to a quarter of all studied animal and plant groups on earth are gravely threatened (due to human impact).
- Ecosystem losses have accelerated over the past five decades universally
- Any devastation to tropical areas, which are endowed with greater biodiversity than other regions, is worrisome.
- If the world continues to pursue the current model of economic growth without factoring in environmental costs, one million species could go extinct, many in a matter of decades.
Concerns:
Catastrophic erosion of ecosystems is being driven by –
- unsustainable use of land and water
- direct harvesting of species
- climate change
- pollution and
- release of alien plants and animals in new habitats
The global rate of species extinction is at least tens to hundreds of times higher today than the average rate over the past 10 million years, and it is accelerating alarmingly.
Marine plastic pollution has increased tenfold since 1980, affecting at least 267 species, including 86% of marine turtles, 44% of seabirds and 43% of marine mammals.
Ecological economists have always warned about ever-increasing consumption which courts modifying terrestrial, marine and freshwater ecosystems to suit immediate needs, such as raising agricultural and food output and extracting materials.
Such modifications severely affect other functions such as water availability, pollination, maintenance of wild variants of domesticated plants and climate regulation.
US and China account for half of world’s military spending
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – International affairs; Defence/Security issues
In news:
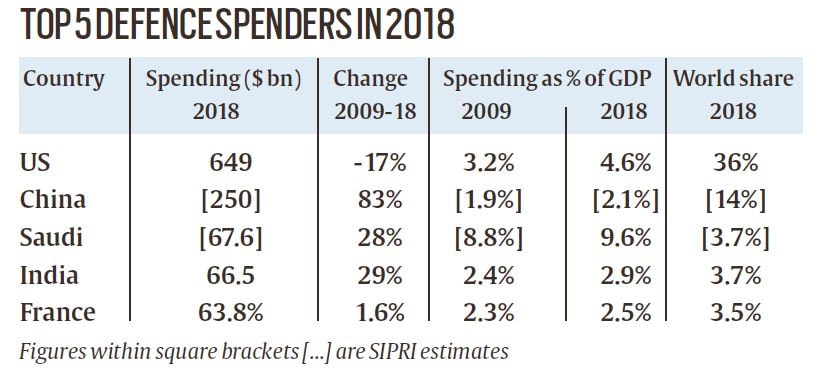
According to think-tank Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) –
- Total world military expenditure rose to $1,822 billion in 2018, representing an increase of 2.6% from 2017.
- The five biggest spenders in 2018 were the United States, China, Saudi Arabia, India and France, which together accounted for 60% of global military spending.
- Military spending by the US increased for the first time since 2010, while spending by China grew for the 24th consecutive year.
- In 2018, India increased its military spending by 3.1% to $66.5 billion while military expenditure by Pakistan grew by 11% (the same level of growth as in 2017), to reach $11.4 billion in 2018.
Pic: https://images.indianexpress.com/2019/05/defence.jpg
In news: Pattachitra paintings
Context
- Cyclone Fani teared down artists’ village in Odisha. Many pieces of art (especially Pattachitra, a traditional cloth-based scroll painting) in heritage hub have been damaged.
About Pattachitra
- Pattachitra is a general term for traditional, cloth-based scroll painting, based in the eastern Indian state, Odisha.
- In the Sanskrit language, “Patta” literally means “cloth” and “Chitra” means “picture”. Most of these paintings depict stories of Hindu deities.
- The Pattachitras are known for its intricate designs and was given the GI tag in 2008.
- These paintings are made on a canvas, which is prepared by mashing an old cotton cloth and palm leaves. When the canvas dries up, it is hardened using a paste of tamarind, turmeric, chalk and granite powder. The colours used in these paintings are made from from coal, conch shells, turmeric, chalk powder, leaves of selected plants and soft stones.
Person in news: Subhash Kapoor
ASI identifies rare Indian artefacts seized from smuggler
In news:
- A range of Indian antiquities and artefacts that were smuggled by Subhash Kapoor have been identified by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) during a team’s recent visit to the United States.
- Idols dating back to the Gupta period (5th-6th Century AD) to terracotta objects of the Harappan culture were seized by the Immigration and Customs Enforcement of U.S. Department of Homeland Security from the storage of Kapoor.
- The smuggler was extradited to India and is currently in the custody of Tamil Nadu police, the ASI said.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General studies 2
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate
India-US ties face tough terrain
Below are some of the major issues between India and US
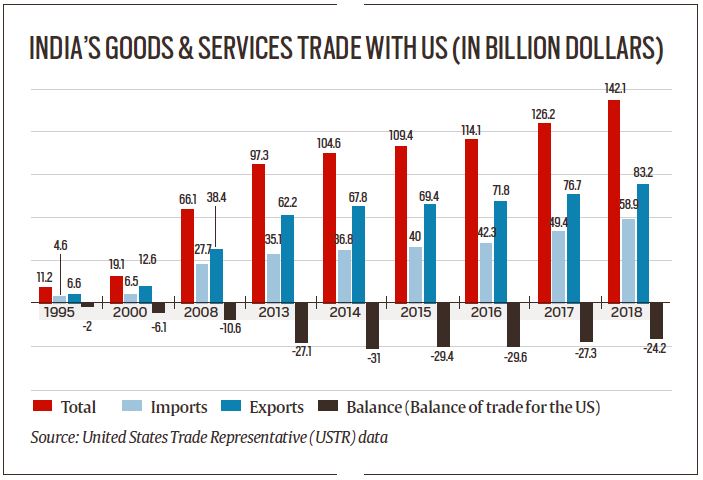
Issues in India-US trade
1. U.S.’s decision to not extend Iran sanctions waivers to India
- This decision will have notable implications for India-U.S. relations, given the importance of New Delhi’s energy relationship with Tehran.
2. U.S.’s decision to withdraw GSP benefits for Indian exports
- Trump administration decided to withdraw GSP benefits for Indian exports in retaliation for Indian tariffs that the U.S. deemed to be prohibitively high
- US has also expressed deep discontent over India’s policies on e-commerce, intellectual property rights and data localisation.
3. India’s tariff structure
- According to Trump administration, India was at number 13 in the list of US export markets because of its “overly restrictive market access barriers”. India’s average applied tariff rate was “the highest of any major world economy”.
- According to World Trade Organisation (WTO) data, India’s average applied tariff is now around 13.5% — and there are plans to move towards ASEAN tariff rates progressively (approximately 5% on average).
- Over the last five years, however, there has been a move by the government to increase duties on a number of items.
4. Disputes under the WTO
Seven disputes between India and US are at various stages of the Dispute Settlement Mechanism under the WTO. These pertain to –
- poultry and poultry products from the US
- countervailing duties against India’s export of steel products
- measures against import of solar cells and modules under the National Solar Mission,
- the US’s Sub-Federal Renewable Energy Programmes
- US measures concerning non-immigrant visas
- India’s export promotion schemes and
- the US tariff hike on steel and aluminium products.
5. Capping prices of cardiac stents and knee implants
- In 2017, India capped the prices of cardiac stents and knee implants, slashing prices by over 70% and 60% respectively.
- The move impacted US giants like Abbott, Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
6. Walmart issue and data localization
- Two other issues that the US side has specifically raised during the latest round of negotiations are the “treatment of Walmart after their acquisition of Flipkart”, and the problems on data localisation reportedly faced by companies such as MasterCard and Visa.
Impact:
- India will scale up oil imports from other top producers
- GSP withdrawal will have minimal impact on India’s economy (we have covered comprehensively in previous month DNA articles)
- S.-India CEO Forum and the India-U.S. Commercial Dialogue is expected to ease tensions
- However, a full-fledged strategic partnership, which both countries endorse, will be difficult to achieve amid such multiple and long-standing disconnects on the trade and economic side.
Conclusion:
- Bilateral ties should go beyond technology transfers, arms sales, joint exercises, and foundational agreements on defence in order to achieve a robust and multifaceted strategic partnership.
- India-U.S. relations have potential to extend well beyond security, especially initiatives ranging from clean energy to innovation.
- The U.S. and India have long struggled to agree on what a strategic partnership should look like. Any strategic partnership must be broad-based, with trust and cooperation present across a wide spectrum of issues and not just limited to close collaborations in the guns-and-bombs category.
- In this regard, a true strategic partnership remains, at least for now, elusive between India and the U.S.
Connecting the dots:
- India’s “US” policy has seen both continuity and change. Comment.
- India and US share a strong strategic partnership in the changing global order. Critically analyse.
- Has the dynamics of Indo-US relations changed after the election of Donald Trump as the President? Critically evaluate.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Pattachitra is
- A cloth-based scroll painting of Odisha
- A traditional dance form of Odisha
- Block painting of Buddhism faith
- Paintings done on dry leaves and preserved
Q.2) With regard to ‘Pattachitra’ consider the following statements
- These are paintings based on Hindu mythology and specially inspired by Jagannath and Vaishnava sect.
- Pattachitra is registered under the identity of Odisha Pattachitra (GI tag).
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- None
MUST READ
A travesty of justice
A wake-up call on proprietary seeds
Forcing a woman to adhere to purdah system is unconstitutional, so is dragging one out of it
How China, followed by India, has led greening efforts across world
Democratic values and the role of our educational institutions











