IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 10th August 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
National Crisis Management Committee
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III Disaster Management
In News
- Recently Cabinet Secretary chairs NCMC meeting to review flood situation in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala and Gujarat.
- At the national level, Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) and National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) are the key committees involved in the top-level decision-making wrt Disaster Management (DM).
- NDMC is a temporary committee set up in the wake of a natural calamity. Its key function includes
- Effective coordination and implementation of relief measures and operations.
- Overseeing the command, control and coordination of the disaster response.
- Composition of NDMC:
- Cabinet Secretary (Chairperson).
- Secretaries of Ministries / Departments and agencies with specific Disaster management responsibilities
Sex-ratio at birth
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS I – Society
In News
- The sex ratio at birth (SRB) in the country, defined as the number of female births per 1,000 male births
- SRB improved from 914 to 919 between the third and fourth National Family Health Surveys (NFHS), carried out in 2005-06 and 2015-16 respectively
- The highest improvement was in Punjab at 126 points to reach SRB of 860
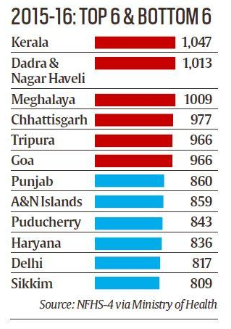
- Second highest improvement in SRB was in Kerala, by 122 points from 925 in 2005-06 to 1,047 in 2015-16 (the highest SRB among all states)
- The sharpest decline was in Sikkim, where the SRB dropped 175 points to reach 809, (the lowest SRB among all states)
- SRB has been falling in states like Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh and Assam
- Projects such as Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (PC-PNDT) Act, Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act
https://images.indianexpress.com/2019/08/sds.jpg
Article 371F
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS II – Indian Federalism
In News
- Sikkim CM assures people of state that Centre will not interfere with Article 371F and also rejected any possibility of merger of Sikkim and Darjeeling hills,
- Article 371F of the Constitution, is the result of the agreement in 1975 between the Union of India, the king of Sikkim and the State’s political parties
- Article 371F (36th Amendment Act, 1975): To protect the rights and interests of various sections of the population of Sikkim, Parliament may provide for the number of seats in the Assembly to be filled only by candidates from those sections
Do You know?
- Articles 369 through 392 (including some that have been removed) appear in Part XXI of the Constitution, titled ‘Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions’.
- Article 370 dealt with ‘Temporary Provisions with respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir’ which was read down recently by Presidential order.
- Article 371, Maharashtra and Gujarat: Governor has “special responsibility” to establish “separate development boards” for “Vidarbha, Marathwada, and the rest of Maharashtra”, and Saurashtra and Kutch in Gujarat.
- Articles 371A through 371J were incorporated subsequently.
- Article 371A (13th Amendment Act, 1962), Nagaland
- Article 371B (22nd Amendment Act, 1969), Assam
- Article 371C (27th Amendment Act, 1971), Manipur
- Article 371D (32nd Amendment Act, 1973, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana
- Article 371E: it allows for the establishment of a university in Andhra Pradesh by a law of Parliament. But this is not a “special provision” in the sense of the others in this part.
- Article 371G (53rd Amendment Act, 1986), Mizoram
- Article 371H (55th Amendment Act, 1986), Arunachal Pradesh
- Article 371J (98th Amendment Act, 2012), Karnataka
- Article 371I deals with Goa, but it does not include any provision that can be deemed ‘special’.
Prevention of money laundering act (PMLA)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS II – Public administration
In News
- The Centre has issued a notification on certain changes in PMLA
- An explanation added to Section 45 clarifies that all PMLA offences will be cognisable and non-bailable.
- Therefore, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) officers are empowered to arrest an accused without warrant, subject to certain conditions.
- New change does away with the pre-requisite of an FIR or chargesheet by other agencies that are authorised to probe the offences listed in the PMLA schedule.
- Now, under Section 44, the Special Court, while dealing with the offence under this Act shall not be dependent upon any orders passed in respect of the scheduled offence, and the trial of both sets of offences by the same court shall not be construed as joint trial.
- The scope of “proceeds of crime”, under Section 2, has been expanded to empower the agency to act against even those properties which “may directly or indirectly be derived or obtained as a result of any criminal activity relatable to the scheduled offence”.
Virasat-e-Khalsa
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS II – Public administration
In News
- The Virasat-e-Khalsa museum is set to find a place in Asia Book of Records for becoming the most visited museum in the Asian sub-continent on a single day.
- Virasat-e-Khalsa was built to commemorate the rich history and culture of Punjab and Sikhism.
- It was inaugurated in 2011 and located in Anandpur Sahib town in Punjab
- This would be the third entry for the museum in record books. Earlier, Virasat-e-Khalsa made it to Limca Book of Records in the February 2019 edition and India Book of Records.
(MAINS FOCUS)
HEALTH
TOPIC:
General studies 2
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes
General studies 3
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health
Every child to get Rotavirus vaccine
Context:
- Health Minister plans to provide it across all States and UTs by this September
Concerns:
- In India, every year, 37 out of every 1,000 children born are unable to celebrate their 5th birthday, and one of the major reasons for this is diarrhoeal deaths. Out of all the causes of diarrhoea, Rotavirus is a leading cause of diarrhoea in children less than 5 years of age Rotavirus
- Diarrhoea was one of the biggest killers in children and Rotavirus was one of the most common causes of severe diarrhoea in children less than 2 years of age.
- It is estimated that Rotavirus cause 8,72,000 hospitalisations; 32,70,000 outpatient visits and estimated 78,000 deaths annually in India. Rotavirus diarrhoea can be prevented through vaccination
What is Rotavirus?
- Rotavirus can cause diarrohea, which can lead to dehydration (not having enough water in the body).
- Rotavirus is a contagious disease that spreads easily from child to child.
- Rotavirus spreads when a person comes in contact with the feces of someone who has rotavirus and then touches their own mouth. For example, rotavirus can spread when a child with rotavirus doesn’t wash their hands properly after going to the bathroom and then touches food or other objects.
Symptoms
- Severe diarrohea
- Throwing up
- Dehydration
- Fever
- Stomach pain
World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends that the first dose of rotavirus vaccine be administered as soon as possible after 6 weeks of age, along with DTP vaccination (diptheria, tetanus and pertussis).
WHO has recommended the inclusion of rotavirus vaccine in the National Schedules of the countries where under five mortality due to diarrhoeal diseases is more than 10%.
Currently, two vaccines are available against rotavirus:
- Rotarix (GlaxoSmithKline): is a monovalent vaccine recommended to be orally administered in two doses at 6-12 weeks.
- Rota Teq (Merck) is a pentavalent vaccine recommended to be orally administered in three doses starting at 6-12 weeks of age.
Monovalent vaccine and Pentavalent vaccine
- Monovalent vaccines are designed to immunize against a single antigen or single microorganism.
- Pentavalent vaccine provides protection to a child from five life-threatening diseases – Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Hepatitis B and Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib).
Initiatives to be taken by the government:
- The Health Ministry has drawn an ambitious plan under the 100 days agenda of the newly elected government, wherein it has been decided to provide Rotavirus vaccine to every child across all States and Union Territories by September, 2019
- Rotavirus vaccine along with proper sanitation, hand washing practices, ORS and zinc supplementation will go a long way in reducing the mortality and morbidity due to diarrhoea in children.
- The government was also committed to increasing the full immunisation coverage and ensuring that the benefit of the life-saving vaccines was provided to every child.
- Diarrhoea can be prevented through general measures like good hygiene, frequent hand washing, safe water and safe food consumption, exclusive breastfeeding and vitamin A supplementation.
- Rotavirus vaccine was introduced in 2016 in a phased manner, beginning with 4 States initially and later expanded to 7 more States.
- The Rotavac has been introduced in India’s Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) including Inactivated Polio Vaccine(IPV), Measles, Rubella (MR) vaccine, Adult Japanese Encephalitis (JE) vaccine, Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, Pneumonia and Meningitis due to Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib).
Connecting the dots:
- Discuss the measures taken by Government to control the communicable diseases?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about National Crisis Management Committee
- It is a statutory body established under Disaster Management Act, 2005
- Its function includes overseeing the command, control and coordination of the disaster response.
- It is headed by Prime Minister
Which of the statement(s) given above is / are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Prevention of Money Laundering Act
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) officers are empowered to arrest an accused without warrant, subject to certain conditions.
- There is pre-requisite of an FIR or chargesheet by other authorized agencies, for ED officers to begin investigation into any money laundering cases
Which of the statement(s) given above is / are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB)
- It is defined as the number of female births per 1 lakh male births
- Sikkim has the lowest SRB as per National Family Health Survey –IV, 2015-16
- The highest improvement of SRB (between 2005-06 and 2015-16) was in Punjab
Which of the statement(s) given above is / are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q.4) Consider the following statements about Article 371F
- It is a special provision to protect the rights and interests of various sections of the population of Nagaland
- It is introduced by 52nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1985
Which of the statement(s) given above is / are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2











