IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 5th September 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Security
In News
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) declared four individuals – Masood Azhar, Hafiz Saeed, Zaki-ur-Rehman Lakhvi and Dawood Ibrahim – as terrorists under Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967.
- UAPA was first enacted in 1967 and amended in 2004,2008,2012 and 2019.
- Some of the key provisions of amended act are
- It empowers the government to designate individuals as terrorists. Previously, only an organisation could be designated as one.
- It empowers the National Investigation Agency (NIA) to seize properties, which previously required permission from the Director General of Police.
- It allows NIA officers, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases. Before only DySP or ACP or above could do so.
- Opposition parties have raised concern over the 2019 amendment act, saying it could also be misused against political opponents and civil society activists who spoke against the government may be branded as “terrorists.”
Do You Know?
- NIA was created after the 2008 Mumbai terror attacks with the enactment of the National Investigation Agency Act 2008.
- NIA is the Central Counter Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency of India and it works under overall guidance of Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Jurisdiction of NIA:
- The agency is empowered to deal with terror related crimes across states without special permission from the states.
- A State Government may request the Central Government to hand over the investigation of a case to the NIA, provided the case has been registered for the offences as contained in the schedule to the NIA Act.
- NIA has registered and investigated 244 cases till date. After submission of charge sheets, 37 cases have been finally or partially decided in trial. Of these, 35 cases have ended in conviction giving NIA an enviable conviction percentage of 91.3%.
Apache helicopters
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III – Security
In News
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) formally inducted 8 US-made Apache AH-64E helicopters at Pathankot Air Force station
- In September 2015, IAF had signed a multi-billion dollar contract with US government and Boeing Ltd for 22 Apache helicopters.
- The first 8 helicopters have been delivered on schedule and last batch of helicopters is to be delivered by March 2020.
- Apache attack helicopters are being purchased to replace the Mi-35 fleet and will be deployed in the Western regions of India.
- Apache is one of world’s most advanced multi-role combat helicopters, some of its features include:
- Capability to shoot fire and forget anti-tank guided missiles, air to air missiles, rockets and other ammunitions.
- Capable of delivering variety of weapons such as: air to ground Hellfire missiles, 70 mm Hydra rockets and air to air Stinger missiles
- It has modern EW (Electronic Warfare) capabilities to provide versatility to helicopter in a network centric aerial warfare
- These are day/night, all weather capable and have high agility and survivability against battle damage.
ASEAN-US Maritime Exercise (AUMX)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – International Affairs
In News
- The first AUMX between the ASEAN regional bloc and U.S. kicked off at the Sattahip Naval Base in Thailand.
- It will see participation of navies of USA and all 10 members of ASEAN – Thailand, Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore and Vietnam
- Navies of these countries will take part in the naval exercises which include boarding of target vessels to simulate search and seizure.
- The exercise will stretch into international waters in Southeast Asia, including Gulf of Thailand and South China Sea and conclude in Singapore.
- This mega maritime exercise comes at a time of stepped-up US engagement in region and tensions between China, US and Southeast Asian nations over South China Sea (SCS).
Do You Know?
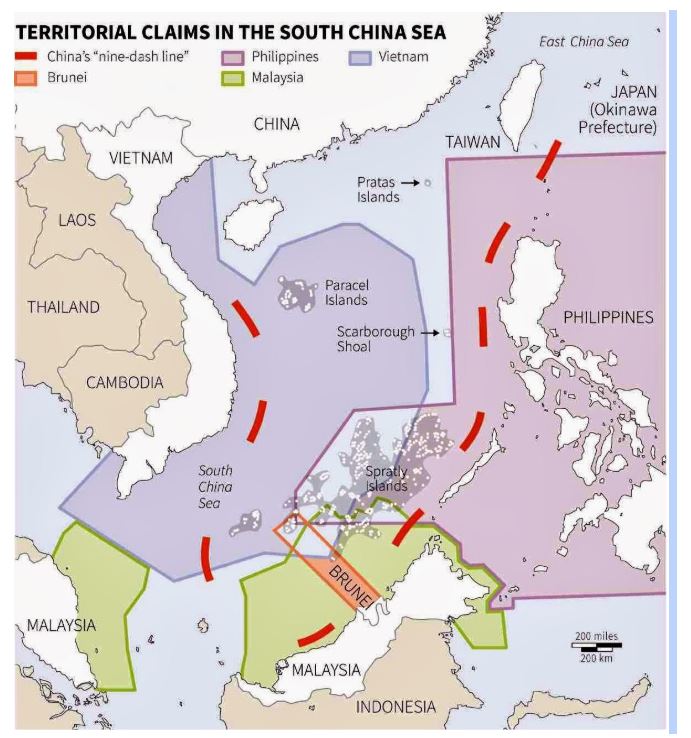
- China is claiming its sovereignty over much of SCS by invoking its so-called nine-dash line as supposed historical justification to the waters, which are key global shipping route.
- Its claim is overlapping parts of SCS are claimed by Brunei, Malaysia, Vietnam and Philippines.
https://en.reseauinternational.net/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/07/nine-dash-line-china.jpg
Dadabhai Naoroji
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-I – Modern Indian History
In News
- September 4, 2019 was the 194th birth anniversary of Dadabhai Naoroji, the “Grand Old Man of India”
- He was among the first leaders who stirred national consciousness in the country.
- Naoroji was a professor of Gujarati, mathematics, and natural philosophy, and also worked as a businessman.
- Naoroji began rousing public opinion in England on Indian issues in 1855, after he moved from India to Liverpool for business
- During this period, Naoroji worked closely with Irish leaders in England, who found common cause with the Indian nationalist movement.
- In 1865 and 1866, Naoroji helped found the London Indian Society and the East India Association respectively.
- First Indian member of the British parliament : Naoroji first ran for the British Parliament in 1886, but did not get elected. His second bid in 1892 was successful, when he won the Central Finsbury seat on a Liberal Party ticket.
- In 1893, he helped form an Indian parliamentary committee to attend to Indian interests. The membership of the committee significantly grew in numbers in the coming years, becoming an important lobbying force.
- Dadabhai Naoroji was among the key proponents of the ‘Drain Theory’, disseminating it in his 1901 book ‘Poverty and Un-British Rule in India’
(MAINS FOCUS)
HEALTH
Topic: General studies 2
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
Screening for communicable diseases
Context:
- In India, screening for disease is usually associated with non-communicable rather than communicable diseases. However, Since August 2019, India has embarked on a large-scale plan to screen all children for leprosy and tuberculosis.
Concerns:
- Both diseases are infectious and India has a substantial burden — its tuberculosis burden is the highest in the world.
- Children tend to be more prone to catching infectious diseases from their peers because of long hours in confined spaces and more bodily contact than in adults.
Why screening of the two diseases is necessary?
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae. It usually affects the skin and peripheral nerves, but has a wide range of clinical manifestations. The disease is characterised by a long incubation period that is generally 5-7 years. It is a leading cause of permanent physical disability. Timely diagnosis and treatment of cases, before nerve damage has occurred, is the most effective way of preventing disability due to leprosy.
Tuberculosis infection, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is one of the most common communicable diseases in India, its transmission fuelled by unhygienic, crowded living conditions. It is said that most Indians carry the bacterium and the infection flares up when their immunity levels are low, like when they are malnourished or suffering from conditions like AIDS in which the body’s immune system is compromised.
Statistics in India:
- India eliminated leprosy in 2005 — WHO defines elimination as an incidence rate of less than one case per 10,000 population.
- All states except Chhattisgarh and the Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli have eliminated leprosy. However, 1.15 lakh to 1.2 lakh new leprosy cases are still detected every year, Health Ministry officials said.
- TB kills an estimated 4,80,000 Indians every year — an average over 1,300 every day.
Why the disease prevalence is more?
- India also has more than a million “missing” cases every year that are not notified.
- Most remain either undiagnosed or unaccountably and inadequately diagnosed and treated in the private sector.
- The problem in the latter case is that many of these patients do not complete the full course of the antibiotic, thus exposing the bacterium to the medicine without fully killing it.
- This is trigger enough for the bacterium to evolve into a version of itself that is resistant to that particular drug.
Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram
- Launched in 2013 under the National Health Mission (NHM), is focused on preventing disease and disability in children.
- This initiative is aimed at screening children from 0 to 18 years for 4Ds – Defects at birth, Diseases, Deficiencies and Development Delays including Disabilities.
- Children diagnosed with illnesses shall receive follow up including surgeries at tertiary level, free of cost under NHM.
Conclusion:
- Until now, neither leprosy nor TB were a part of the programme. In 2017, India had set a target of elimination of leprosy by 2018, going by the Budget speech that year. The deadline has passed but leprosy remains a challenge in a country that launched the National Leprosy Eradication Programme way back in 1955.
- For tuberculosis, the global Sustainable Development Goal target is to end the disease is 2030. However, there is a new urgency in India’s TB control efforts since last year, when Prime Minister Narendra Modi suo motu advanced the deadline for India to end TB to 2025.
Connecting the dots:
- Discuss the measures taken by Government of India to control communicable diseases?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) He was a professor of Gujarati, mathematics, and natural philosophy. He moved from India to Liverpool for business and began rousing public opinion on Indian issues. He was the first Indian to get elected to British Parliament on Labour Party ticket. He helped form an Indian parliamentary committee which became an important lobbying force for Indian interest. He acted as a liaison between nationalist Indians and British parliamentarians.
Identify the Indian National leader mentioned in the above write-up.
- Shapurji Dorabji Saklatvala
- Dadabhai Naoroji
- Sir Macherjee M. Bhownaggree
- None of the above
Q.2) Nine-dash line often seen in news is related to which of the following?
- Border of North Korea & South Korea
- Israel-Palestine Conflict
- South China Sea
- None of the above
Q.3) Consider the following statements
- Only an organisation could be designated as terrorist under Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act.
- NIA is the Central Counter Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency of India and it works under overall guidance of Ministry of Defence
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Must Read:
Tending to the heart
Let it slide
India’s climate score: high on vulnerability, low on resilience
Making India an arbitration hub











