IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 16th March 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Spanish Flu
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In News:
- As COVID-19 grows into a global health crisis, parallels are being drawn with the Spanish influenza of 1918-19,
- Spanish Flu is considered the most devastating pandemic in recent history, with an estimated toll of 20-50 million lives.
- The 1918 influenza pandemic (1918-20; colloquially known as the Spanish flu) was the first of the two pandemics involving H1N1 influenza virus, with the second being the swine flu in 2009.
- The focal point of that pandemic a century ago was India (brought to India by World War I soldiers returning home), where between 10-20 million Indians died
National Creche Scheme (NCS)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Governance
In News:
- As on 11th March 2020, 6453 creches are functional across the country under NCS
- National Creche Scheme (earlier named as Rajiv Gandhi National Creche Scheme) is being implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Objective: To provide day care facilities to children (age group of 6 months to 6 years) of working mothers.
- The salient features of the National Creche Scheme are as follows:
- Daycare Facilities including Sleeping Facilities.
- Early Stimulation for children below 3 years and pre-school Education for 3 to 6 years old children.
- Supplementary Nutrition ( to be locally sourced)
- Growth Monitoring
- Health Check-up and Immunization
J&K will soon have a domicile policy: Home Minister
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Polity- Federalism
In News:
- A proper domicile police for J&K ensure protection to domiciles of J&K in government jobs, educational institutions and land rights.
- On August 5, 2019, the Centre revoked the special status of J&K under Article 370 and Article 35A of the Constitution.
- These two revoked provisions had enabled the J&K Assembly to decide the “permanent residents” of the erstwhile State, prohibiting people from outside from buying property and ensuring job reservation for residents.
Did you know?
- Article 371 grants some temporary, transition and special provisions to some states in the country.
- Ranging from Article 371-A to Article 371-J, this Article gives special provisions for the states of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Nagaland, Assam, Manipur, Andhra Pradesh, Sikkim, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa and Karnataka.
Chaitra Jatra Festival
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I- Culture
In News:
- The annual Chaitra Jatra festival scheduled to be held on March 17 at Odisha’s Tara Tarini hill shrine is cancelled as a precautionary measure against COVID-19 infection.
- Tara Tarini hill shrine on banks of the Rushikulya river, is a major centre of Shakti worship in Odisha.
Prelims Value Addition
- After Gahirmatha in Kendrapara district of Odisha, the Rushikulya river mouth in Ganjam district has emerged as the second largest nesting site of the endangered olive ridley turtles.
- Indian Navy’s sailboat INSV Tarini was named after Tara Tarini hill shrine.
- The first Indian all-woman crew had circumnavigated the globe in INSV Tarini.
Sepsis
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Health
In News:
- Sepsis is a common cause of death from Coronavirus
- Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by the body’s immune system overreacting in response to an infection.
- This overactive, toxic response can lead to tissue damage, multiple organ failure and death.
- Cause: Sepsis can be triggered by a variety of pathogens- Viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites
- Treatment: The blood is examined, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is administered, and sufficient blood circulation and ventilation are ensured.
Notified disaster and State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Disaster Management
In News:
- Ministry of Home Affairs decided to treat COVID-19 as a notified disaster for the purpose of providing assistance under SDRF.
- The SDRF is constituted under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 and is the primary fund available with state governments for responses to notified disasters.
- The Central government contributes
- 75% towards the SDRF allocation for general category states and UTs.
- 90% for special category states/UTs, which includes north-eastern states, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand).
Value Addition for Prelims
- For SDRF, the Centre releases funds in two equal instalments as per the recommendation of the Finance Commission.
- On the other hand, the National Disaster Response Fund, which is also constituted under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 supplements the SDRF of a state, in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in the SDRF.
Did You Know?
- In a similar move, US President also declared a national emergency in the country invoking the Stafford Act, as per which, the federal government contributes about 75% to the cost of relief for states.
Herd Immunity
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Health
In News:
- Chief scientific adviser to the UK government had suggested to UK that authorities need to contain the spread of the virus but would “not suppress it completely”.
- Elaborating further it was suggested that a 60 per cent infection rate would help build up a degree of ‘herd immunity’.”
- Herd immunity is a form of indirect protection from infectious disease that occurs when a large percentage of a population has become immune to an infection, thereby providing a measure of protection for individuals who are not immune
What happens in the case of coronavirus where there is no vaccine?
- The approach would require those exposed to the virus to build natural immunity and stop the human-to-human transmission.
- If a high enough proportion of individuals in a population are immune, the majority will protect the few susceptible people because the pathogen is less likely to find a susceptible person
Is it the model which UK is planning to fight coronavirus?
- On the face of criticism of such soft approach and high human cost involved, UK government stated that herd immunity was not the government’s policy or goal.
(MAINS FOCUS)
International Affairs
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Policies and politics of developed and developing countries
Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) :A dam of contention in Africa
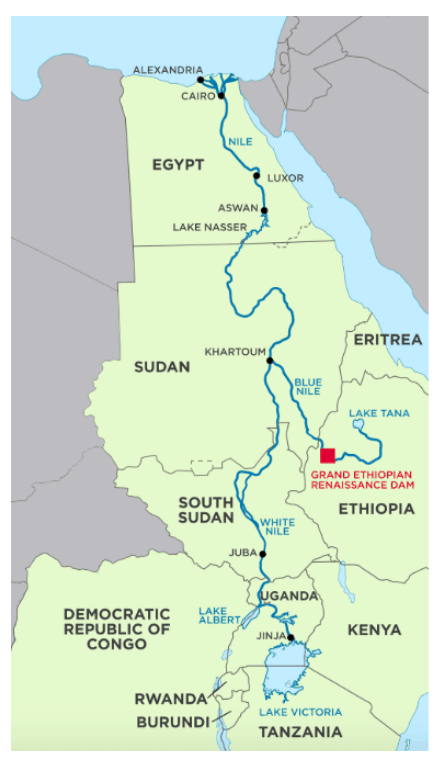
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 16th March 2020
Pic Source
About GERD
- It was formerly known as the Millennium Dam and sometimes referred to as Hidase Dam
- It will be Africa’s biggest hydropower project (6.45 GW) when completed as well as the seventh largest in the world
- The hydroelectric dam is being built on the world’s longest river Nile (north-flowing river in Africa), in the lowlands of Ethiopia.
- GERD’s storage capacity of 74 billion cubic meters of water (Bhakra Dam in India on Sutlej river has maximum capacity of 9 billion cubic meters of water)
- Ethiopia began construction in 2011 (think political turmoil in Egypt at that time!)at a cost of $4 billion and is approximately 70% complete as of Nov 2019
- Ethiopia wants to fill up the gigantic reservoir in 6 years
However, the mega dam has caused a row between Egypt and Ethiopia, with Sudan caught in between, which some fear could lead to war, and the US is now helping to mediate.
Significance of the dam for Ethiopia
- Ethiopia, Africa’s second-most populated country and a manufacturing hub, views the mega dam as a symbol of its sovereignty.
- Bridges Infrastructure Gap: Ethiopia has an acute shortage of electricity, with 60% of its population not connected to the grid.
- Export Potential: The energy generated will be enough to have its citizens connected and sell the surplus power to neighbouring countries.
- Economic Resurgence: There is an element of national pride in the timely completion of the GERD, as Ethiopia’s recent economic resurgence has revived the old vision of Great Ethiopia.
- Politically Important: There is also a lot at stake for the government of Mr. Ahmed (PM of Ethiopia), who faces a difficult general election this year after the euphoria of the 2018 peace process with Eritrea has largely faded.
Does anyone else benefit?
- Yes. Neighbouring countries including Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya, Djibouti and Eritrea are likely to benefit from the power generated by the dam.
- Many of these countries have huge power deficits.
- For Sudan there is the added advantage that the flow of the river would be regulated by the dam – meaning it would be the same all-year round.
- Usually the country suffers from serious flooding in August and September.
Concerns Raised by Egypt
- Egypt fears the project will allow Ethiopia to control the flow of Africa’s longest river
- Hydroelectric power stations do not consume water, but the speed with which Ethiopia fills up the dam’s reservoir will affect the flow downstream.
- The longer it takes to fill the reservoir, the less impact there will be on the level of the river.
- Heart of the dispute: Ethiopia wants to fill the reservoir in 6 years whereas Egypt wants to fill the reservoir, between 10 and 21 years, and for the release of a minimum of 40 billion cubic metres annually.
- Egypt, which relies on the Nile for 90% of its freshwater supply, is apprehensive that a rapid filling of the reservoir in upstream Ethiopia would cause a drastic reduction in supplies.
- Egypt perceives that the project would lead to diversion of waters to its own High Aswan Dam.
- Resistance by Egypt is rooted in History and Geopolitics:
- A 1929 treaty (and a subsequent one in 1959) gave Egypt and Sudan rights to nearly all of the Nile waters.
- The colonial-era document also gave Egypt veto powers over any projects by upstream countries that would affect its share of the waters.
- Neither agreement made any allowance for the water needs of the other riparian states that were not parties to the deal, including Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya and Rwanda.
- Lack of Consultation: Ethiopia has said it should not be bound by the decades-old treaty and went ahead and started building its dam at the start of the Arab Spring in March 2011 without consulting Egypt.
Challenges Ahead
- Ethiopia has stated that the dispute over the dam project is only a trilateral issue involving Egypt and Sudan.
- Ethiopia asserts its rights for an equitable share of the Blue Nile flows from the Cooperative Framework Agreement (CFA) signed by some of the 10 Nile Basin Initiative nations
- The establishment of the Nile River Basin Commission mandated by the CFA has not materialised so far.
- Ethiopia is concerned that a long delay in filling the reservoir would jeopardise returns on its investments and hamper the prospects for overall growth.
- The mediation role played by US highlights the significance of the issue and the potential conflict it holds if unresolved. However, the mediation has not been able to progress substantially due to lack of true intentions from both sides.
- Impact regional & International Trade: An escalated tensions between Ethipia & Egypt would threaten the vital international trade route through the Suez Canal and along the Horn of Africa.
Way forward
- An agreement involving Egypt, Ethiopia and others river basin countries for equitable sharing of water
- Sustainable use of river water given the ever increasing problem of pollution and climate change.
- These countries can take inspiration from Indus Water Treaty signed between India and Pakistan brokered by World Bank in 1960. The treaty has been functioning smoothly and has endured three wars over nearly six dacades.
Conclusion
- The challenges for the fair utilisation of waters among the riparian states have only been compounded by the pressures of population growth and the effects of global warming
- While the parties have sought international mediation they also need to rely on regional cooperation for long enduring solution.
International Affairs
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Is the global economy headed for recession? Businesses impacted
Context: How deep has the impact of COVID-19 been on businesses around the world? And which are the ones that have been hit the hardest?
- The global death toll due to COVID-19 has crossed the 5,300 mark, with over 1.42 lakh people infected.
- India, where 88 people have been infected, saw two casualties as of March 15th 2020
What does it mean to the global economy?
- Analysts fear that the global economy may tip into a recession unless the virus turns out to be seasonal.
- A recession sets in when the economy shows two consecutive quarters of contraction
- The problem with current predictions is no one knows how long the virus will remain potent
- Rabobank has stated that a global recession now is all but certain. It has predicted global GDP growth to be 1.6% for 2020, a figure that was 2.9% the last year, as per IMF estimates.
- the Institute for International Finance had said that global economic growth could turn out to be as low as 1%, and this was even before the OPEC club and Russia fell out on production agreements to maintain stable oil prices
- The UN’s United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), said the virus outbreak could cost the global economy up to $2-trillion this year
Why should the economy be affected?
- If we engage less with the outer world, and avoid work, education, fitness and entertainment, a lot less economic activity would occur.
- Businesses face the challenge of disrupted supply of components to make products, or of having to shut some of their factories temporarily
Which are the industries impacted?
- When China was faced the COVID-19 outbreak, the Indian pharmaceutical, automobile and mobile phone industries were immediately impacted.
- India depends on China for supplies of components for products that these sectors make.
- The Indian pharma industry, which depends on China for 70% of raw materials needed to manufacture drugs here, has seen input costs go up by 50% as of February 2020
- The pesticides sector is another that has been affected as manufacturers depend on China for raw materials. While there are comforting stock levels for now in India, farmers may soon face pesticide availability issues unless the situation resolves quickly.
- The Indian gem and jewellery makers are impacted due to the partial closure of the Chinese and Hong Kong markets (which accounts for 70% of India’s exports), which is likely to result in a loss of about $1-billion by April 2020.
- Software Services: Decision-making in the West, a key market for software services, may have been hit, with in-bound travel restricted and the U.S. declaring emergency.
- Security and safe health of employees have been at the top of priorities rather than the pricing of a technology contract
- Entertainment and Sport: The very popular Indian Premier League has been postponed. In football, all Union of European Football Association (UEFA) competitions have been postponed. Same is with US sports.
How will it hit the travel sector?
- Travel has been hit severely as countries issue advisories to eliminate unnecessary travel and go into lockdown mode.
- The U.S., for instance, has halted all in-bound travel from Europe.
- India has temporarily stopped grant of visas except for emergency situations.
- The impact on profits of — and jobs at — airlines, airport authorities and oil marketing companies is obvious and immediate
- It has also impacted the economy around air travel — the vendor of shops and outlets in the Airport & surrounding region.
- Boeing executives have indicated there had been a 50% reduction in daily flight count in the Asia-Pacific region.
Is there a silver lining at all?
- Sales of medical supplies, soaps, hand sanitisers and essentials to be stocked up at home will evidently rise.
- Digital shopping may see even more traction.
- It is said that after the SARS epidemic in China in 2003, shoppers began to prefer buying online, to avoid crowded spaces and that e-commerce major Alibaba’s fortunes zoomed after this.
- With schools shutting down temporarily, online learning platforms are likely to get a boost.
When normalcy returns, wouldn’t pent-up demand make up for lack of economic activity now?
- Only some of the expenses that are being held back by consumers can be made up for later when pent-up demand is unleashed after the situation returns to normal. Ex: Postponing a vacation
- But micro-expenses, which contribute significantly to an economy, such as a cab fare or buying snacks for a commute, can never be made up for during this slowdown
- For instance: cab drivers cannot quite afford to have their cabs out of circulation for even as short a period as a week, if they have to put food on the table for their families. Curtailed travel and commutes can be devastating for them unless the situation resolves quickly.
Has the Central Banks done anything?
- U.S. Federal Reserve held an emergency meeting and cut interest rates by a half percentage point.
- The stock markets reacted favourably for a short while before losing steam and spiralling downwards.
- Nevertheless, the U.S. declaring a state of emergency over the spread of the virus will help allocate the significant quantum of funds needed to deal with a health-care requirement of this magnitude.
- Likewise, the Euro markets remained unmoved even after the European Central Bank announced fresh stimulus measures to help the economy cope with the growing cost of the COVID-19 epidemic
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Consider the following statements about State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF)
- It is a statutory body constituted under the Disaster Management Act, 2005
- National Disaster Response Fund supplements the SDRF of a state, in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in the SDRF.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 2. Consider the following statements about Rushikulya River
- It originates from Daringbadi hills of the Eastern Ghats range and flows into Bay of Bengal
- Rushikulya river mouth has emerged as India’s second largest nesting site of the endangered olive ridley turtles.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 3. Consider the following statements about Circuit Breakers in Stock Exchanges
- Gujarat, Nagaland, Assam, Manipur, Karnataka are among the few states who enjoy special provisions under Article 371
- One of the main objectives behind the Article 371 granting special provisions to some states is to meet the unique needs of the backward regions of these states
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 4. Consider the following statements about National Creche Scheme
- It is Centrally Sponsored Scheme implemented by Ministry of Women and Child Development
- It aims to provide day care facilities to children (age group of 6 months to 6 years) of working mothers.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 5. Global Migration report 2020 is released by which body?
- International Organisation for Migration
- World Economic Forum
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
- Amnesty International
ANSWERS FOR 14 March 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | B |
| 5 | A |
Must Read
About Transparency in Political Parties
About Education and riots:
About Agri reforms in past decade:













