IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 23rd March 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Census and NPR exercise postponed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Polity and Governance
In News:
- The Union government may postpone the house-listing Census and updating of the National Population Register (NPR) owing to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Both exercises were scheduled to kick off in certain States on April 1.
Do you know?
- President Ram Nath Kovind was supposed to be the first Indian to be enumerated in the Census and NPR exercise. (as President is the first citizen of India)
- Difference between NPR and NRC? And NPR and Census?
Important value additions:
About NPR
- It is a register of usual residents of the country being prepared at all levels – local, district, state and national.
- A usual resident is defined, for the purposes of the NPR, as a person who has resided in a local area for the past six months or more, or a person who intends to reside in that area for the next six months.
- It is conducted under provisions of the Citizenship Act 1955 and the Citizenship (Registration of Citizens and issue of National Identity Cards) Rules, 2003.
- The NPR exercise was to be carried out between April and September 2020 in all states and UTs, except Assam.
- The objective of the NPR is to create a comprehensive identity database of every usual resident in the country. The database would contain demographic as well as biometric particulars.
About Census
- The decennial census is the largest single source of a variety of statistical information on different characteristics of the people of India.
- It is conducted on the basis of the Census Act enacted in 1948.
- The census, 2021 will be done in two phases.
- In the first phase, census will be conducted from April to September, 2020.
- In the second phase, it will be done from February 9 to February 28, 2021.
Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains GS-II- Governance; GS-I- Modern History
About the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897
- This law enables states to ban public gatherings, ask schools and large institutions to stop functioning, and issue advisories to companies to explore work-from-home models.
- It also gives the state a right to penalise media organisations spreading misinformation.
Background:
- It was introduced by British government to tackle the epidemic of bubonic plague that had spread in the erstwhile Bombay Presidency in the 1890s.
Key features of the Act:
- It empowers state governments/UTs to take special measures and formulate regulations for containing the outbreak, like inspection of persons travelling by railways, segregation in hospitals etc.
- It empowers state to prescribe such temporary regulations to be observed by the public
- It provides penalties for disobeying any regulation or order made under the Act.
- It gives legal protection to the implementing officers acting under the Act.
Do you know?
- In 1897, the year the law was enforced, freedom fighter Bal Gangadhar Tilak was punished with 18 months’ rigorous imprisonment after his newspapers Kesari and Mahratta admonished imperial authorities for their handling of the plague epidemic.
- Health is a State subject.
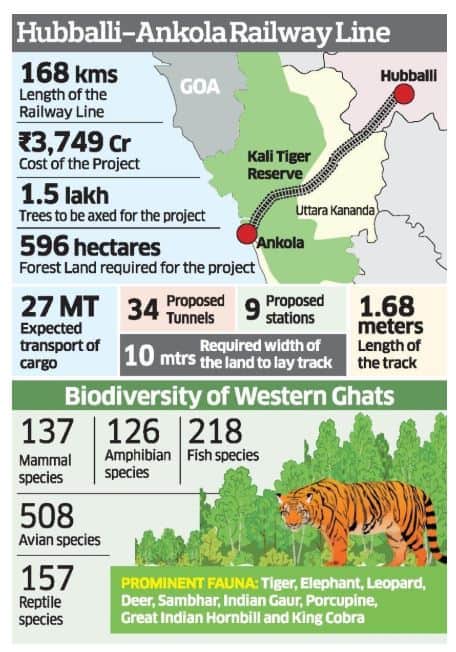
Biodiversity hotspot in danger due to proposed railway line
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment and Conservation
In News:
- The proposed Hubballi-Ankola railway line cleared by Karnataka state government, might pose danger to the biodiversity of the region. (Western Ghats)
According to an expert committee,
- More than 2 lakh trees could be felled.
- Might affect Western Ghats forests (especially the Bedthi Conservation Reserve, closer to Dandeli Hornbill Conservation Reserve and located in the buffer region of Anshi-Dandeli Tiger Reserve).
- The railway line could be a leading cause of wildlife mortality as it intersects with the elephant movement corridor.
Do you know?
- The railway line passes through different types of forests, including evergreen, semi-evergreen, moist deciduous, and dry deciduous forests with a high canopy density.
- The forests along the proposed project zone are also rich in fauna. Majority of mammals belong to IUCN Red List and most of them are protected under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 23rd March 2020
Image source: https://www.deccanherald.com/state/rly-minister-red-signals-710375.html
Important Value Additions
Bedthi Conservation Reserve
- It spans over 59.07 sq.km and is situated in Uttar Kannada and functions as Hornbill habitats.
- Medicinal plant species like Coscinium fenestratum is also found here.
Dandeli Hornbill Conservation Reserve
- Dandeli forests of Karnataka have received the status of Hornbill Conservation Reserve.
- In the wildlife conservation history, this is the first time of its kind to have a special conservation reserve declared to protect single and endangered bird species i.e., Hornbills.
- Dandeli forests are home to four types of hornbills i.e., Malabar Pied, Malabar Grey, Great Pied and Indian Grey.
Do you know?
- Difference between Conservation Reserves and Community Reserves?
Rushikulya River: Over one lakh turtles have laid eggs along its coast
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains GS-I- Geography
Key points:
- Rushikulya is one of the major rivers in the state of Odisha
- It originates from Daringbadi hills of the Eastern Ghats range and flows into Bay of Bengal
- After Gahirmatha in Kendrapara district of Odisha, the Rushikulya river mouth in Ganjam district has emerged as the second largest nesting site of the endangered olive ridley turtles.
Carissa kopilii: A new Plant Species found in Assam
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains GS-III- Environment
Key points:
- Carissa kopilii is a wilder variety of the more familiar Carissa carandas (also known as karonda in Hindi, kalakkai in Tamil, koromcha in Bengali and karja tenga in Assamese)
- Carissa kopilii is distributed sparsely along the Kopili riverbed at altitudes ranging from 85-600 metres above sea level.
- Kopili River is an interstate river that flows through the states of Meghalaya and Assam and is the largest south bank tributary of the Brahmaputra in Assam
- The plant is threatened by a hydroelectric project on the river and water turned acidic because of coal mining in Meghalaya upstream.
Did You Know?
- The Carissa carandas was among several thorny plants the British used for a 1,100-mile barrier – called Great Hedge of India- apparently to enforce taxes and stop the smuggling of salt.
- Carissa carandas has been used as a traditional herbal medicine for a number of ailments such as diarrhoea, anaemia, constipation, indigestion, skin infections and urinary disorders.
India and France conduct joint patrols
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In News:
- India and France have conducted joint patrols from the Reunion Island for the first time.
- The patrol was conducted by a P-8I aircraft with French Navy personnel on board.
- The surveillance was done in the southern Indian Ocean off Mauritius.
Do you know?
- Réunion Island is a French department in the Indian Ocean.
- It is known for its volcanic, rainforested interior, coral reefs and beaches.
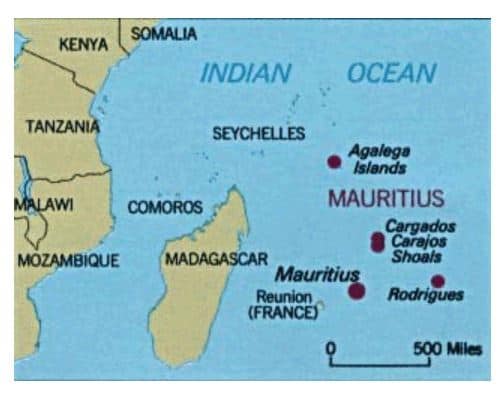
Image source: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/5418462026656127/
Important Value Additions:
- France is the first country to deploy a liaison officer at the Indian Navy’s Information Fusion Centre (IFC-IOR) as part of efforts to improve maritime domain awareness (MDA).
- France has steadily emerged as a major strategic partner for India with defence deals and increased military-to-military engagement.
- The Indian Navy is currently inducting French Scorpene conventional submarines, being built in India under technology transfer.
- The Indian Air Force will soon get the first batch of its 36 Rafale fighter jets.
OTT platforms: Telecos ask OTTS to reduce video quality to reduce load on networks
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains GS-III – Economy (Infrastructure)
What is OTT service?
- An over-the-top (OTT) media service is a streaming media service offered directly to viewers via the Internet i.e. they deliver content to customers on top of network infrastructure that is owned and maintained by internet service providers (ISPs)
- OTT bypasses cable, broadcast, and satellite television platforms, the companies that traditionally act as a controller or distributor of such content.
- OTT is commonly applied to video-on-demand platforms (NETFLIX, HOTSTAR), but also refers to audio streaming, messaging services or internet-based voice calling solutions (WHATSAPP).
Bulk drug parks approved
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II Welfare Schemes; Health
In News:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a scheme for promotion of bulk drug parks with a financial assistance of Rs. 3,000 crore for the next five years.
Key takeaways:
- Union Cabinet has also approved a Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for promotion of domestic manufacturing of critical drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) with a financial assistance of Rs. 6,940 crore for the next eight years.
- Government will give grants-in-aid to States with a maximum limit of Rs. 1,000 crore per bulk drug park.
- The park will have common facilities such as solvent recovery plant, distillation plant, power and steam units, common effluent treatment plant etc.
Do you know?
- The bulk drugs parks scheme is expected to reduce the manufacturing cost of bulk drugs in the country.
- It will also bring down the dependency on other countries for such drugs.
- The Production Linked Incentive Scheme will lead to expected incremental sales of Rs. 46,400 crore.
- It will also lead to significant additional employment generation.
Ayush Wellness Centre to come under NAM
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Welfare schemes; Health
In News:
- The Union Cabinet has approved the inclusion of the AYUSH Health and Wellness Centre (AYUSH HWC) component of Ayushman Bharat in the National AYUSH Mission (NAM).
Key takeaways:
- The move is aimed at establishing a holistic wellness model based on AYUSH principles and practices.
- It focuses on preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative healthcare by integrating with the existing public health care system.
- The National Health Policy 2017 (NHP, 2017) has advocated mainstreaming the potential of AYUSH systems (Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-rigpa and Homoeopathy) within a pluralistic system of Integrative healthcare.
- NHP, 2017 also empowers masses for ‘self-care’ to reduce the disease burden and out of pocket expenditure and to provide informed choice to the needy public.
Important Value Addition
National AYUSH Mission
- Department of AYUSH, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the National Ayush Mission (NAM) in 2014.
- It a centrally sponsored scheme.
- It was launched with the basic objective of promoting Ayurveda, Yoga, Siddha & Unani and Homoeopathy (AYUSH) medical system through cost effective services, strengthening of educational systems, sustainable availability of ASU & H raw-materials and facilitate the enforcement of quality control of (ASU &H) drugs.
Ayushman Bharat
- Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) is a flagship scheme of the Indian government’s National Health Policy.
- It aims to provide free health coverage at the secondary and tertiary level to its bottom 40% poor and vulnerable population.
- PM-JAY is the world’s largest and fully state sponsored health assurance scheme.
Enkasu card launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and Technology
In News:
- Karur Vysya Bank has launched Enkasu, a pre-paid card, in Karur (Tamil Nadu) to reduce cash transactions.
- En-Kasu in Tamil means – “My Money”
Key takeaways:
- Enkasu works on Near Field Communication Technology in a semi-closed loop.
- The cardholder can make tap-and-go payment for all purchases, even as meagre as Rs. 1.
- The Enkasu card will be beneficial to both merchants and customers alike.
- They can be accepted online as well as offline.
- Internet access is not mandatory for usage.
- It can be recharged through multiple means – through KVB’s mobile App DLite, UPI, NEFT or through KVB branches in Karur.
- Non-customers can also get an Enkasu card even if they do not have a bank account anywhere.
- Most merchant establishments across Karur will accept the card.
- KVB is also planning to expand the usage of Enkasu to other districts in Tamil Nadu.
Prelims Value Addition
Near Field Communication
- Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless connectivity standard that uses magnetic field induction to enable communication between devices when they’re touched together, or brought within a few centimetres of each other.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Science & Technology
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Awareness in the fields of IT
Quantum Technology
Context: India’s slow progress of research in Quantum technology whereby serious experimental work has been under way for only about five years, and in few locations.
In contrast countries like US, Europe & China have focused on the field since past two decades and are on the verge of major breakthroughs
Constraints on India’s progress
- Lack of sufficient resources
- Inadequate high quality manpower
- Lack of timeliness and flexibility
- Slow Implementation: A programme called Quantum Enabled Science and Technology has been fully rolled out now, more than two years after the call for proposals.
What is Quantum Technology?
It is a class of technology that works by using the principles of quantum mechanics (the physics of sub-atomic particles), including quantum entanglement and quantum superposition.
- Quantum entanglement is when two atoms are connected, or entangled, despite being separated.
- Quantum superposition is the theory that sub-atomic particles exist in multiple states simultaneously.
A timeline of Quantum Mechanics
- It was developed in the early 20th century to describe nature in the small — at the scale of atoms and elementary particles.
- It helped in understanding of the physical world, including the interaction of light and matter and on subjects such as gravity and black holes.
- It led to ubiquitous inventions such as lasers and semiconductor transistors
- A second revolution is currently under way with the goal of controlling and harnessing the properties of quantum mechanics.
Quantum field has not yet matured for commercialization, due to the extreme scientific challenges involved some of which are:
- Technical Difficulties: The challenge lies in harnessing the properties of quantum superposition and entanglement in a highly controlled manner by building a system composed of carefully designed building blocks called quantum bits or qubits.
- Fragility of Qubits: A qubit or quantum bit is the basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the binary bit (0 and 1) in classical computing
- These qubits tend to be very fragile and lose their “quantumness” if not controlled properly, and a careful choice of materials, design and engineering is required to get them to work.
- Theoretical Challenges of creating the algorithms and applications for quantum computers
Recent Developments:
- Google’s Sycamore demonstrated the quantum supremacy
- China demonstrated secure quantum communication links between terrestrial stations and satellites.
About National Mission on Quantum Technologies & Applications (NM-QTA)
- The mission will oversee the development of quantum technologies for communications, computing, materials development and cryptography.
- The mission addresses the constraints (listed above) that led to slow progression of country in quantum field, through adoption of holistic approach.
- Announced in Budget 2020
- Period: Five years (2020-25)
- Total Funds: Rs 8000 years
- Implementing Body: Department of Science & Technology (DST)
Significance of the mission:
- The mission may eventually lead to the creation of a super-secure communication network
- It will help prepare next generation skilled manpower, boost translational research and also encourage entrepreneurship and start-up ecosystem development.
- It will find utility in finding solution for complex problems in fields of computing, communications, sensing, chemistry, cryptography, imaging and mechanic
- The mission will enable India to emerge as Global leader in the field through increased investment & focus in Quantum Technologies
Way Forward
- Increase private funding, both via industry and philanthropy, as they can play an outsized role even with much smaller amounts and compliment the efforts of government
- Institutional Autonomy as there is a need to create a vibrant intellectual environment to help attract top researchers.
- Industry- Academia Collaboration: Connections with Indian industry from the start would help quantum technologies become commercialised successfully.
Connecting the dots:
- Cryptography- utility & challenges
- Artificial Intelligence – its utility and challenges
- Block Chain technology
Governance
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
COVID-19: The perils of an all-out lockdown
Context: Impending health and economic crisis in the face of COVID-19 spreading in India.
Staying at home (shutdown) has two motives:
- Self-protection motive, where a person acts out of fear of being infected
- A public-purpose motive, where a person participates in collective efforts to stop the spread of the virus.
Unlike the health crisis, the economic crisis is not class-neutral but hurts poor people the most.
Impact on Lockdown on Poor
- Informal Sector: India’s Informal sector employs approximately 85% of all workers (Source: Niti Aayog ‘s Strategy for New India at 75, released in 2018). This sector whose earnings is usually on daily basis will be severely hit due to economic standstill caused by the lock-down.
- Internal Migration: Mass-layoffs in informal sector & factories have forced migrant workers to head back home, some without being paid.
- Shut down of essential services like Public transport, administrative offices, court hearings and immunization drives to varying degrees in many states – has lead to aggravation of hardships faced by poor people who are heavily dependent on them.
- Transport Sector dislocated: Essential commodities like wheat & food grains which were transported by road transport are facing the brunt because of the disruption caused due to lack of private sector participation.
- Lack of Social Security to the poor in India: Unlike in developed countries, the insurance & pension coverage in India is meagre. This lack of social security will make poor man’s life difficult during these times of shutdown.
If the Poor are asked to stay at home, they will need help which can be offered by the government through the following ways:
- Public services that help poor people without creating a major health hazard should continue to function as far as possible. For example: PDS, administrative offices at district & local levels
- Utilizing Existing Social Schemes to support the poor:
-
- Advance payment of pensions
- Enhanced PDS rations
- Immediate payment of MGNREGA wage arrears
- Expanded distribution of take-home rations at schools and anganwadis.
- Displaying creativity: An explicit list of essential services and official guidelines on coronavirus readiness at the workplace needs to be drafted & advertised by the governments.
-
- For instance, anganwadis could play a vital role of public-health outreach at this time, even if children have to be kept away.
- Many public spaces could be used, with due safeguards, to disseminate information or to impart good habits such as distancing and washing hands
- Increase resources and labs for testing along with enhanced awareness about the disease so that people don’t go for testing without solid grounds.
-
- For instance: The ‘Break the Chain’ campaign started by Kerala government advocates ideas of basic cleanliness and hygiene
Conclusion
If the poor must stay at home, they need income support and essential services. Government should hence come up with economic blueprint to tackle the economic challenges posed by the pandemic. The constitution of task force headed by the Union Finance Minister is a step in the right direction.
Connecting the dots
- Universal Basic Income – its utility and challenges
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Consider the following statements:
- National Population Register will be prepared at national level
- Census is held after every 15 years.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 2. Dandeli Hornbill Conservation Reserve is located in which of the following states?
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Telangana
- Kerala
Q 3. India and France conducted joint patrols from which of the following islands recently?
- Reunion Island
- Maldives
- Seychelles
- Rodrigues
Q 4. Consider the following statements:
- Bulk drugs are known as active pharmaceutical ingredients (API).
- Bulk drugs parks scheme is expected to reduce the manufacturing cost.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 5. Consider the following statements:
- National AYUSH Mission is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Ayushman Bharat is the world’s largest health assurance scheme.
Which of the above statement is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 6. Consider the following statements about The Great Hedge of India
- It was built by British during 19th Century
- It was a wall of thorny shrubs that ran from the Indus in the Punjab to the Mahanadi in Odisha, cutting across Northern India
- It was built to enforce taxes and stop the smuggling of salt.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q 7. Consider the following statements about Kopili River
- It is a tributary of Brahmaputra river
- It is an inter-state river between Assam and Arunachal Pradesh
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 8. Consider the following statements about Rushikulya River
- It is one of the major rivers of Andhra Pradesh
- Its river mouth is one of the largest nesting site of the endangered olive ridley turtles.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 21 March 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | C |
| 5 | B |
Must Read
About COVID-19 and China’s model
About India & SAARC
About Impact of COVID-19 on the need for reform
















