IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 15th April 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
India looks to secure Dollar Swap Line
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations & GS-III – Economy
In News:
- India is working with the United States to secure a dollar swap line.
- It would help in better management of its external account.
- It would also provide extra safeguard in the event of an abrupt outflow of funds due to coronavirus-led lockdown.
Important value additions:
Currency swap agreements
- Such agreements involve trade in local currencies, where countries pay for imports and exports at pre-determined rates of exchange without the involvement of a third country currency like the US dollar.
- India already has a $75 billion bilateral currency swap line with Japan.
- The Reserve Bank of India also offers similar swap lines to central banks in the SAARC region within a total corpus of $2 billion.
- Benefits:
-
- These swap operations carry no exchange rate or other market risks, as transaction terms are set in advance.
- It reduces the risk of volatility against the third currency.
- It does away with the charges involved in multiple currency exchanges.
- It would discourage speculative attacks on the domestic currency.
Pooled Testing advisory issued by Indian Council of Medical Research
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Governance & GS-III – Science and Technology
In News:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has issued an advisory for using pooled samples for testing of COVID-19.
Key takeaways:
- ICMR recommendations:
- The number of samples should not exceed five samples at a time. This is to avoid sample dilution, which can lead to false negatives.
- This method can be used in areas where the prevalence of COVID-19 is low, which means a positivity rate of less than 2%.
- In areas with a positivity rate between 2 to 5%, sample pooling of PCR screening may be done among asymptomatic individuals
- Pooling of sample is not recommended in areas or population with positivity rates of over 5%.
Important value additions:
- In a pooled testing algorithm, samples of multiple individuals are put together in a tube and screened through the PCR test.
- In case the pooled test turns out to be positive, individual samples are tested, known as pool de-convolution.
- If there’s no positive result, all individual samples in the pool are regarded as negative.
- Benefits:
- Substantial costs and testing kits are saved.
- Pooled screening can also help in tracking down the asymptomatic cases, thereby helps in tracking community transmission.
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- It is the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research.
- It is one of the oldest and largest medical research bodies in the world.
- The ICMR is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Bank Sakhi / BC Sakhi plays vital role in financial inclusion
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Governance
In News:
- Self Help Group women working as BC Sakhis and Bank Sakhis are playing a vital role in disbursement of Rs.500/- to women having PMJDY accounts (Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana) amidst COVID-19 Lockdown.
Important value additions:
- BC Sakhis are Self-Help Groups (SHGs) women working as Business Correspondents for banks.
- A Bank Sakhi is someone who has been an SHG member involved in conducting banking and book-keeping activities of the group.
- As a Bank Sakhi, she provides a range of financial services on behalf of the bank to her community.
- She is supported by the local SHG federation which provides capacity development, training, and financial awareness in the community.
- She is paid a commission by the bank for different services, which covers her costs and provides her with an income.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
- It is a financial inclusion program of Government of India.
- It is open to all Indian citizens.
- It aims to expand and make affordable access to financial services such as bank accounts, remittances, credit, insurance and pensions.
Miscellaneous
CollabCAD
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog and National Informatics Centre (NIC) have jointly launched CollabCAD recently.
- The aim of this initiative is to provide a great platform to students of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) across country to create and modify 3D Computer Aided Designs with free flow of creativity and imagination.
Pattachitra
- COVID-19 pandemic has impacted the livelihood of the Pattachitra artists, residing in Heritage crafts village of Raghurajpur in Odisha.
- It is a picture painted on a piece of cloth.
- It is based in the states of West Bengal and Odisha.
| Bengal tradition | Odisha tradition |
| It is centered around Kalighat (in Kolkata). | It is centered around Puri. |
| Theme is not much devotional. | These paintings are based on Hindu mythology and specially inspired by Jagannath and Vaishnava sect. |
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL/ HEALTH
Topic: General Studies 1 & 2:
- Contemporary World History (UN & its challenges)
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
WHO and its funding
Context: US has halted the funding to the WHO over its handling of the coronavirus pandemic.
About WHO
- WHO, founded in 1948, is a specialized agency of the United Nations with a broad mandate to act as a coordinating authority on international health issues.
- The main decision-making body at WHO is the annual World Health Assembly (WHA), attended by all member-states.
- There is also the Executive Board (EB) comprising technically qualified persons from 34 countries, elected based on geographic representation from across the globe.
What were the reasons given by US President for stopping the funds to WHO?
- WHO was being too lenient with China in the earliest days of the pandemic
- WHO’s delay in declaring COVID-19 as Public Health Emergency of International Concern(PHEIC) and as a result failed to impose a travel ban on China
- WHO must be held accountable for its inefficient working.
Do You Know?
- USA is the biggest overall donor to WHO, contributing more than $400 million in 2019, roughly 15% of its budget.
- China’s contribution to WHO for 2018-2019 was almost $76 million in assessed contributions and some $10 million in voluntary funding
- The WHO has been appealing for more than $1 billion to fund operations against the COVID-19 pandemic
How is the WHO funded?
- Assessed Contributions
- These are the dues countries pay in order to be a member of the Organization.
- The amount each Member State must pay is calculated relative to the country’s wealth and population.
- These contributions have declined, and now account for less than one-fourth of its funding.
- Voluntary Contributions
- These come from Member States (in addition to their assessed contribution) or from other partners (organisations & individuals)
- They can range from flexible to highly earmarked.
- Top funders include Bill and Melinda Gates (USD 367.7 million), GAVI Vaccine Alliance, World Bank, Rotary International and the European Commission
Consequences of the US decision
- Politicization of the Pandemic
- Reduces WHO’s ability to coordinate the fight against pandemic in coming months
- WHO’s significance will decline in long run if the shortfall in funding is not addressed
- Impacts the Public Health prospects of Africa: Half of all spending of WHO was in Africa.
- Impacts Health programs of WHO: A quarter of WHO budget went to polio eradication, 12% on access to healthcare, 5% on outbreak prevention and control
- It provides further scope for China to increase its funding and influence in WHO
- Signals US intention of retreating from Global affairs thus creating vacuum in Global Leadership role
Trend of US retreating from Global leadership role
Since Trump Presidency (2016 onwards), US has
- Quit the U.N. Human Rights Council and U.N. cultural agency UNESCO
- Pulled out of Paris accord and Iran nuclear deal
- Cut funding for the U.N. Population Fund (UNFPA) and U.N. agency that helps Palestinian refugees (UNRWA)
- Opposed a U.N. migration pact
Way Ahead
- US should hold WHO accountable not by suspending its funding but by setting up actionable committee to look into lapses in WHO’s response during pandemic
- Institutional Reforms in WHO
- Increase the flexible funding
- Reduction in bureaucratic complexity to ease the process
- Reduce reliance on voluntary contributions and instead increase assessed contributions
- Empowering the Executive board for quick decision making backed by scientific data
- More Democratic functioning of the body – needs to insulate from global power politics
Connecting the dots:
- WTO, UNO – Democratic deficit in their structure and functioning
- Impact of decline in WHO’s funding on India’s health funding
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
COVID-19: Eurozone and challenges
Context: EU- the most progressive post-national regional arrangement was not proactive while dealing with the spread of COVID-19 pandemic. This resulted in its member states turning inward for solutions.
About European Union(EU)
- It is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe.
- Objective of EU and its policies
- Ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market,
- Enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development
Below is the schematic representation of EU
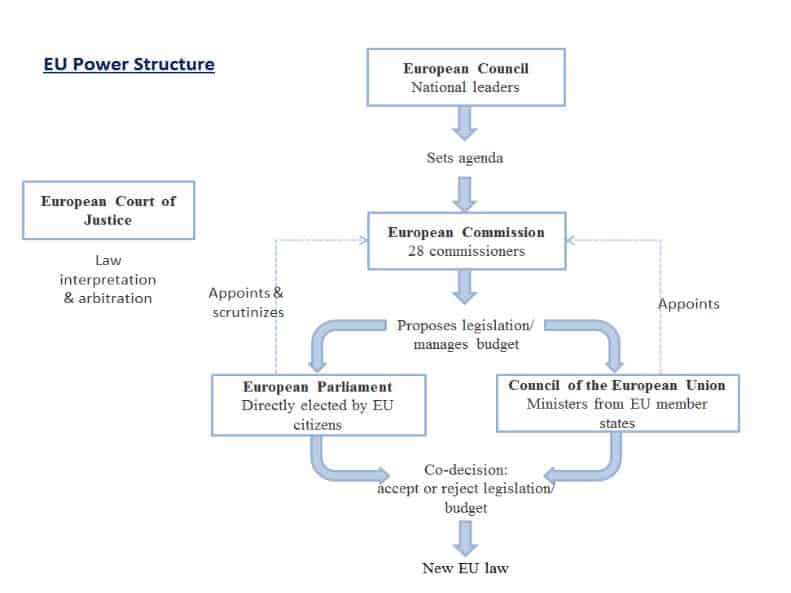
Image Source: Google
What are the recent steps taken by the EU to fight COVID-19?
- Emergency rescue package amounting to €540-billion
- Opening up of an emergency credit line for member countries
- Raise the lending capacity of the European Investment Bank
- European Commission’s €100- billion unemployment insurance scheme
- European Central Bank has decided to expand its asset purchase programme by €750-billion over the next nine months
Challenges ahead
- Apprehensions about intrusive EU inspections with regard to relief package
- Discontent with regard to burden-sharing between the richer members in the north (like Germany & France) and the poorer states in the south (like Greece & Portugal)
- Demand from Italy (worse affected) that pandemic credit to be issued by the European Stability Mechanism should not be attached with any conditionalities.
- Greece and Ireland had received financial bailouts from EU in 2009 but were accompanied by fiscal austerity measures (reduction in welfare spending)
- No progress on joint issuance of Eurobonds (dubbed corona bond).
- These are Common debt instrument which would pool borrowing among EU nations to fight the crisis.
- Implementation Challenges: Utilization of relief package would be slowed down by bureaucratic complexities
- Unsatisfied pro-European elites: The support measures by EU is considered as too little and not holistic
- Strains in National Coalition governments over the strategy to be adopted to tackle the pandemic, especially in the backdrop of EU’s less-enthusiastic role
- For instance: Netherlands’ ruling coalition unhappy over the government’s orthodox fiscal stance, where the opposition parties advocate Eurobonds.
- High Stakes: Failure to tackle the pandemic can affect European Solidarity especially after the difficulties faced in the aftermath of 2008 financial crisis and the recent Brexit.
Way Ahead
- When the pandemic hit the continent self-help and not regional coordination, was countries first instinct- which doesn’t bode well for EU.
- Therefore, bigger economies like Germany, France & Netherlands need to compromise to ensure sustainability of the grouping
Connecting the dots:
- SAARC and India’s initiative for collaboration on tackling pandemic
- Difference in structure between EU and ASEAN
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- According to ICMR recommendations, no more than five samples are allowed for pooled sampling.
- ICMR is one of the oldest and largest Medical Research bodies in the world.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements:
- BC Sakhi has been involved in conducting banking and financial services for her Self Help Group.
- Bank Sakhis are business correspondents for the banks.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 CollabCAD was recently launched by which of the following?
- IIT Mumbai
- IIM Ahmedabad
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences
- Niti Aayog
Q,4 Consider the following statements regarding pattachitra?
- In Bengal tradition, it is centred around Kalighat
- Theme is based on Hindu mythology.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 14th April 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | C |
Must Read
Article by former RBI Governor on Fiscal measures to tackle COVID-19:
About Economic liberalization and its faults:
About Sociological analysis of rumours:













