IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims and Mains – Environment
Context: The average global sea surface temperature (SST) — the temperature of the water at the ocean surface — for February 2024 stood at 21.06 degree Celsius, the highest ever in a dataset that goes back to 1979.
Background:-
- The previous record of 20.98 degree Celsius was set in August 2023.
Why are the oceans getting warmer?
- Since the Industrial Revolution kicked off in the 19th Century, human activities such as burning fossil fuels have released high levels of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and nitrous oxide are some of the notable GHGs, which essentially trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming. As a result, the average global temperature has risen at least 1.2 degree Celsius above pre-industrial times.
- Notably, almost 90 per cent of the extra heat trapped by GHGs has been absorbed by the oceans, making them steadily warmer over the decades.
- There are other factors which have led to a spike in ocean temperatures. For instance, El Niño — a weather pattern that refers to an abnormal warming of surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean — has contributed to both ocean warming and rising global surface temperatures.
- There is also less dust blowing off the Sahara Desert recently due to weaker-than-average winds. Typically, the dust forms a “giant umbrella that shades” the Atlantic water and reduces ocean temperatures.
Why are rising sea surface temperatures a cause of worry?
- Higher ocean temperatures can have irreversible consequences for marine ecosystems. For instance, warmer oceans lead to an increase in ocean stratification — the natural separation of an ocean’s water into horizontal layers by density, with warmer, lighter, less salty, and nutrient-poor water layering on top of heavier, colder, saltier, nutrient-rich water. Usually, ocean ecosystems, currents, wind, and tides mix these layers.
- The rise in temperatures, however, has made it harder for water layers to mix with each other. Due to this, oceans are able to absorb less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and the oxygen absorbed isn’t able to mix properly with cooler ocean waters below, threatening the survival of marine life.
- Nutrients are also not able to travel up to the surface of the oceans from below. This could threaten the population of phytoplankton — single-celled plants that thrive on the ocean surface and are the base of several marine food webs. Phytoplankton are eaten by zooplankton, which are consumed by other marine animals such as crabs, fish, and sea stars. Therefore, if the phytoplankton population plummets, there could be a collapse of marine ecosystems.
- Warmer oceans cause marine heat waves (MHWs), which occur when the surface temperature of a particular region of the sea rises to 3 or 4 degree Celsius above the average temperature for at least five days.
- MHWs contribute to coral bleaching, which reduces the reproductivity of corals and makes them more vulnerable to life-threatening diseases. They also impact the migration pattern of aquatic animals.
- Higher ocean temperatures may also result in more frequent and intense storms like hurricanes and cyclones. Warmer temperatures lead to a higher rate of evaporation as well as the transfer of heat from the oceans to the air. When storms travel across hot oceans, they gather more water vapour and heat. This results in more powerful winds, heavier rainfall, and more flooding when storms reach the land — meaning heightened devastation.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: India has decided to join at least one of the four cooperative work programmes unveiled last week under the ‘clean energy pillar’ of the U.S.-led Indo Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) – the one on facilitating and promoting carbon-market activities.
Background:
- The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) is an economic initiative launched by U.S. President Joe Biden on May 23, 2022. The framework launched with fourteen participating founding member nations in the Indo-Pacific region with an open invitation for other countries to join.
About Indo Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF):
- IPEF was launched jointly by the USA and other partner countries of the Indo-Pacific region on May 23, 2022 at Tokyo.
- IPEF has 14 partner countries including Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam & USA.
- It seeks to strengthen economic engagement among partner countries with the goal of advancing growth, peace and prosperity in the region.
- The framework is structured around four pillars relating to Trade (Pillar I); Supply Chains (Pillar II); Clean Economy (Pillar III); and Fair Economy (Pillar IV).
- Seen by many analysts as an attempt by the U.S. to counter China’s growing influence in the region, the IPEF aims at having a common set of rules and standards around the four pillars.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims : Science
Context: Recently, astronomers detected 7 potentials ‘ghost particles’ that passed through planet.
Background:
- Scientists using data from the Ice Cube Neutrino Observatory in Antarctica believe they have potentially found the first evidence for astrophysical tau neutrinos, called “ghost particles”.
About Ghost Particles:
- “Ghost Particles” is a nickname for neutrinos, which are tiny subatomic particles.
- They are often called ‘ghost particles’ because they barely interact with anything else.
Key points about Neutrinos:
- Source: Neutrinos come from various sources and are often the product of heavy particles turning into lighter ones, a process called “decay”.
- Family: They belong to the family of particles known as leptons.
- There are three main leptons, namely electrons, muons, and tau particles.
- The last has proven to be especially difficult to observe and detect, earning the moniker of “ghost particle.”
- Characteristics: A neutrino is very similar to an electron, but has no electrical charge and a very small mass. They are the most common particle in the universe. Approximately 100 trillion neutrinos pass completely harmlessly through our body every second.
- Detection: They are extraordinarily difficult to detect, as they rarely collide with atoms. Of the four fundamental forces in the universe, neutrinos only interact with two — gravity and the weak force.
- Variety: They come in different types and can be thought of in terms of flavors, masses, and energies.
- In recent developments, China is constructing the world’s largest “ghost particle” detector, a massive underwater telescope in the South China Sea, designed to detect neutrinos.
- The telescope, named Tropical Deep-sea Neutrino Telescope (TRIDENT),is expected to span 7.5 cubic kilometers and be 10,000 times more sensitive than existing underwater telescopes.
Source: Frontline
Syllabus
- Prelims -Economy
Context: As per a recent report the number of complaints filed under the Reserve Bank’s ombudsman schemes increased by over 68 per cent to 7.03 lakh in the fiscal 2022-23.
Background:
- The complaints pertained to mobile/electronic banking, loans and advances, ATM/debit cards, credit cards, pension payments, remittances, and para banking, among others.
About RESERVE BANK INTEGRATED OMBUDSMAN SCHEME (RB-IOS)
- The Reserve Bank Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (RB-IOS) was launched on November 12, 2021.
- This scheme integrates the three erstwhile Ombudsman schemes of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), namely:Banking Ombudsman Scheme 2006, Ombudsman Scheme for Non-Banking Financial Companies 2018,Ombudsman Scheme for Digital Transactions
- The RB-IOS aims to provide cost-free redress of customer complaints involving ‘deficiency in service’ on the part of entities regulated by the RBI.
- If these complaints are not resolved to the satisfaction of the customers or not replied to within a period of 30 days by the regulated entity, the scheme steps in.
- The scheme also includes under its ambit additional Regulated Entities (REs), namely, Non-Scheduled Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks with a deposit size of ₹50 crore and above and Credit Information Companies.
- The scheme adopts a ‘One Nation One Ombudsman’ approach by making the RBI’s Ombudsman mechanism jurisdiction neutral.
Salient Features:
- Deficiency in Service: The grounds for filing a complaint are defined as “deficiency in service”, with a specified list of exclusions.
- Centralized Processing: A Centralized Receipt and Processing Centre has been set up at RBI, Chandigarh, for handling physical and email complaints in any language.
- Principal Nodal Officer: The responsibility of representing the regulated entity and furnishing information lies with the Principal Nodal Officer (ranked as a General Manager in a Public Sector Bank or equivalent).
- No Right to Appeal: Regulated entities cannot appeal when an Award is issued by the Ombudsman against them for not providing satisfactory and timely information/documents.
- Appellate Authority: The Executive Director-in-charge of Consumer Education and Protection Department at RBI serves as the Appellate Authority under the scheme.
- Filing Complaints: Complaints can be filed online on the RBI website.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Vietnam asks China to respect Gulf of Tonkin delimitation agreement.
Background:
- Gulf of Tonkin delimitation agreement was signed in 2000 that outlines the borders of territorial seas, exclusive economic zones, and continental shelves in the Gulf of Tonkin.
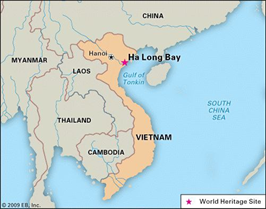
About GULF OF TONKIN:
- The Gulf of Tonkin, historically marked by cooperative relations between Vietnam and China, now faces a fresh sea dispute due to China’s unilateral expansion of territorial boundaries.
- The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf located at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, off the coasts of Tonkin (northern Vietnam) and South China.
- It serves as a vital waterway connecting the South China Sea to the Beibu Gulf (known as the Gulf of Tonkin in Vietnam).
Source: Times Of India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3
Context: The financial assistance for the Rubber sector under the ‘Sustainable & Inclusive Development of Natural Rubber Sector (SIDNRS)’ has been increased by 23% from Rs 576.41 crore to Rs 708.69 crore for the next 2 financial years (2024-25 and 2025-26).
Background:
- This comes amid a shortfall in availability of natural rubber which has resulted in rising import of natural rubber from countries such as Vietnam, Malaysia and other Southeast Asian nations.
Sustainable & Inclusive Development of Natural Rubber Sector (SIDNRS) Scheme:
- It is an initiative by the Government of India to promote the sustainable and inclusive development of the natural rubber sector in India which was launched in the FY 2017-18.
- It is implemented by the Rubber Board, a statutory body under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Objectives:
- To improve the productivity and quality of natural rubber production.
- To promote the adoption of sustainable rubber production practices.
- To improve the income and livelihoods of rubber growers.
- To create employment opportunities in the rubber sector.
- To promote the development of the rubber-based industry.
Components of the Scheme:
- Financial assistance is provided to rubber growers for replanting old and uneconomic rubber trees with high-yielding and disease-resistant varieties.
- Financial assistance was provided to rubber growers for intercropping rubber with other crops such as pineapple, banana, and cocoa. Intercropping helps to improve soil fertility, conserve moisture, and provide additional income to rubber growers.
- Training and extension services provided to rubber growers on best practices in rubber production, processing, and marketing.
- Financial assistance was provided for the development of infrastructure facilities such as roads, water harvesting structures, and processing units in rubber-growing areas.
- Financial assistance was provided for the establishment and expansion of rubber-based industries such as tire manufacturing, footwear manufacturing, and latex processing units.
Source: PIB
Practice MCQs
Q1.) The Gulf of Tonkin is a maritime region located in the northwestern portion of the
- Black Sea
- Red Sea
- South China Sea
- Arabian Sea
Q2.) With reference to Reserve Bank Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (RB-IOS), consider the following statements:
- RB-IOS aims to provide cost-free redress of customer complaints involving ‘deficiency in service’ on the part of entities regulated by the RBI.
- RBI Governor serve as the Appellate Authority under the scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.) Consider the following statements about ‘Ghost Particles’:
- Ghost Particles are miniscule subatomic particles that hardly interact with anything.
- They belong to the family of particles known as leptons.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th March 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 19th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d











