IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan, Rapid Revision Series (RaRe)
Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Friday)
- CSAT has been an Achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 10 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (35 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
Important Note
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
- Let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 35 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2023 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 35 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 35
1. Question
Which among the following parameters is/are used for the calculation of GDP at Basic Price?
- Cost of factors of production, such as land, labour and capital
- Production subsidies
- Product taxes
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Cost of factors of production, such as land, labour and capital are one of the parameters used for calculation of GDP at Basic Price. Production subsidies is one of the parameters used for calculation of GDP at Basic Price. Product taxes is not a parameter used for calculation of GDP at Basic Price. Note:
The Basic Price is the price expected to be received by the producer.
It is calculated as:
‘Factor Cost ‘+ ‘Production Taxes ‘– ‘Production Subsidies ‘.
Hence,
GDP at Basic Price = ‘GDP at Factor Cost’ + ‘Production Taxes’ – ‘Production Subsidies’.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Cost of factors of production, such as land, labour and capital are one of the parameters used for calculation of GDP at Basic Price. Production subsidies is one of the parameters used for calculation of GDP at Basic Price. Product taxes is not a parameter used for calculation of GDP at Basic Price. Note:
The Basic Price is the price expected to be received by the producer.
It is calculated as:
‘Factor Cost ‘+ ‘Production Taxes ‘– ‘Production Subsidies ‘.
Hence,
GDP at Basic Price = ‘GDP at Factor Cost’ + ‘Production Taxes’ – ‘Production Subsidies’.
-
Question 2 of 35
2. Question
Which among the following can be considered either as ‘Production tax/taxes or Production subsidy/subsidies?
- Stamp Duty
- Goods and Services Tax (GST)
- Subsidies on food and kerosene
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect Stamp Duty à Production Tax GST à Product Tax Subsidies on food and kerosene à Product Subsidy Note:
Production Taxes or Production Subsidies:
Production taxes or production subsidies are paid or received with relation to production and are independent of the volume of actual production.
- Some examples of production taxes are land revenues, stamps and registration fees, and tax on profession.
- Some production subsidies include subsidies to the railways, input subsidies to the farmers, subsidies to the village and small industries, administrative subsidies to the corporations or co-operatives, etc.
Product Tax or Product Subsidy:
Product taxes or subsidies are paid or received on per unit of product.
- Some examples of product taxes are excise tax, sales tax, service tax, and import and export duties.
- Product subsidies include food, petroleum and fertilizer subsidies, interest subsidies given to the farmers, households, etc.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect Stamp Duty à Production Tax GST à Product Tax Subsidies on food and kerosene à Product Subsidy Note:
Production Taxes or Production Subsidies:
Production taxes or production subsidies are paid or received with relation to production and are independent of the volume of actual production.
- Some examples of production taxes are land revenues, stamps and registration fees, and tax on profession.
- Some production subsidies include subsidies to the railways, input subsidies to the farmers, subsidies to the village and small industries, administrative subsidies to the corporations or co-operatives, etc.
Product Tax or Product Subsidy:
Product taxes or subsidies are paid or received on per unit of product.
- Some examples of product taxes are excise tax, sales tax, service tax, and import and export duties.
- Product subsidies include food, petroleum and fertilizer subsidies, interest subsidies given to the farmers, households, etc.
-
Question 3 of 35
3. Question
Which among the following correctly depicts/depict the nature of relationship between the GDP at Factor Cost, Basic Price and Market Price?
- GDP at Market Price = GDP at Factor Cost + Product Taxes – Product Subsidies
- GDP at Basic Price = GDP at Factor Cost + Production taxes – Production Subsidies
- GDP at Market Price = GDP at Basic Price + Product Taxes – Product Subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Relationship between GDP at Market Price and GDP at Basic Price:
- GDP at Market Price = GDP at Basic Price + Product Taxes – Product Subsidies
Relationship between GDP at Market Price and GDP at Factor Cost:
- GDP at Basic Price = GDP at Factor Cost + Production Taxes – Production Subsidies
Substituting the value of GDP at Basic Price with GDP at Factor Cost in equation 1,
GDP at Market Price = (GDP at Factor Cost + Production Taxes – Production Subsidies) + Product Taxes – Product Subsidies
GDP at Market Price = GDP at Factor Cost + (Production Taxes + Product Taxes) – (Production Subsidies + Product Subsidies)
GDP at Market price = GDP at Factor Cost + Indirect Taxes – Subsidies
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Relationship between GDP at Market Price and GDP at Basic Price:
- GDP at Market Price = GDP at Basic Price + Product Taxes – Product Subsidies
Relationship between GDP at Market Price and GDP at Factor Cost:
- GDP at Basic Price = GDP at Factor Cost + Production Taxes – Production Subsidies
Substituting the value of GDP at Basic Price with GDP at Factor Cost in equation 1,
GDP at Market Price = (GDP at Factor Cost + Production Taxes – Production Subsidies) + Product Taxes – Product Subsidies
GDP at Market Price = GDP at Factor Cost + (Production Taxes + Product Taxes) – (Production Subsidies + Product Subsidies)
GDP at Market price = GDP at Factor Cost + Indirect Taxes – Subsidies
-
Question 4 of 35
4. Question
If the Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) of a particular country is positive, what would it denote?
Correct
Solution (b)
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders, by both the citizens and the noncitizens.
On the other hand, the Gross National Product (GNP) measures the value of goods and services produced by only the country’s citizens, but both domestically and abroad.
GNP = GDP + Income earned by the Indians outside India – Income earned by the foreigners within India.
GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA).
Incorrect
Solution (b)
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders, by both the citizens and the noncitizens.
On the other hand, the Gross National Product (GNP) measures the value of goods and services produced by only the country’s citizens, but both domestically and abroad.
GNP = GDP + Income earned by the Indians outside India – Income earned by the foreigners within India.
GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA).
-
Question 5 of 35
5. Question
With reference to the GDP estimation in India, consider the following statements:
- The GDP is estimated at the Market Prices, instead of the Factor Cost.
- The base year for the calculation of the GDP is 2011-12.
- The GDP is estimated by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct The GDP is estimated at the Market Prices, instead of the Factor Cost. The base year for the calculation of the GDP is 2011-12. The GDP is estimated by the National Statistical Office (NSO). Note:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within an economy.
Recent changes in the GDP estimation (2015):
- Change in the base year from 2004-05 to 2011-12. Usually, the base years are revised at a frequency of 7-10 years by taking into account the changing economic landscape of the country.
- Change in the GDP estimation from the GDP at the Factor Cost to GDP at the Market Prices.
- Change in the database for capturing economic activity from RBI’s database to the MCA-21 database of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- This database is basically used for two purposes:
- Estimate the production of goods and services in the organized sector, based upon the tax returns.
- Extrapolate the production of goods and services in the unorganized sector, based upon the organized sector activity.
- The GDP is estimated by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct The GDP is estimated at the Market Prices, instead of the Factor Cost. The base year for the calculation of the GDP is 2011-12. The GDP is estimated by the National Statistical Office (NSO). Note:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within an economy.
Recent changes in the GDP estimation (2015):
- Change in the base year from 2004-05 to 2011-12. Usually, the base years are revised at a frequency of 7-10 years by taking into account the changing economic landscape of the country.
- Change in the GDP estimation from the GDP at the Factor Cost to GDP at the Market Prices.
- Change in the database for capturing economic activity from RBI’s database to the MCA-21 database of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- This database is basically used for two purposes:
- Estimate the production of goods and services in the organized sector, based upon the tax returns.
- Extrapolate the production of goods and services in the unorganized sector, based upon the organized sector activity.
- The GDP is estimated by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
-
Question 6 of 35
6. Question
With reference to the ‘Veblen Goods’, consider the following statements:
- The demand for these goods increases with the increase in their prices.
- These goods are normally considered to be the ‘Inferior Goods’.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect ‘Veblen Goods‘ are the goods for which the demand increases as the price increases. Veblen goods are typically high-quality goods that are made well, are exclusive and are a status symbol. Veblen goods are generally sought after by the affluent consumers, who place a premium on the utility of the goods.
Some of the examples include diamonds, iPhones, etc.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect ‘Veblen Goods‘ are the goods for which the demand increases as the price increases. Veblen goods are typically high-quality goods that are made well, are exclusive and are a status symbol. Veblen goods are generally sought after by the affluent consumers, who place a premium on the utility of the goods.
Some of the examples include diamonds, iPhones, etc.
-
Question 7 of 35
7. Question
Consider the following statements:
- All the Giffen Goods are Inferior Goods, but all the Inferior Goods are not Giffen Goods.
- The demand for the Giffen Goods increases with the increase in their prices.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Correct A Giffen good is a type of inferior good, but not all inferior goods are Giffen goods. An inferior good is a good for which the quantity demanded decreases as its price increases, meaning that as the consumer’s income increases, they will demand less of the good. A Giffen good is a specific type of inferior good for which an increase in price leads to an increase in the quantity demanded, resulting in a violation of the basic law of demand. This occurs because the good is so poor in quality and expensive that as the price increases, it becomes a luxury item and consumers demand more of it. Giffen Goods are those goods whose demand increases with the increase in their prices. Note:
Giffen Goods:
- In economics and consumer theory, a Giffen good is a product that people consume more of as the price rises and vice versa—violating the basic law of demand in microeconomics.
- For any other sort of good, as the price of the good rises, the substitution effect makes consumers purchase less of it, and more of substitute goods; for most goods, the income effect (due to the effective decline in available income due to more being spent on existing units of this good) reinforces this decline in demand for the good.
- But a Giffen good is so strongly an inferior good in the minds of consumers (being more in demand at lower incomes) that this contrary income effect more than offsets the substitution effect, and the net effect of the good’s price rise is to increase demand for it.
- This phenomenon is known as the Giffen paradox.
- A Giffen good is considered to be the opposite of an ordinary good. There are three necessary preconditions for this situation to arise:
- the good in question must be an inferior good,
- there must be a lack of close substitute goods, and
- the goods must constitute a substantial percentage of the buyer’s income, but not such a substantial percentage of the buyer’s income that none of the associated normal goods are consumed.
- Some examples of it are wheat, potatoes and Rice.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Correct A Giffen good is a type of inferior good, but not all inferior goods are Giffen goods. An inferior good is a good for which the quantity demanded decreases as its price increases, meaning that as the consumer’s income increases, they will demand less of the good. A Giffen good is a specific type of inferior good for which an increase in price leads to an increase in the quantity demanded, resulting in a violation of the basic law of demand. This occurs because the good is so poor in quality and expensive that as the price increases, it becomes a luxury item and consumers demand more of it. Giffen Goods are those goods whose demand increases with the increase in their prices. Note:
Giffen Goods:
- In economics and consumer theory, a Giffen good is a product that people consume more of as the price rises and vice versa—violating the basic law of demand in microeconomics.
- For any other sort of good, as the price of the good rises, the substitution effect makes consumers purchase less of it, and more of substitute goods; for most goods, the income effect (due to the effective decline in available income due to more being spent on existing units of this good) reinforces this decline in demand for the good.
- But a Giffen good is so strongly an inferior good in the minds of consumers (being more in demand at lower incomes) that this contrary income effect more than offsets the substitution effect, and the net effect of the good’s price rise is to increase demand for it.
- This phenomenon is known as the Giffen paradox.
- A Giffen good is considered to be the opposite of an ordinary good. There are three necessary preconditions for this situation to arise:
- the good in question must be an inferior good,
- there must be a lack of close substitute goods, and
- the goods must constitute a substantial percentage of the buyer’s income, but not such a substantial percentage of the buyer’s income that none of the associated normal goods are consumed.
- Some examples of it are wheat, potatoes and Rice.
-
Question 8 of 35
8. Question
Which of the following is/ are the characteristics of a mixed economy?
- Maintaining private ownership.
- Economic freedom in the use of capital.
- Government control of the means of production of public goods.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct Mixed economies typically maintain private ownership and control of most of the means of production, but often under government regulation. A mixed economic system protects private property and allows a level of economic freedom in the use of capital, but also allows for the governments to interfere in the economic activities, in order to achieve social aims. A mixed economy is an economy organized with some free-market elements and some socialistic elements, which lies on a continuum, somewhere between pure capitalism and pure socialism. Mixed economies socialize select industries that are deemed essential or that produce public goods.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Correct Mixed economies typically maintain private ownership and control of most of the means of production, but often under government regulation. A mixed economic system protects private property and allows a level of economic freedom in the use of capital, but also allows for the governments to interfere in the economic activities, in order to achieve social aims. A mixed economy is an economy organized with some free-market elements and some socialistic elements, which lies on a continuum, somewhere between pure capitalism and pure socialism. Mixed economies socialize select industries that are deemed essential or that produce public goods.
-
Question 9 of 35
9. Question
Which of the following economic activities come under the tertiary sector of the economy?
- Transport
- Storage
- Food processing
- Communication
- Banking
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4 Statement 5 Correct Correct Incorrect Correct Correct Transportation is part of Tertiary Sector Storage is part of Tertiary Sector Food Processing is part of Primary or Secondary Sector Communication is part of Tertiary Sector Banking is part of Tertiary Sector Note:
Primary Sector:
- When we produce goods by exploiting the natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector.
- This is because it forms the base for all other products that we subsequently make.
- Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing and forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector.
Secondary Sector:
- The secondary sector covers activities in which the natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity.
- It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature, but has to be made and, therefore, some process of manufacturing is essential.
- This could be in a factory, a workshop or at home. For example, using cotton fibre from the plant, we spin yarn and weave cloth.
Tertiary Sector:
- After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under the tertiary sector and is different from the above two.
- These are the activities that help in the development of the primary and the secondary sectors.
- These activities, by themselves, do not produce goods, but they are an aid or a support for the production process.
- For example, goods that are produced in the primary or secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in the wholesale and retail shops.
- At times, it may be necessary to store these in godowns.
- Transport, storage, communication, banking and trade are some examples of tertiary activities. Since these activities generate services rather than goods, the tertiary sector is also called the service sector.
- Service sector also includes some essential services that may not directly help in the production of goods. For example, we require teachers, doctors, and those who provide personal services, such as washermen, barbers, cobblers, lawyers and people to do administrative and accounting works.
- In recent times, certain new services, based on information technology, such as internet cafe, ATM booths, call centres, software companies, etc., have become important.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4 Statement 5 Correct Correct Incorrect Correct Correct Transportation is part of Tertiary Sector Storage is part of Tertiary Sector Food Processing is part of Primary or Secondary Sector Communication is part of Tertiary Sector Banking is part of Tertiary Sector Note:
Primary Sector:
- When we produce goods by exploiting the natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector.
- This is because it forms the base for all other products that we subsequently make.
- Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, dairy, fishing and forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector.
Secondary Sector:
- The secondary sector covers activities in which the natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity.
- It is the next step after primary. The product is not produced by nature, but has to be made and, therefore, some process of manufacturing is essential.
- This could be in a factory, a workshop or at home. For example, using cotton fibre from the plant, we spin yarn and weave cloth.
Tertiary Sector:
- After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under the tertiary sector and is different from the above two.
- These are the activities that help in the development of the primary and the secondary sectors.
- These activities, by themselves, do not produce goods, but they are an aid or a support for the production process.
- For example, goods that are produced in the primary or secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in the wholesale and retail shops.
- At times, it may be necessary to store these in godowns.
- Transport, storage, communication, banking and trade are some examples of tertiary activities. Since these activities generate services rather than goods, the tertiary sector is also called the service sector.
- Service sector also includes some essential services that may not directly help in the production of goods. For example, we require teachers, doctors, and those who provide personal services, such as washermen, barbers, cobblers, lawyers and people to do administrative and accounting works.
- In recent times, certain new services, based on information technology, such as internet cafe, ATM booths, call centres, software companies, etc., have become important.
-
Question 10 of 35
10. Question
Consider the following statements about the Human Capital Index:
- It is published by the World Economic Forum.
- It is a measure of poverty in various countries.
- Income per household is one of the components used by the Index.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Incorrect Incorrect Human Capital Index is published by the World Bank. The Human Capital Index (HCI) measures the human capital that a child born today can expect to attain by her 18th birthday, given the risks of poor health and poor education prevailing in her country. Components : 1: Survival from birth to school age, measured using under-5 mortality rates.
Component
2: Expected years of learning-adjusted school, combining information on the quantity and quality of education.
Component
3: Health – In the absence of a single broadly-accepted, directly measured and widely available metric, the overall health environment is captured by two proxies-
a) Adult survival rates, defined as the fraction of 15-year-olds who survive until age 60
b) The rate of stunting for children under age 5.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Incorrect Incorrect Human Capital Index is published by the World Bank. The Human Capital Index (HCI) measures the human capital that a child born today can expect to attain by her 18th birthday, given the risks of poor health and poor education prevailing in her country. Components : 1: Survival from birth to school age, measured using under-5 mortality rates.
Component
2: Expected years of learning-adjusted school, combining information on the quantity and quality of education.
Component
3: Health – In the absence of a single broadly-accepted, directly measured and widely available metric, the overall health environment is captured by two proxies-
a) Adult survival rates, defined as the fraction of 15-year-olds who survive until age 60
b) The rate of stunting for children under age 5.
-
Question 11 of 35
11. Question
Which of the following are the examples of human capital?
- Knowledge of the bus driver.
- Construction of a factory.
- Increase in the number of doctors.
- Publication of school books.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4 Correct Incorrect Correct Incorrect The owner of a physical capital, say a bus, need not be present in the place where it is used; whereas, a bus driver, who possesses the knowledge and ability to drive the bus, should be present when the bus is used for transportation of people and materials. Construction of a factory is a physical capital. Increase in the number of doctors is an increase in the human capital. Publication of school books is a part of physical capital. However, it helps in augmenting human capital. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4 Correct Incorrect Correct Incorrect The owner of a physical capital, say a bus, need not be present in the place where it is used; whereas, a bus driver, who possesses the knowledge and ability to drive the bus, should be present when the bus is used for transportation of people and materials. Construction of a factory is a physical capital. Increase in the number of doctors is an increase in the human capital. Publication of school books is a part of physical capital. However, it helps in augmenting human capital. -
Question 12 of 35
12. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the World Bank’s classification of the world economies:
- The World Bank classifies the world’s economies into four income groups namely high, upper-middle, lower-middle and low.
- The classification is based on estimates of a country’s Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
- India and China fall in the same category of the World Bank’s classification.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
The World Bank classifies economies for analytical purposes into four income groups: low, lower-middle, upper-middle, and high income. For this purpose, it uses gross national income (GNI) per capita data in U.S. dollars, converted from local currency using the World Bank Atlas method, which is applied to smooth exchange rate fluctuations.
Estimates of GNI are obtained from economists in World Bank country units who rely primarily on official data published by the countries; the size of the population is estimated by World Bank demographers from a variety of sources, including the UN’s biennial World Population Prospects.
Countries are classified each year on July 1, based on the estimate of their GNI per capita for the previous calendar year. Income groupings remain fixed for the entire World Bank fiscal year (i.e., until July 1 of the following year), even if GNI per capita estimates are revised in the meantime.
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
The World Bank classifies the world’s economies into four income groups – high, upper-middle, lower- middle, and low.
This assignment is based on Gross National Income (GNI) per capita (current US$). The classification is updated each year on July 1st.
India currently falls in the World Bank’s lower-middle income category while China currently falls in the upper-middle income category. Incorrect
Solution (b)
The World Bank classifies economies for analytical purposes into four income groups: low, lower-middle, upper-middle, and high income. For this purpose, it uses gross national income (GNI) per capita data in U.S. dollars, converted from local currency using the World Bank Atlas method, which is applied to smooth exchange rate fluctuations.
Estimates of GNI are obtained from economists in World Bank country units who rely primarily on official data published by the countries; the size of the population is estimated by World Bank demographers from a variety of sources, including the UN’s biennial World Population Prospects.
Countries are classified each year on July 1, based on the estimate of their GNI per capita for the previous calendar year. Income groupings remain fixed for the entire World Bank fiscal year (i.e., until July 1 of the following year), even if GNI per capita estimates are revised in the meantime.
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
The World Bank classifies the world’s economies into four income groups – high, upper-middle, lower- middle, and low.
This assignment is based on Gross National Income (GNI) per capita (current US$). The classification is updated each year on July 1st.
India currently falls in the World Bank’s lower-middle income category while China currently falls in the upper-middle income category. -
Question 13 of 35
13. Question
The maximum amount of income available within a domestic economy for the consumption of goods and services is termed as:
Correct
Solution (c)
- National Disposable Income is the maximum amount of goods and services a country has which could be used for the purpose of saving and consumption.
- It is obtained by adding Net National Product at market prices with current transfers from the rest of the world.
- It gives an idea of what is the maximum amount of goods and services the domestic economy has at its
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- National Disposable Income is the maximum amount of goods and services a country has which could be used for the purpose of saving and consumption.
- It is obtained by adding Net National Product at market prices with current transfers from the rest of the world.
- It gives an idea of what is the maximum amount of goods and services the domestic economy has at its
-
Question 14 of 35
14. Question
With reference to “Income elasticity of demand”, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Normal goods have a positive income elasticity of demand.
- Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Correct
Correct
Normal goods have a positive income elasticity of demand. As incomes rise, more goods are demanded at each price level. The quantity demanded for normal necessities will increase with income, but at a slower rate than luxury goods. This is because consumers, rather than buying more of the necessities, will likely use their increased income to purchase more luxury goods and services.
Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand – the quantity demanded for inferior goods falls as incomes rise. For example, the quantity demanded for generic food items tends to decrease during periods of increased incomes. Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Correct
Correct
Normal goods have a positive income elasticity of demand. As incomes rise, more goods are demanded at each price level. The quantity demanded for normal necessities will increase with income, but at a slower rate than luxury goods. This is because consumers, rather than buying more of the necessities, will likely use their increased income to purchase more luxury goods and services.
Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand – the quantity demanded for inferior goods falls as incomes rise. For example, the quantity demanded for generic food items tends to decrease during periods of increased incomes. -
Question 15 of 35
15. Question
“These are final goods that are of a durable character. They make the production of other commodities feasible, but they themselves don’t get transformed into the production goods. They gradually undergo wear and tear, and thus are repaired or gradually replaced over time”
Which of the following is described in the above passage?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Final Goods are the items which are meant for final use and will not pass through any more stages of production or transformations are called a final
- Of the final goods, we can distinguish between consumption goods and capital
- Consumption goods are goods like food and clothing and services like recreation that are consumed when purchased by their ultimate
- Capital goods are those goods that are of a durable character which are used in the production These are tools, implements, and machines. While they make the production of other commodities feasible, they themselves don’t get transformed into the production process.
- Consumer durables are commodities like television sets, automobiles or home computers, although they are for ultimate consumption, have one characteristic in common with capital goods – they are also
- Of the total production taking place in the economy a large number of products do not end up in final consumption and are not capital goods Such goods may be used by other producers as material inputs. Examples are steel sheets used for making automobiles and copper used for making utensils. These are intermediate goods.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Final Goods are the items which are meant for final use and will not pass through any more stages of production or transformations are called a final
- Of the final goods, we can distinguish between consumption goods and capital
- Consumption goods are goods like food and clothing and services like recreation that are consumed when purchased by their ultimate
- Capital goods are those goods that are of a durable character which are used in the production These are tools, implements, and machines. While they make the production of other commodities feasible, they themselves don’t get transformed into the production process.
- Consumer durables are commodities like television sets, automobiles or home computers, although they are for ultimate consumption, have one characteristic in common with capital goods – they are also
- Of the total production taking place in the economy a large number of products do not end up in final consumption and are not capital goods Such goods may be used by other producers as material inputs. Examples are steel sheets used for making automobiles and copper used for making utensils. These are intermediate goods.
-
Question 16 of 35
16. Question
Which of the following is/are observed in an economy during the expansion phase of the economic cycle?
- High-interest rates
- Moderate to high inflation
- Increased unemployment
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Incorrect
Correct
Incorrect
During the expansion phase, the economy experiences relatively rapid growth, interest rates tend to be low, and production increases.
During the expansion phase, the economy experiences relatively moderate to high inflation due to rise in aggregate demand.
In the expansion phase, there is an increase in various economic factors, such as production, employment, output, wages, profits, demand and supply of products, and sales. Thus, there is decrease in unemployment.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Incorrect
Correct
Incorrect
During the expansion phase, the economy experiences relatively rapid growth, interest rates tend to be low, and production increases.
During the expansion phase, the economy experiences relatively moderate to high inflation due to rise in aggregate demand.
In the expansion phase, there is an increase in various economic factors, such as production, employment, output, wages, profits, demand and supply of products, and sales. Thus, there is decrease in unemployment.
-
Question 17 of 35
17. Question
In an open economy, for the barter system to operate successfully, which of the following principle must be completely satisfied?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Double coincidence of wants is a situation where two economic agents have complementary demand for each other’s surplus It refers to the simultaneous fulfilment of mutual wants of buyers and sellers.
- For example, a person with a particular good has to find a person who has the goods of his wants and he should also possess the wanted good of the other
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Double coincidence of wants is a situation where two economic agents have complementary demand for each other’s surplus It refers to the simultaneous fulfilment of mutual wants of buyers and sellers.
- For example, a person with a particular good has to find a person who has the goods of his wants and he should also possess the wanted good of the other
-
Question 18 of 35
18. Question
In the Product method or Gross Value Added (GVA) method, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is calculated by adding the gross value added (GVA) of all firms in the economy.
Which of the following are used to find the GVA of a firm?
- Sales of the firm
- Change in inventories
- Value of intermediate goods used
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Correct
In the Product method or Gross Value Added (GVA) method, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is calculated by adding the gross value added (GVA) of all firms in the economy. GVA = Value of sales by the firm + Value of change in inventories – Value of intermediate goods used by the firm. This equation has been derived by using; Change in inventories of a firm during a year = Production of the firm during the year – Sale of the firm during the year.
Gross value added of firm = Gross value of the output produced by the firm – Value of intermediate goods used by the firm. Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Correct
In the Product method or Gross Value Added (GVA) method, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is calculated by adding the gross value added (GVA) of all firms in the economy. GVA = Value of sales by the firm + Value of change in inventories – Value of intermediate goods used by the firm. This equation has been derived by using; Change in inventories of a firm during a year = Production of the firm during the year – Sale of the firm during the year.
Gross value added of firm = Gross value of the output produced by the firm – Value of intermediate goods used by the firm. -
Question 19 of 35
19. Question
Factor Cost is a measure of national income or output based on the cost of factors of production. Which of the following are included in the factor cost?
- Government grants
- Subsidies
- Customs duty
- Service tax
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
The total cost incurred in deploying all factors, which led to the production or generation of goods and commodities available in the market, is known as factor cost.
Taxes paid to the government are not included in the factor cost since they are not directly engaged in the production process and so are not a component of the direct production cost.
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Statement 4
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Incorrect
Factor cost refers to the actual cost of the various factors of production that includes government grants. Factor cost refers to the actual cost of the various factors of production that even includes subsidies. Factor cost excludes custom duty. Factor cost excludes indirect taxes like service tax. Incorrect
Solution (c)
The total cost incurred in deploying all factors, which led to the production or generation of goods and commodities available in the market, is known as factor cost.
Taxes paid to the government are not included in the factor cost since they are not directly engaged in the production process and so are not a component of the direct production cost.
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Statement 4
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Incorrect
Factor cost refers to the actual cost of the various factors of production that includes government grants. Factor cost refers to the actual cost of the various factors of production that even includes subsidies. Factor cost excludes custom duty. Factor cost excludes indirect taxes like service tax. -
Question 20 of 35
20. Question
Consider the following statements regarding GDP calculation.
- Newly produced goods are counted.
- Final goods and services are counted.
- Central Statistics Office (CSO) added care economy to calculate GDP.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the single standard indicator used across the globe to indicate the health of a nation’s economy: one single number that represents the monetary value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific period. Only newly produced goods are counted.
Transactions in existing goods, such as second-handed cars, are not included as these do not involve the production of new goods. GDP measures the monetary value of final goods and services that is, those that are bought by the final user produced in a country in a given period of time
Much of the work done by women at home taking care of the children, aged, chores etc. which is called care economy is outside the GDP.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the single standard indicator used across the globe to indicate the health of a nation’s economy: one single number that represents the monetary value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific period. Only newly produced goods are counted.
Transactions in existing goods, such as second-handed cars, are not included as these do not involve the production of new goods. GDP measures the monetary value of final goods and services that is, those that are bought by the final user produced in a country in a given period of time
Much of the work done by women at home taking care of the children, aged, chores etc. which is called care economy is outside the GDP.
-
Question 21 of 35
21. Question
Consider the following statements:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change notifies the green hydrogen standard for India.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) is the nodal authority for accreditation of agencies for the certification of green hydrogen production projects.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (b)
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy notifies the green hydrogen standard for India. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- Green hydrogen is the hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources, either via electrolysis or biomass conversion. It also encompasses green energy preserved in energy storage systems.
- The emission thresholds for the production of hydrogen to be classified as ‘green’ are – Green hydrogen having a well-to-gate emission of not more than two kg carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent per kg hydrogen(H2).
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power will be the nodal authority for the accreditation of agencies for the monitoring, verification, and certification of green hydrogen production projects. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy notifies the green hydrogen standard for India. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- Green hydrogen is the hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources, either via electrolysis or biomass conversion. It also encompasses green energy preserved in energy storage systems.
- The emission thresholds for the production of hydrogen to be classified as ‘green’ are – Green hydrogen having a well-to-gate emission of not more than two kg carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent per kg hydrogen(H2).
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power will be the nodal authority for the accreditation of agencies for the monitoring, verification, and certification of green hydrogen production projects. Hence statement 2 is correct.
-
Question 22 of 35
22. Question
He was born on 25th December 1924. He was elected 10 times to the Lok Sabha from four different States. He was twice a member of the Rajya Sabha. He was the first non-Congress Prime Minister to have finished a full term. His birthday is observed as Good Governance Day. He advocated and practiced positive nationalism. He proudly took Hindi to the United Nations first time and spoke it in the UN General Assembly. He envisaged and executed the first round of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana which connected rural India. He conducted the nuclear test in Pokhran.
The above paragraph refers to which of the following personality?
Correct
Solution (d)
Atal Bihari Vajpayee was born on 25th December 1924. He was elected 10 times to the Lok Sabha from four different States. He was twice a member of the Rajya Sabha. He was the first non-Congress Prime Minister to have finished a full term. He was Prime Minister thrice in 1996, 1998-1999, and 1999-2004. His birthday is observed as Good Governance Day. He advocated and practiced positive nationalism. He proudly took Hindi to the United Nations first time and spoke it in the UN General Assembly. He rode a bus to Lahore for Indo-Pak peace. He envisaged and executed the first round of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana which connected rural India. He conducted the nuclear test in Pokhran. He brought in the National Highway Development Project leading to East West North South Corridor or the Golden Quadrilateral. The New Telecom Policy of 1999 brought in by him was also a crucial part of the Indian telecom revolution. He was awarded Padma Vibhushan in 1992 and India’s highest civilian honor, Bharat Ratna in 2015. Hence option d is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Atal Bihari Vajpayee was born on 25th December 1924. He was elected 10 times to the Lok Sabha from four different States. He was twice a member of the Rajya Sabha. He was the first non-Congress Prime Minister to have finished a full term. He was Prime Minister thrice in 1996, 1998-1999, and 1999-2004. His birthday is observed as Good Governance Day. He advocated and practiced positive nationalism. He proudly took Hindi to the United Nations first time and spoke it in the UN General Assembly. He rode a bus to Lahore for Indo-Pak peace. He envisaged and executed the first round of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana which connected rural India. He conducted the nuclear test in Pokhran. He brought in the National Highway Development Project leading to East West North South Corridor or the Golden Quadrilateral. The New Telecom Policy of 1999 brought in by him was also a crucial part of the Indian telecom revolution. He was awarded Padma Vibhushan in 1992 and India’s highest civilian honor, Bharat Ratna in 2015. Hence option d is correct.
-
Question 23 of 35
23. Question
Which of the following are the factors that influence the intensity of southwest monsoons in India?
- Strengths of high pressure over Tibet
- Strengths of low pressure over the southern Indian Ocean
- Somali Current
- Indian Ocean branch of Walker Cell
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (b)
The factors that influence the intensity of southwest monsoons in India:
- Strengths of low pressure over Tibet
- Strengths of high pressure over the southern Indian Ocean
- Somali Current
- Indian Ocean branch of Walker Cell
- Indian Ocean Dipole
- Somali Jet
Hence option b is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
The factors that influence the intensity of southwest monsoons in India:
- Strengths of low pressure over Tibet
- Strengths of high pressure over the southern Indian Ocean
- Somali Current
- Indian Ocean branch of Walker Cell
- Indian Ocean Dipole
- Somali Jet
Hence option b is correct.
-
Question 24 of 35
24. Question
Consider the following statements about the Grant for Research and Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) scheme:
- It aims to support individuals and companies to translate prototypes into technologies & products, including commercialization.
- It is launched by the Ministry of Textiles to provide much-needed impetus for the development of the technical textiles startup ecosystem in India.
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (c)
- The Grant for Research and Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) scheme aims to support individuals and companies to translate prototypes into technologies and products, including commercialization. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is launched by the Ministry of Textiles to provide much-needed impetus for the development of the technical textiles startup ecosystem in India, especially in niche sub-segments such as bio-degradable and sustainable textiles, high-performance and specialty fibers, and smart textiles. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The Grant for Research and Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) scheme aims to support individuals and companies to translate prototypes into technologies and products, including commercialization. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is launched by the Ministry of Textiles to provide much-needed impetus for the development of the technical textiles startup ecosystem in India, especially in niche sub-segments such as bio-degradable and sustainable textiles, high-performance and specialty fibers, and smart textiles. Hence statement 2 is correct.
-
Question 25 of 35
25. Question
Consider the following statements about the State of India’s Birds Report 2023:
- About 70% of bird species show clear declines over the past decades.
- Forest degradation, urbanization, and energy infrastructure are the major threats faced by birds.
- Raptors, migratory shorebirds, and ducks have experienced the most significant declines.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Zero-day attack refers to an unknown vulnerability that can be exploited by any malicious The findings of the State of India’s Birds Report 2023 released by the State of India’s Birds Partnership are:
- About 39% of bird species show clear declines over the past decades. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- 178 species classified as of High Conservation Priority, and require immediate attention.
- Forest degradation, urbanization, and energy infrastructure are the major threats faced by birds. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Long-distance migratory birds, such as those from Eurasia and the Arctic, have suffered significant declines.
- Several species like the Indian Peafowl, Rock Pigeon, Asian Koel, and House Crow are thriving and increasing in both abundance and distribution.
- Raptors, migratory shorebirds, and ducks have experienced the most significant declines. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Zero-day attack refers to an unknown vulnerability that can be exploited by any malicious The findings of the State of India’s Birds Report 2023 released by the State of India’s Birds Partnership are:
- About 39% of bird species show clear declines over the past decades. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- 178 species classified as of High Conservation Priority, and require immediate attention.
- Forest degradation, urbanization, and energy infrastructure are the major threats faced by birds. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Long-distance migratory birds, such as those from Eurasia and the Arctic, have suffered significant declines.
- Several species like the Indian Peafowl, Rock Pigeon, Asian Koel, and House Crow are thriving and increasing in both abundance and distribution.
- Raptors, migratory shorebirds, and ducks have experienced the most significant declines. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 26 of 35
26. Question
Consider the following statements about Seethakali folk art:
- It is a centuries-old folk art form that originated in Kerala.
- It is based on certain episodes taken from the Indian epic Ramayana.
- Its props and instruments are made of natural materials like bamboo and palm leaves.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Seethakali folk art is a centuries-old folk art form that originated in Kerala. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- This art form was first performed some 150 years back by the people of Vedar and Pulayar communities.
- It is based on certain episodes taken from the Indian epic Ramayana. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Mythic characters such as Rama, Seetha, Ravana, and Hanuman come alive in Seethakali performances that portray the tale of Seetha’s journey, from the time she accompanied Rama to the woods to her ascent to the heavens.
- Its props and instruments are made of natural materials like bamboo and palm leaves. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The costumes and the make-up are loud and eye-catching. The characters of Rama and Laxmana appear in green since the colour is used to represent gods and goddesses in Kathakali.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Seethakali folk art is a centuries-old folk art form that originated in Kerala. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- This art form was first performed some 150 years back by the people of Vedar and Pulayar communities.
- It is based on certain episodes taken from the Indian epic Ramayana. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Mythic characters such as Rama, Seetha, Ravana, and Hanuman come alive in Seethakali performances that portray the tale of Seetha’s journey, from the time she accompanied Rama to the woods to her ascent to the heavens.
- Its props and instruments are made of natural materials like bamboo and palm leaves. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The costumes and the make-up are loud and eye-catching. The characters of Rama and Laxmana appear in green since the colour is used to represent gods and goddesses in Kathakali.
-
Question 27 of 35
27. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the features of Nataraja:
- The upper left hand holds the drum which signifies the sound of creation.
- The upper right hand holds the eternal fire which signifies the destruction.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay Mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid.
- The lower left hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Nataraja is the representation of the Hindu god Shiva during his form as the cosmic dance. It is represented in metal or stone in many Shaivite temples, particularly in South India. It is an important piece of Chola sculpture.
The features of Nataraja are:
- The upper right hand holds the drum which signifies the sound of creation. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The upper left hand holds the eternal fire which signifies the destruction. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay Mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The lower left hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation. Hence statement 4 is correct.
- Shiva is dancing on the figure of a small dwarf. The dwarf symbolizes ignorance and the ego of an individual.
- The matted and flowing locks of Shiva represent the flow of the river Ganges.
- In ornamentation, one ear of Shiva has a male earring while the other has a female. This represents the fusion of male and female and is often referred to as
- A snake is wrapped around the arm of Shiva. The snake symbolizes the kundalini power, which resides in the human spine in the dormant stage.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Nataraja is the representation of the Hindu god Shiva during his form as the cosmic dance. It is represented in metal or stone in many Shaivite temples, particularly in South India. It is an important piece of Chola sculpture.
The features of Nataraja are:
- The upper right hand holds the drum which signifies the sound of creation. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The upper left hand holds the eternal fire which signifies the destruction. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay Mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- The lower left hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation. Hence statement 4 is correct.
- Shiva is dancing on the figure of a small dwarf. The dwarf symbolizes ignorance and the ego of an individual.
- The matted and flowing locks of Shiva represent the flow of the river Ganges.
- In ornamentation, one ear of Shiva has a male earring while the other has a female. This represents the fusion of male and female and is often referred to as
- A snake is wrapped around the arm of Shiva. The snake symbolizes the kundalini power, which resides in the human spine in the dormant stage.
-
Question 28 of 35
28. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Horn of Africa:
- It consists of Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Libya, and Djibouti
- It is equidistant from the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- It is a UNESCO Biodiversity Hotspot.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
- The Horn of Africa consists of Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Djibouti. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The Greater Horn of Africa region includes Burundi, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda.
- It is equidistant from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- It extends out into the Arabian Sea for hundreds of kilometers.
- It is located along the south of the Gulf of Aden.
- It is a UNESCO Biodiversity Hotspot. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- The Horn of Africa consists of Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Djibouti. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The Greater Horn of Africa region includes Burundi, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda.
- It is equidistant from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- It extends out into the Arabian Sea for hundreds of kilometers.
- It is located along the south of the Gulf of Aden.
- It is a UNESCO Biodiversity Hotspot. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 29 of 35
29. Question
‘Chail Wildlife Sanctuary’ which was in news recently is located in?
Correct
Solution (a)
- Chail Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It encompasses hills, valleys, forests, and grasslands.
- Its flora includes oak, pine, cedar, rhododendron, and grasslands.
- Its fauna includes pheasants, Himalayan bears, deer, langurs, and porcupines.
- It comprises part of the catchment area of a tributary of the Giri River.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- Chail Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It encompasses hills, valleys, forests, and grasslands.
- Its flora includes oak, pine, cedar, rhododendron, and grasslands.
- Its fauna includes pheasants, Himalayan bears, deer, langurs, and porcupines.
- It comprises part of the catchment area of a tributary of the Giri River.
-
Question 30 of 35
30. Question
The Kampala Declaration is related to?
Correct
Solution (d)
- The Kampala Declaration is related to climate change. Hence option d is correct.
- Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment, and Climate Change (KDMECC) was signed in 2022 at Kampala, Uganda by 15 African states.
- Its objective is to address the nexus of human mobility and climate change in the continent.
- It is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
- The Kampala Declaration is related to climate change. Hence option d is correct.
- Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment, and Climate Change (KDMECC) was signed in 2022 at Kampala, Uganda by 15 African states.
- Its objective is to address the nexus of human mobility and climate change in the continent.
- It is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
-
Question 31 of 35
31. Question
A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) and B = (25% of P) + (20% of Q). In which of the following cases is A – B positive?
Correct
Solution (b)
We will check by substituting the values for each option:
For option (a): A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) = 0.45 × 700 – 0.15 × 400 = 255 B = (25% of P) + (20% of Q) = 0.25 × 700 + 0.20 × 400 = 255 Clearly, A = B, hence option (a) is wrong.
For option (b): A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) = 0.45 × 700 – 0.15 × 300 = 315 – 45 = 270 B = (25% of P) + (20% of Q) = 0.25 × 700 + 0.20 × 300 = 175 + 60 = 235
For option (c): A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) = 0.45 * 700 – 0.15 * 500 = 315 – 75 = 240
B = ( 25% of P ) + ( 20% of Q) = ( 0.25 * 700) + ( 0.2 * 500 ) = ( 175 + 100 ) = 275
A-B = -35.
Clearly, A-B > 0 Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
We will check by substituting the values for each option:
For option (a): A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) = 0.45 × 700 – 0.15 × 400 = 255 B = (25% of P) + (20% of Q) = 0.25 × 700 + 0.20 × 400 = 255 Clearly, A = B, hence option (a) is wrong.
For option (b): A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) = 0.45 × 700 – 0.15 × 300 = 315 – 45 = 270 B = (25% of P) + (20% of Q) = 0.25 × 700 + 0.20 × 300 = 175 + 60 = 235
For option (c): A = (45% of P) – (15% of Q) = 0.45 * 700 – 0.15 * 500 = 315 – 75 = 240
B = ( 25% of P ) + ( 20% of Q) = ( 0.25 * 700) + ( 0.2 * 500 ) = ( 175 + 100 ) = 275
A-B = -35.
Clearly, A-B > 0 Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
-
Question 32 of 35
32. Question
A ball is dropped on the ground from a height of 1000 metre. Each time the ball bounces 4/5 times of the height of its every last bounce. Find the total distance covered by the ball before coming to rest.
Correct
Solution (d)
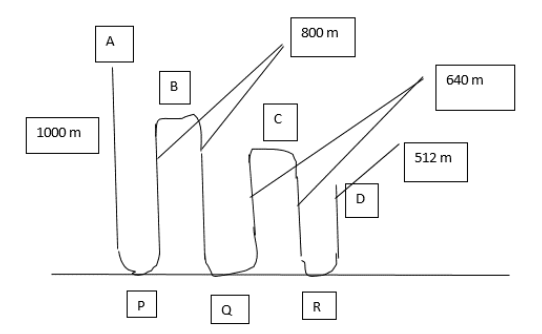
Distance covered in the 1st round = AP + PB = 1000 + (4/5)×1000 = 1000 + 800 = 1800 m.
Distance covered in the 2nd round = BQ + QC = 800 + (4/5)×800 = 800 + 640 = 1440 m.
Distance covered in the 3rd round = CR + RD = 640 + 4/5×640 = 640 + 512 = 1152 m and so on.
So, the total distance covered = 1800 + 1440 + 1152 + ……………….∞ terms.
This is an infinite G.P. (geometric progression) with common ratio 4/5.
So, Sum, S∞ = a/1-r ,
a = first term = 1800 and r = common ratio = 4/5.
Hence, the required distance = 1800/(1-4/5) = 1800/(1/5) = 9000 m
Incorrect
Solution (d)

Distance covered in the 1st round = AP + PB = 1000 + (4/5)×1000 = 1000 + 800 = 1800 m.
Distance covered in the 2nd round = BQ + QC = 800 + (4/5)×800 = 800 + 640 = 1440 m.
Distance covered in the 3rd round = CR + RD = 640 + 4/5×640 = 640 + 512 = 1152 m and so on.
So, the total distance covered = 1800 + 1440 + 1152 + ……………….∞ terms.
This is an infinite G.P. (geometric progression) with common ratio 4/5.
So, Sum, S∞ = a/1-r ,
a = first term = 1800 and r = common ratio = 4/5.
Hence, the required distance = 1800/(1-4/5) = 1800/(1/5) = 9000 m
-
Question 33 of 35
33. Question
Tina goes to her office by car. She usually reaches the office at 10:10 AM. One day she drove at 4/5th (four- fifth) of her usual speed and reached the office at 10:30 AM. What is the time taken by her to reach the office at her usual speed?
Correct
Solution (b)
New speed = 4/5 of its usual speed
So, New time taken = 5/4 of the usual time
[time = distance/speed, if distance is constant then time ∝ 1/speed ]
So, (5/4 of the usual time) – (usual time) = 20 min
➱ (5/4 -1) of the usual time = 20 min
➱ ¼ of the usual time = 20 min
➱ usual time = (4×20) min
= 80 min.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
New speed = 4/5 of its usual speed
So, New time taken = 5/4 of the usual time
[time = distance/speed, if distance is constant then time ∝ 1/speed ]
So, (5/4 of the usual time) – (usual time) = 20 min
➱ (5/4 -1) of the usual time = 20 min
➱ ¼ of the usual time = 20 min
➱ usual time = (4×20) min
= 80 min.
-
Question 34 of 35
34. Question
A student took five papers in an examination, where the full marks were the same for each paper. His marks in these papers were in the proportion of 4:5:6:7:8. In all papers together, the candidate obtained 60% of the total marks. Then the number of papers in which he got at least 70% marks is:
Correct
Solution (c)
Let the marks scored in five subjects be 4x, 5x, 6x, 7x and 8x (on a scale of 100).
Average score = 60% = 60 marks
So, (4x+5x+6x+7x+8x) / 5 = 60
or x = 10.
So, the marks obtained are 40, 50, 60, 70 and 80.
Hence the number of papers in which he got at least 70% marks = 2 (70 & 80).
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Let the marks scored in five subjects be 4x, 5x, 6x, 7x and 8x (on a scale of 100).
Average score = 60% = 60 marks
So, (4x+5x+6x+7x+8x) / 5 = 60
or x = 10.
So, the marks obtained are 40, 50, 60, 70 and 80.
Hence the number of papers in which he got at least 70% marks = 2 (70 & 80).
-
Question 35 of 35
35. Question
In an exam 12% students scored less than 30 marks, 6% students scored more than 200 marks, 22% students scored more than 100 marks, and 990 students scored between 30 and 100 marks. How many students scored between 100 and 200 marks?
Correct
Solution (b)
According to the question:
Students who scored more than 100 marks = 22%
And students who scored more than 200 = 6%
Hence, students who scored between 100 and 200 = 22 – 6 = 16%
Now, students who scored less than 30 = 12%
Students who scored between 30 and 100 = 100 – (22 + 12) = 66% = 990
So, Total number of students = 990 × (100/66) = 1500
Students who scored between 100 and 200 = 16% = (16/100) × 1500 = 240
Incorrect
Solution (b)
According to the question:
Students who scored more than 100 marks = 22%
And students who scored more than 200 = 6%
Hence, students who scored between 100 and 200 = 22 – 6 = 16%
Now, students who scored less than 30 = 12%
Students who scored between 30 and 100 = 100 – (22 + 12) = 66% = 990
So, Total number of students = 990 × (100/66) = 1500
Students who scored between 100 and 200 = 16% = (16/100) × 1500 = 240
All the Best
IASbaba











