IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan, Rapid Revision Series (RaRe)
Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Friday)
- CSAT has been an Achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 10 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (35 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
Important Note
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
- Let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 35 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2023 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 35 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 35
1. Question
During the festival season, the people usually withdraw large amount of money from the banks, leading to an increase in the Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR). What is the impact of the Money Multiplier?
Correct
Solution (b)
- The Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR) is the ratio of money held by the public in currency to that they hold in the bank deposits.
- It reflects the people’s preference for liquidity.
- For example, the Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR) increases during the festive season, as the people convert the deposits to cash balance for meeting extra expenditure during such periods.
- If the CDR increases, that means that the public is holding more of its money out of the banks, rather than depositing it.
- Hence, the Money Multiplier will go down.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- The Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR) is the ratio of money held by the public in currency to that they hold in the bank deposits.
- It reflects the people’s preference for liquidity.
- For example, the Currency Deposit Ratio (CDR) increases during the festive season, as the people convert the deposits to cash balance for meeting extra expenditure during such periods.
- If the CDR increases, that means that the public is holding more of its money out of the banks, rather than depositing it.
- Hence, the Money Multiplier will go down.
-
Question 2 of 35
2. Question
Which of the following statements correctly describes the meaning of Fiduciary Money?
Correct
Solution (c)
Fiduciary Money:
- Fiduciary Money is the money which is accepted on the basis of the trust it commands.
- Unlike Fiat Money, it is not declared as a legal tender by the government.
- It means that the people are not required by law to accept it as a means of payment.
- Examples of Fiduciary Money include cheques, bank notes or drafts.
Note:
Bank Deposits:
- Bank deposits consist of money placed into banking institutions for safekeeping.
- These deposits are made to deposit accounts such as savings accounts, checking accounts, and money market accounts.
- The account holder has the right to withdraw deposited funds, as set forth in the terms and conditions governing the account agreement.
Legal Tender:
- Legal Tender Money is anything recognised by law as a means to settle a public or private debt or meet a financial obligation, including tax payments, contracts, and legal fines or damages, is considered legal tender.
- In almost every country, the national currency is legal tender.
- A creditor is required by law to accept legal tender as payment for a debt.
Fiat Money:
- Fiat Money doesn’t have intrinsic value—through an objective calculation—its value is set by the government that issues the currency.
- Fiat money is a government-issued currency that is not backed by a physical commodity, such as gold or silver, but rather by the government that issued it.
- The value of fiat money is derived from the relationship between supply and demand and the stability of the issuing government, rather than the worth of a commodity backing it.
- Most modern paper currencies are fiat currencies, including the U.S. dollar, the euro, and other major global currencies.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Fiduciary Money:
- Fiduciary Money is the money which is accepted on the basis of the trust it commands.
- Unlike Fiat Money, it is not declared as a legal tender by the government.
- It means that the people are not required by law to accept it as a means of payment.
- Examples of Fiduciary Money include cheques, bank notes or drafts.
Note:
Bank Deposits:
- Bank deposits consist of money placed into banking institutions for safekeeping.
- These deposits are made to deposit accounts such as savings accounts, checking accounts, and money market accounts.
- The account holder has the right to withdraw deposited funds, as set forth in the terms and conditions governing the account agreement.
Legal Tender:
- Legal Tender Money is anything recognised by law as a means to settle a public or private debt or meet a financial obligation, including tax payments, contracts, and legal fines or damages, is considered legal tender.
- In almost every country, the national currency is legal tender.
- A creditor is required by law to accept legal tender as payment for a debt.
Fiat Money:
- Fiat Money doesn’t have intrinsic value—through an objective calculation—its value is set by the government that issues the currency.
- Fiat money is a government-issued currency that is not backed by a physical commodity, such as gold or silver, but rather by the government that issued it.
- The value of fiat money is derived from the relationship between supply and demand and the stability of the issuing government, rather than the worth of a commodity backing it.
- Most modern paper currencies are fiat currencies, including the U.S. dollar, the euro, and other major global currencies.
-
Question 3 of 35
3. Question
Which of the following steps have been taken to expedite and enable the resolution of the Non-Performing Assets of the Public Sector Banks?
- Promulgation of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
- Framing of Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act.
- Stressed Asset Management Verticals.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had initiated an ‘Asset Quality Review’ (AQR) in 2015 to clean up the Balance Sheets of the banks.
- As a result of the AQR and subsequent transparent recognition by the banks, stressed accounts were reclassified as NPAs (Non-Performing Assets) and expected losses on stressed loans, not provided for earlier under the flexibility given to the restructured loans, were provided for.
- The steps taken to expedite and enable the resolution of the NPAs of the PSBs (Public Sector Banks) include:
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016
- Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, and
- Stressed Asset Management Verticals.
- The NPAs declined as a result of the government’s ‘4Rs’ strategy of-
- Recognition
- Resolution
- Recapitalization and
- Reforms
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had initiated an ‘Asset Quality Review’ (AQR) in 2015 to clean up the Balance Sheets of the banks.
- As a result of the AQR and subsequent transparent recognition by the banks, stressed accounts were reclassified as NPAs (Non-Performing Assets) and expected losses on stressed loans, not provided for earlier under the flexibility given to the restructured loans, were provided for.
- The steps taken to expedite and enable the resolution of the NPAs of the PSBs (Public Sector Banks) include:
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016
- Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, and
- Stressed Asset Management Verticals.
- The NPAs declined as a result of the government’s ‘4Rs’ strategy of-
- Recognition
- Resolution
- Recapitalization and
- Reforms
-
Question 4 of 35
4. Question
Which of the following can lead to an increase in the Money Multiplier within the Indian economy?
- Decrease in the Cash Reserve Ratio
- Decrease in the Statutory liquidity Ratio
- Decrease in the rate of interest on loans
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Money Multiplier:
- The Money Multiplier refers to how an initial deposit can lead to a bigger final increase in the total money supply. For example, if the commercial banks gain deposits of Re. 1, this may lead to a final money supply of Rs. 6. The Money Multiplier is 6.
- It is calculated as (1/R), where R denotes the Reserve Ratio.
- The money multiplier indicates how quickly the money supply will grow as a result of bank lending. The higher the reserve ratio, the fewer deposits available for lending, resulting in a lower money multiplier.
- An increase in the Cash Reserve Ratio and Statutory Liquidity Ratio prevents the banks from lending more money and reduces the money multiplier. As the CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) and the SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) reduce, the Money Multiplier increases.
- Similarly, an increase in the financial inclusion also leads to an increase in the Money Multiplier. An increase in the banking habit of the population will increase the lending, thereby will lead to more deposits in the banking system, hence increasing the money multiplier.
- Decrease in the rate of interest on loans can lead to more borrowings by the people. This more lending by the banks would further lead to an increase in the Money Multiplier within the Indian economy.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Money Multiplier:
- The Money Multiplier refers to how an initial deposit can lead to a bigger final increase in the total money supply. For example, if the commercial banks gain deposits of Re. 1, this may lead to a final money supply of Rs. 6. The Money Multiplier is 6.
- It is calculated as (1/R), where R denotes the Reserve Ratio.
- The money multiplier indicates how quickly the money supply will grow as a result of bank lending. The higher the reserve ratio, the fewer deposits available for lending, resulting in a lower money multiplier.
- An increase in the Cash Reserve Ratio and Statutory Liquidity Ratio prevents the banks from lending more money and reduces the money multiplier. As the CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) and the SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) reduce, the Money Multiplier increases.
- Similarly, an increase in the financial inclusion also leads to an increase in the Money Multiplier. An increase in the banking habit of the population will increase the lending, thereby will lead to more deposits in the banking system, hence increasing the money multiplier.
- Decrease in the rate of interest on loans can lead to more borrowings by the people. This more lending by the banks would further lead to an increase in the Money Multiplier within the Indian economy.
-
Question 5 of 35
5. Question
Consider the following statements related to the Scheduled Banks in India:
- They are listed under the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934.
- They need to have a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 1,000 Crore.
- All the Cooperative Banks and the Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are categorized under the Scheduled Banks.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect The Scheduled Banks in India constitute those banks which have been included in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934. These banks should fulfil two conditions: 1. The paid-up capital and collected funds of the bank should not be less than Rs. 5 lakhs.
2. Any activity of the bank will not adversely affect the interests of the depositors.
All the categories of the Cooperative Banks are not categorized as the Scheduled Banks. For example, some of the Urban Cooperative Banks are categorized as the Non-Scheduled Banks. Note:
Scheduled Banks:
The list includes the State Bank of India and its subsidiaries (like State Bank of Travancore), all nationalized banks (Bank of Baroda, Bank of India etc.), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), foreign banks (HSBC Holdings Plc, Citibank NA) and some co-operative banks.
Regional Rural Banks:
- Regional Rural Banks were established in accordance with the provisions of an Ordinance promulgated on September 26, 1975, and the RRB Act, 1976, with the goal of ensuring adequate institutional credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- The Regional Rural Banks were created with the intention of combining the strengths of cooperative and commercial banks.
- It was hoped that these would provide cheap and adequate credit while also being operationally efficient and easy to access.
- The primary goal of Regional Rural Banks was to end the rural debt culture and close the credit gap that existed between geographical regions.
- RRBs are operationally sponsored by scheduled banks, which are typically public sector commercial banks.
- Instead of burdening commercial banks by extending their operations over large areas and spreading resources thin, RRBs were thought to be able to function intensively and confine their operations to a single region consisting of one or two contiguous districts.
- Thus, RRBs operate similarly to commercial banks, albeit with a smaller geographical reach for each of them.
- The Central Government, State Governments, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and smaller banks all work together to establish new RRBs and assist them in their operations.
- Since 1978, the RBI has primarily carried out promotional functions, while state governments carry out statutory functions.
- RRBs are jointly owned by Gol, the relevant State Government, and Sponsor Banks; the issued capital of an RRB is divided among the owners in the proportions of 50%, 15%, and 35%, respectively.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect The Scheduled Banks in India constitute those banks which have been included in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934. These banks should fulfil two conditions: 1. The paid-up capital and collected funds of the bank should not be less than Rs. 5 lakhs.
2. Any activity of the bank will not adversely affect the interests of the depositors.
All the categories of the Cooperative Banks are not categorized as the Scheduled Banks. For example, some of the Urban Cooperative Banks are categorized as the Non-Scheduled Banks. Note:
Scheduled Banks:
The list includes the State Bank of India and its subsidiaries (like State Bank of Travancore), all nationalized banks (Bank of Baroda, Bank of India etc.), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), foreign banks (HSBC Holdings Plc, Citibank NA) and some co-operative banks.
Regional Rural Banks:
- Regional Rural Banks were established in accordance with the provisions of an Ordinance promulgated on September 26, 1975, and the RRB Act, 1976, with the goal of ensuring adequate institutional credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- The Regional Rural Banks were created with the intention of combining the strengths of cooperative and commercial banks.
- It was hoped that these would provide cheap and adequate credit while also being operationally efficient and easy to access.
- The primary goal of Regional Rural Banks was to end the rural debt culture and close the credit gap that existed between geographical regions.
- RRBs are operationally sponsored by scheduled banks, which are typically public sector commercial banks.
- Instead of burdening commercial banks by extending their operations over large areas and spreading resources thin, RRBs were thought to be able to function intensively and confine their operations to a single region consisting of one or two contiguous districts.
- Thus, RRBs operate similarly to commercial banks, albeit with a smaller geographical reach for each of them.
- The Central Government, State Governments, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and smaller banks all work together to establish new RRBs and assist them in their operations.
- Since 1978, the RBI has primarily carried out promotional functions, while state governments carry out statutory functions.
- RRBs are jointly owned by Gol, the relevant State Government, and Sponsor Banks; the issued capital of an RRB is divided among the owners in the proportions of 50%, 15%, and 35%, respectively.
-
Question 6 of 35
6. Question
With reference to the Payments Banks in India, consider the following statements:
- The Payments Banks cannot accept deposits of more than Rs. 1 lakh from a single customer.
- The Payments Banks can issue both debit and credit cards.
- The Payments Banks are required to invest minimum 75% of their deposits in the Government Securities (G-Secs).
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Correct The Payments Banks cannot accept deposits of more than Rs. 1 lakh from a single customer. These banks can issue debit cards, but not credit cards. The Payments Banks cannot undertake lending activities. They are required to invest minimum 75% of their ‘demand deposit balances’ in the Government Securities/Treasury Bills, with maturity up to one year, that are recognized by the RBI as eligible securities for the maintenance of the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) and hold maximum 25% in current and time/fixed deposits with other Scheduled Commercial Banks for operational purposes and liquidity management. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Correct The Payments Banks cannot accept deposits of more than Rs. 1 lakh from a single customer. These banks can issue debit cards, but not credit cards. The Payments Banks cannot undertake lending activities. They are required to invest minimum 75% of their ‘demand deposit balances’ in the Government Securities/Treasury Bills, with maturity up to one year, that are recognized by the RBI as eligible securities for the maintenance of the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) and hold maximum 25% in current and time/fixed deposits with other Scheduled Commercial Banks for operational purposes and liquidity management. -
Question 7 of 35
7. Question
With reference to the printing of the currency notes by the RBI, consider the following statements:
- The RBI needs to maintain certain minimum reserves of foreign currency and gold to print the currency notes in India.
- The RBI Act, 1934 imposes statutory limit on the printing of the currency notes by the RBI.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect As per the RBI Act, 1934, the RBI needs to maintain minimum reserves of Rs. 200 crores (Rs. 115 Crore – Gold and Rs. 85 crore – Foreign Currency Assets) in order to print the currency notes. Based upon the maintenance of the minimum reserves, the RBI can print unlimited currency notes. As such, there is no statutory limit on the printing of the currency notes by the RBI. Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect As per the RBI Act, 1934, the RBI needs to maintain minimum reserves of Rs. 200 crores (Rs. 115 Crore – Gold and Rs. 85 crore – Foreign Currency Assets) in order to print the currency notes. Based upon the maintenance of the minimum reserves, the RBI can print unlimited currency notes. As such, there is no statutory limit on the printing of the currency notes by the RBI. -
Question 8 of 35
8. Question
Which of the following is/are considered as the legal tender in India?
- Currency notes
- Coins
- Cheques and demand drafts.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Legal tender in India. Legal tender in India. Not a legal tender in India. Note:
Legal Tender:
- ‘Legal tender’ is the money that is recognised by the law of the land as valid for payment of the debt. It must be accepted for discharge of the debt.
- Both currency notes and coins are considered to be the legal tender. However, cheques and demand drafts are not considered to be the legal tender.
- Legal tender can be limited or unlimited in character. In India, coins function as limited legal tender. Therefore, 50 paise coins can be offered as the legal tender for dues up to Rs. 10. Coins of Re. 1 and above can be offered as the legal tender for dues up to Rs. 1,000. Currency notes are unlimited legal tender and can be offered as payment for dues of any size.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Correct Incorrect Legal tender in India. Legal tender in India. Not a legal tender in India. Note:
Legal Tender:
- ‘Legal tender’ is the money that is recognised by the law of the land as valid for payment of the debt. It must be accepted for discharge of the debt.
- Both currency notes and coins are considered to be the legal tender. However, cheques and demand drafts are not considered to be the legal tender.
- Legal tender can be limited or unlimited in character. In India, coins function as limited legal tender. Therefore, 50 paise coins can be offered as the legal tender for dues up to Rs. 10. Coins of Re. 1 and above can be offered as the legal tender for dues up to Rs. 1,000. Currency notes are unlimited legal tender and can be offered as payment for dues of any size.
-
Question 9 of 35
9. Question
Which of the following steps is/are not likely to be taken by the RBI to promote economic growth and development?
- Adopt Calibrated Tightening Monetary Policy stance
- Decrease Repo Rates and Marginal Standing Facility rates
- Decrease Reverse Repo
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect The Calibrated Tightening Monetary Policy stance is adopted to control higher rates of inflation. As it will take out the liquidity from the market, it is not likely to be taken by the RBI to promote economic growth and development.
The RBI reduces various policy rates, such as Repo, Marginal standing facility (MSF) etc., to inject more liquidity into the economy, and promote economic growth and development. The RBI reduces various policy rates, such as Reverse Repo Rate, to inject more liquidity into the economy, and promote economic growth and development. Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Incorrect The Calibrated Tightening Monetary Policy stance is adopted to control higher rates of inflation. As it will take out the liquidity from the market, it is not likely to be taken by the RBI to promote economic growth and development.
The RBI reduces various policy rates, such as Repo, Marginal standing facility (MSF) etc., to inject more liquidity into the economy, and promote economic growth and development. The RBI reduces various policy rates, such as Reverse Repo Rate, to inject more liquidity into the economy, and promote economic growth and development. -
Question 10 of 35
10. Question
Which of the following are the eligible instruments that can be maintained by the banks to fulfill their Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) requirements?
- Treasury Bills
- Dated Securities of the Government
- State Development Loans
- Recapitalization Bonds
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR):
- Under the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), the banks are required to maintain certain percentage of Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) in the form of cash, gold and eligible G-Secs.
- These financial instruments include-
- Treasury Bills
- Dated Securities of the Government
- State Development Loans and
- Any other instrument as may be notified by the Reserve Bank of India.
- However, Recapitalization Bonds are not eligible instruments to fulfill the SLR requirements.
Recapitalisation Bonds:
- Recapitalisation bonds are dedicated bonds to be issued at the behest of the government for recapitalizing the trouble hit Public Sector Banks (PSBs).
- The government issues bonds which are subscribed by banks. The money collected by the government goes to banks in the form of equity capital as the government increases its share of equity holding, thereby shoring up banks’ capital reserves.
- The money invested by banks in recapitalisation bonds is classified as an investment which earns them an interest.
- This helps the government in maintaining its fiscal deficit target as no money directly goes out from its coffers.
- The term recapitalisation means giving equity money to cover debt of an entity. In the case of PSBs, their NPAs (debts) will be replaced by equity capital from recapitalisation by the government.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR):
- Under the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), the banks are required to maintain certain percentage of Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) in the form of cash, gold and eligible G-Secs.
- These financial instruments include-
- Treasury Bills
- Dated Securities of the Government
- State Development Loans and
- Any other instrument as may be notified by the Reserve Bank of India.
- However, Recapitalization Bonds are not eligible instruments to fulfill the SLR requirements.
Recapitalisation Bonds:
- Recapitalisation bonds are dedicated bonds to be issued at the behest of the government for recapitalizing the trouble hit Public Sector Banks (PSBs).
- The government issues bonds which are subscribed by banks. The money collected by the government goes to banks in the form of equity capital as the government increases its share of equity holding, thereby shoring up banks’ capital reserves.
- The money invested by banks in recapitalisation bonds is classified as an investment which earns them an interest.
- This helps the government in maintaining its fiscal deficit target as no money directly goes out from its coffers.
- The term recapitalisation means giving equity money to cover debt of an entity. In the case of PSBs, their NPAs (debts) will be replaced by equity capital from recapitalisation by the government.
-
Question 11 of 35
11. Question
With reference to the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), consider the following statements:
- The Cash Reserve Ratio refers to the percentage of the depositors’ money which the banks are required to maintain with the RBI in the form of cash.
- The banks are required to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on all the days.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is the percentage of the depositors’ money which the banks are required to maintain with the RBI in the form of cash. However, it may be noted that the RBI does not pay any interest to the banks on the CRR deposits.
All the banks are required to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on an average basis during the fortnight. This means that it is not necessary for the banks to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on all the days during the fortnight.
However, the average CRR with the RBI for the entire fortnight has to be 100% of the CRR requirement.
Note:
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is the percentage of the depositors’ money which the banks are required to maintain with the RBI in the form of cash.
- However, it may be noted that the RBI does not pay any interest to the banks on the CRR deposits.
During Inflation: Increase in the CRR
The banks are required to keep higher percentage of depositors’ money with the RBIàLess money available with the banks for giving loansàDecrease in the money supply.
During Slowdown: Decrease in the CRR
The banks are required to keep less percentage of depositors’ money with the RBIàMore money available for giving loansàIncrease in the money supply.
- All the banks are required to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on an average basis during the fortnight.
- This means that it is not necessary for the banks to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on all the days during the fortnight.
- However, the average CRR with the RBI for the entire fortnight has to be 100% of the CRR requirement.
- Further, the RBI stipulates the daily minimum CRR balances for the banks.
- Earlier, it was 90% of the CRR requirement on a daily basis.
- In 2019, the RBI decided to reduce the requirement of minimum daily CRR balance maintenance from 90% to 80%.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is the percentage of the depositors’ money which the banks are required to maintain with the RBI in the form of cash. However, it may be noted that the RBI does not pay any interest to the banks on the CRR deposits.
All the banks are required to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on an average basis during the fortnight. This means that it is not necessary for the banks to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on all the days during the fortnight.
However, the average CRR with the RBI for the entire fortnight has to be 100% of the CRR requirement.
Note:
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is the percentage of the depositors’ money which the banks are required to maintain with the RBI in the form of cash.
- However, it may be noted that the RBI does not pay any interest to the banks on the CRR deposits.
During Inflation: Increase in the CRR
The banks are required to keep higher percentage of depositors’ money with the RBIàLess money available with the banks for giving loansàDecrease in the money supply.
During Slowdown: Decrease in the CRR
The banks are required to keep less percentage of depositors’ money with the RBIàMore money available for giving loansàIncrease in the money supply.
- All the banks are required to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on an average basis during the fortnight.
- This means that it is not necessary for the banks to maintain 100% of the CRR requirement on all the days during the fortnight.
- However, the average CRR with the RBI for the entire fortnight has to be 100% of the CRR requirement.
- Further, the RBI stipulates the daily minimum CRR balances for the banks.
- Earlier, it was 90% of the CRR requirement on a daily basis.
- In 2019, the RBI decided to reduce the requirement of minimum daily CRR balance maintenance from 90% to 80%.
-
Question 12 of 35
12. Question
Consider the following statements related to the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF):
- The Standing Deposit Facility enables the RBI to inject liquidity into the economy, without accepting the G-Secs as collateral from the banks.
- This tool has been introduced through an amendment to the RBI Act, 1934.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Under the SDF route, the RBI would not be required to provide the G-Secs as collateral to the banks for parking its funds. Hence, it would enable the RBI to absorb huge amount of liquidity from the economy, without the G-Secs acting as collateral. The Finance Act (2018), introduced as a part of the Budget, amended the RBI Act, 1934, to enable the RBI to use the new tool of the SDF. Subsequently, the liquidity management framework adopted by the RBI in February, 2020, has decided to use the SDF in India. Note:
Standing Deposit Facility (SDF):
- The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) works similar to the Reverse Repo. However, the SDF is different from the Reverse Repo in the following ways:
- Under the SDF route, the RBI would not be required to provide the G-Secs as collateral to the banks. Hence, it would enable the RBI to absorb huge amount of liquidity from the economy, without the G-Secs acting as collateral.
- The SDF would be lower than the Reverse Repo.
- Reverse Repo exercise is carried out as per the discretion of the RBI, depending upon the market conditions. However, the SDF would enable the banks to keep their surplus funds with the RBI at their own discretion.
- The Finance Act (2018), introduced as a part of the Budget, amended the RBI Act, 1934, to enable the RBI to use the new tool of the SDF.
- Subsequently, the liquidity management framework adopted by the RBI in February, 2020, has decided to use the SDF in India.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Under the SDF route, the RBI would not be required to provide the G-Secs as collateral to the banks for parking its funds. Hence, it would enable the RBI to absorb huge amount of liquidity from the economy, without the G-Secs acting as collateral. The Finance Act (2018), introduced as a part of the Budget, amended the RBI Act, 1934, to enable the RBI to use the new tool of the SDF. Subsequently, the liquidity management framework adopted by the RBI in February, 2020, has decided to use the SDF in India. Note:
Standing Deposit Facility (SDF):
- The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) works similar to the Reverse Repo. However, the SDF is different from the Reverse Repo in the following ways:
- Under the SDF route, the RBI would not be required to provide the G-Secs as collateral to the banks. Hence, it would enable the RBI to absorb huge amount of liquidity from the economy, without the G-Secs acting as collateral.
- The SDF would be lower than the Reverse Repo.
- Reverse Repo exercise is carried out as per the discretion of the RBI, depending upon the market conditions. However, the SDF would enable the banks to keep their surplus funds with the RBI at their own discretion.
- The Finance Act (2018), introduced as a part of the Budget, amended the RBI Act, 1934, to enable the RBI to use the new tool of the SDF.
- Subsequently, the liquidity management framework adopted by the RBI in February, 2020, has decided to use the SDF in India.
-
Question 13 of 35
13. Question
Which of the following categories of banks can use the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) of the RBI to manage their liquidity?
- The Scheduled Commercial Banks
- The Scheduled Cooperative Banks
- The Regional Rural Banks
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF):
- It is a monetary policy tool used largely by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) that controls the liquidity or money supply in the economy.
- It does it by either allowing banks to borrow money via repurchase agreements (repos) or lend loans to the RBI via reverse repo agreements.
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility was recommended by the Narasimhan Committee on Banking Reforms and was introduced by the RBI in 1998.
- There are two main components of Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF):
- Repo Rate: It is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends to other banks.
- Reverse Repo Rate: It is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) borrows from commercial banks.
- Earlier, the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) was applicable only to the Scheduled Commercial Banks and the Scheduled Cooperative Banks.
- Recently, the RBI has decided to extend the LAF and the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) to the Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
- It has also been decided to permit the RRBs to participate in the Call/Notice money market, both as the borrowers and the lenders.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF):
- It is a monetary policy tool used largely by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) that controls the liquidity or money supply in the economy.
- It does it by either allowing banks to borrow money via repurchase agreements (repos) or lend loans to the RBI via reverse repo agreements.
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility was recommended by the Narasimhan Committee on Banking Reforms and was introduced by the RBI in 1998.
- There are two main components of Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF):
- Repo Rate: It is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends to other banks.
- Reverse Repo Rate: It is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) borrows from commercial banks.
- Earlier, the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) was applicable only to the Scheduled Commercial Banks and the Scheduled Cooperative Banks.
- Recently, the RBI has decided to extend the LAF and the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) to the Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
- It has also been decided to permit the RRBs to participate in the Call/Notice money market, both as the borrowers and the lenders.
-
Question 14 of 35
14. Question
With reference to the White Label ATMs in India, consider the following statements:
- These ATMs are set up, owned and operated by the non-banking entities.
- The customers are not charged at all for withdrawing money from such ATM machines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect The ATMs which are set up, owned and operated by non-banks are called the White Label ATMs (WLAs). The customers can be charged for transactions at the ATMs over and above the mandated number of free transactions. Note:
White Label ATMs (WLAs):
- The ATMs which are set up, owned and operated by non-banks are called the White Label ATMs (WLAs).
- The non-bank ATM operators are authorized under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act,2007, by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The rationale to allow the non-bank entities to set up the WLAs has been to increase the geographical spread of the ATMs for increased/enhanced customer service, especially in the semi-urban/rural areas.
- In addition to dispensing cash, the ATMs/WLAs may offer many other services/facilities to the customers. Some of such services include – Account Information; Cash Deposit; Regular Bill Payment; PIN Change; Request for Cheque Book etc.
- The customers can be charged for transactions at the ATMs over and above the mandated number of free transactions.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect The ATMs which are set up, owned and operated by non-banks are called the White Label ATMs (WLAs). The customers can be charged for transactions at the ATMs over and above the mandated number of free transactions. Note:
White Label ATMs (WLAs):
- The ATMs which are set up, owned and operated by non-banks are called the White Label ATMs (WLAs).
- The non-bank ATM operators are authorized under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act,2007, by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The rationale to allow the non-bank entities to set up the WLAs has been to increase the geographical spread of the ATMs for increased/enhanced customer service, especially in the semi-urban/rural areas.
- In addition to dispensing cash, the ATMs/WLAs may offer many other services/facilities to the customers. Some of such services include – Account Information; Cash Deposit; Regular Bill Payment; PIN Change; Request for Cheque Book etc.
- The customers can be charged for transactions at the ATMs over and above the mandated number of free transactions.
-
Question 15 of 35
15. Question
With reference to the ‘Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)’, consider the following statements:
- It was established under the Company Act, 2013.
- It has regulatory oversight over the Insolvency Professionals, Insolvency Professional Agencies, Insolvency Professional Entities and Information Utilities.
- It has been designated as the ‘Authority’ under the Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation Rules), 2017 for regulation and development of the profession of valuers in the country.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Incorrect
Correct
Correct
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India was established on 1st October, 2016 under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (Code). It is a unique regulator which regulates a profession as well as processes. It has regulatory oversight over the Insolvency Professionals, Insolvency Professional Agencies, Insolvency Professional Entities and Information Utilities. It been designated as the ‘Authority’ under the Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation Rules), 2017 for regulation and development of the profession of valuers in the country. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Incorrect
Correct
Correct
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India was established on 1st October, 2016 under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (Code). It is a unique regulator which regulates a profession as well as processes. It has regulatory oversight over the Insolvency Professionals, Insolvency Professional Agencies, Insolvency Professional Entities and Information Utilities. It been designated as the ‘Authority’ under the Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation Rules), 2017 for regulation and development of the profession of valuers in the country. -
Question 16 of 35
16. Question
Which of the following parameters form the basis for the difference between Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) visa-vis Banks?
- NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits.
- NBFCs do not form part of the Payment and Settlement System.
- NBFCs are not under the purview of the deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Correct
Banks can do almost all financial services and products generally authorized to them. They can accept demand deposits, whereas, NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits. While the Banks are part of the payment and settlement system, NBFCs do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheque drawn on itself. The deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation is not available to depositors of NBFCs, unlike in case of banks. Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Correct
Correct
Correct
Banks can do almost all financial services and products generally authorized to them. They can accept demand deposits, whereas, NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits. While the Banks are part of the payment and settlement system, NBFCs do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheque drawn on itself. The deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation is not available to depositors of NBFCs, unlike in case of banks. -
Question 17 of 35
17. Question
In the context of the money supply in an economy, ‘High Powered Money’ includes:
Correct
Solution (d)
- The total liability of the monetary authority of the RBI is called the monetary base or high-powered
- It consists of currency (notes and coins in circulation with the public and vault cash of commercial banks) and deposits held by the Government of India and commercial banks with
- It is also called as reserve money ‘or monetary base’ as it acts as a basis for credit It is denoted by M0.
- Different measures of the money supply can be categorized as follows:
- M1 – It is also called narrow
- It includes currency with public, demand deposit in all banks (e.g., current account, savings account) and Other deposits with RBI
- M2 = M1 + Post office bank savings
- M3 = M1 + Time deposits with commercial banks (Fixed deposits, Recurring deposits).
- M4= M3 + total post office deposits
Incorrect
Solution (d)
- The total liability of the monetary authority of the RBI is called the monetary base or high-powered
- It consists of currency (notes and coins in circulation with the public and vault cash of commercial banks) and deposits held by the Government of India and commercial banks with
- It is also called as reserve money ‘or monetary base’ as it acts as a basis for credit It is denoted by M0.
- Different measures of the money supply can be categorized as follows:
- M1 – It is also called narrow
- It includes currency with public, demand deposit in all banks (e.g., current account, savings account) and Other deposits with RBI
- M2 = M1 + Post office bank savings
- M3 = M1 + Time deposits with commercial banks (Fixed deposits, Recurring deposits).
- M4= M3 + total post office deposits
-
Question 18 of 35
18. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the ‘External Benchmark Based Lending’ by the Reserve Bank of India:
- It refers to the linking of floating rate loans of financial institutions to an external benchmark like the policy repo rate of the Reserve Bank of India.
- It is applicable only to banks and not NBFCs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Correct
Correct
According to External Benchmark based Lending Rate, the banks must link all new floating rate loans to an external benchmark like repo rate, 3-month or 6-month treasury bill yield, or any other benchmark published by the Financial Benchmarks India Pvt. Ltd. The new regime will only apply to banks and not NBFCs. Leading housing finance companies like HDFC will not be under the purview of the new regime. However, if repo-linked rates of other lenders come down, the competition will force NBFCs to match the rates.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Correct
Correct
According to External Benchmark based Lending Rate, the banks must link all new floating rate loans to an external benchmark like repo rate, 3-month or 6-month treasury bill yield, or any other benchmark published by the Financial Benchmarks India Pvt. Ltd. The new regime will only apply to banks and not NBFCs. Leading housing finance companies like HDFC will not be under the purview of the new regime. However, if repo-linked rates of other lenders come down, the competition will force NBFCs to match the rates.
-
Question 19 of 35
19. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Priority Sector Lending Certificates (PSLCs):
- These are tradable certificates issued by the Reserve Bank of India for banks who have failed to meet their Priority Sector Lending targets.
- All Scheduled Commercial Banks, Small Finance Banks, and Payments Banks are eligible to participate in the trading of PSLC.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Incorrect
Incorrect
The Priority Sector Lending Certificates (PSCLs) are certificates issued by banks that have overreached their priority sector lending targets. All Scheduled Commercial Banks (including Regional Rural Banks), Urban Co-operative Banks, Small Finance Banks (when they become operational) and Local Area Banks are eligible to participate in the trading. However, Payment banks are not allowed to give any form of a loan or issue a credit card, which is also a form of unsecured personal loan. Consequently, they are not within the purview of buying or selling PSLCs.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement 1
Statement 2
Incorrect
Incorrect
The Priority Sector Lending Certificates (PSCLs) are certificates issued by banks that have overreached their priority sector lending targets. All Scheduled Commercial Banks (including Regional Rural Banks), Urban Co-operative Banks, Small Finance Banks (when they become operational) and Local Area Banks are eligible to participate in the trading. However, Payment banks are not allowed to give any form of a loan or issue a credit card, which is also a form of unsecured personal loan. Consequently, they are not within the purview of buying or selling PSLCs.
-
Question 20 of 35
20. Question
Which among the following best describes “Bank Run”?
Correct
Solution (d)
- A ‘bank run’ occurs when a large number of customers of a bank or another financial institution withdraw their deposits simultaneously due to concerns about the bank’s
- As more people withdraw their funds, the probability of default increases, thereby prompting more people to withdraw their In extreme cases, the bank’s reserves may not be sufficient to cover the withdrawals.
- When a bank cannot satisfy customer demands for withdrawals—or if there’s a rumor that the bank will be unable to do so—the situation
- Customers fear being the “last one to the exit,” and they attempt to withdraw as much as possible. In a worst-case scenario, a bank may be unable to meet obligations, leading to complete
Incorrect
Solution (d)
- A ‘bank run’ occurs when a large number of customers of a bank or another financial institution withdraw their deposits simultaneously due to concerns about the bank’s
- As more people withdraw their funds, the probability of default increases, thereby prompting more people to withdraw their In extreme cases, the bank’s reserves may not be sufficient to cover the withdrawals.
- When a bank cannot satisfy customer demands for withdrawals—or if there’s a rumor that the bank will be unable to do so—the situation
- Customers fear being the “last one to the exit,” and they attempt to withdraw as much as possible. In a worst-case scenario, a bank may be unable to meet obligations, leading to complete
-
Question 21 of 35
21. Question
Consider the following statements about the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- It was formerly known as the Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC).
- Its members include Australia, Bangladesh, Comoros, French Republic, and India.
- The Council of Foreign Ministers (COM) is the highest decision-making body of IORA.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) was formerly known as the Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Its objective is to ensure the sustainable development of the Indian Ocean region.
- Its Secretariat is located in Cyber City, Ebène, Mauritius.
- It comprises 23 member states and 11 dialogue partners hailing from regions surrounding the Indian Ocean.
- Its members include Australia, Bangladesh, Comoros, French Republic, India, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Madagascar, Malaysia, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Seychelles, Singapore, Somalia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, the United Arab Emirates, the Maldives, and Yemen. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- In 2014, India hosted the first Indian Ocean Dialogue in Kochi, Kerala.
- The Council of Foreign Ministers (COM) is the highest decision-making body of IORA. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- A committee of Senior Officials (CSO) meets twice a year to progress IORA’s agenda and consider recommendations by Working Groups and forums of officials, business and academics.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) was formerly known as the Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Its objective is to ensure the sustainable development of the Indian Ocean region.
- Its Secretariat is located in Cyber City, Ebène, Mauritius.
- It comprises 23 member states and 11 dialogue partners hailing from regions surrounding the Indian Ocean.
- Its members include Australia, Bangladesh, Comoros, French Republic, India, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Madagascar, Malaysia, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Seychelles, Singapore, Somalia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, the United Arab Emirates, the Maldives, and Yemen. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- In 2014, India hosted the first Indian Ocean Dialogue in Kochi, Kerala.
- The Council of Foreign Ministers (COM) is the highest decision-making body of IORA. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- A committee of Senior Officials (CSO) meets twice a year to progress IORA’s agenda and consider recommendations by Working Groups and forums of officials, business and academics.
-
Question 22 of 35
22. Question
Recently in the news, the Chungthang Dam is located on which of the following river?
Correct
Solution (d)
The Chungthang Dam is located on Teesta River in Sikkim. The dam serves as a hydroelectric power generation facility, contributing to Sikkim’s renewable energy portfolio. It is an integral part of the 1200 MW mega Teesta Stage III Hydro Electric Project which is a major source of electricity for Sikkim and West Bengal. Hence option d is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
The Chungthang Dam is located on Teesta River in Sikkim. The dam serves as a hydroelectric power generation facility, contributing to Sikkim’s renewable energy portfolio. It is an integral part of the 1200 MW mega Teesta Stage III Hydro Electric Project which is a major source of electricity for Sikkim and West Bengal. Hence option d is correct.
-
Question 23 of 35
23. Question
Consider the following statements with reference to India’s Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS)
- India’s CCTS is a program designed to allow companies to trade carbon credits.
- The carbon credit market’s regulation in CCTS falls under the regulation of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (a)
- India introduced the CCTS under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001, to manage greenhouse gas emissions.
- The CCTS encourages a market-driven approach, helping India achieve its environmental commitments.
- It is administered by the Ministry of Power (MoP) and Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- India’s CCTS is a program designed to allow companies to trade carbon credits. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The carbon credit market’s regulation in CCTS falls under the regulation of the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC). Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- India introduced the CCTS under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001, to manage greenhouse gas emissions.
- The CCTS encourages a market-driven approach, helping India achieve its environmental commitments.
- It is administered by the Ministry of Power (MoP) and Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- India’s CCTS is a program designed to allow companies to trade carbon credits. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The carbon credit market’s regulation in CCTS falls under the regulation of the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC). Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
-
Question 24 of 35
24. Question
Consider the following statements about the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC)
- It was established by an Act of Parliament in 1963 as a statutory corporation.
- Sahakar Pragya is one of the initiative of the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (c)
- The National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) was established by an Act of Parliament in 1963 as a statutory corporation. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It works under the Ministry of Cooperation.
- It helps in planning, promoting and financing programmes for production, processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce, food stuffs, certain other notified commodities e.g., fertilisers, insecticides, agricultural machinery, lac, soap, kerosene oil, textile, rubber etc.
- Sahakar Pragya is one of the initiative of the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC). It is a capacity development initiative through Laxman Rao Inamdar National Academy for Cooperative Research Development (LINAC). Hence statement 2 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) was established by an Act of Parliament in 1963 as a statutory corporation. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It works under the Ministry of Cooperation.
- It helps in planning, promoting and financing programmes for production, processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce, food stuffs, certain other notified commodities e.g., fertilisers, insecticides, agricultural machinery, lac, soap, kerosene oil, textile, rubber etc.
- Sahakar Pragya is one of the initiative of the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC). It is a capacity development initiative through Laxman Rao Inamdar National Academy for Cooperative Research Development (LINAC). Hence statement 2 is correct.
-
Question 25 of 35
25. Question
Consider the following statements:
- The baltic-connector gas pipeline is a natural gas pipeline between Finland and Denmark.
- The Baltic Sea is a part of the Pacific Ocean which is surrounded by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, and Latvia.
- Baltic states is a geopolitical term typically used to refer to three countries – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
- Baltic-connector gas pipeline is a natural gas pipeline between Finland and Estonia. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The gas pipeline was opened in 2020. It is used to send gas between Estonia and Finland, depending on which country is most in need at any point.
- The pipeline has been Finland’s only natural gas import channel since Russian imports were stopped in 2022.
- The Baltic Sea is a part of the Atlantic Ocean which is surrounded by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North and Central European Plain. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
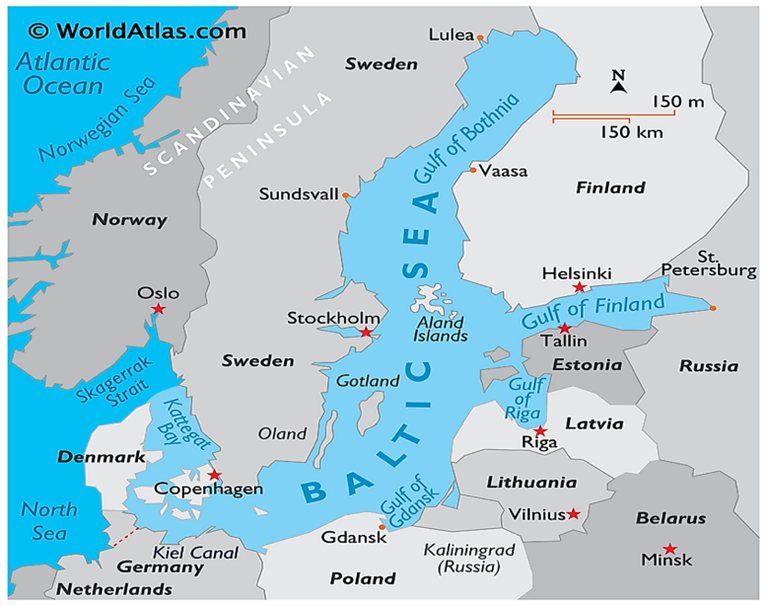
Image: World Atlas
- Baltic states is a geopolitical term typically used to refer to three countries – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- Baltic-connector gas pipeline is a natural gas pipeline between Finland and Estonia. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The gas pipeline was opened in 2020. It is used to send gas between Estonia and Finland, depending on which country is most in need at any point.
- The pipeline has been Finland’s only natural gas import channel since Russian imports were stopped in 2022.
- The Baltic Sea is a part of the Atlantic Ocean which is surrounded by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North and Central European Plain. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.

Image: World Atlas
- Baltic states is a geopolitical term typically used to refer to three countries – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD.
-
Question 26 of 35
26. Question
Consider the following statements:
- P20 is a congregation of Parliamentary Speakers from the Parliaments of G20 nations.
- The theme of the P20 Summit 2023 was “Parliaments for One Earth, One Family, One Future.”
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- P20 is a congregation of Parliamentary Speakers from the Parliaments of G20 nations. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is a meeting that pertains to Speakers and presiding officers of the Parliament from the G20 countries and invitee nations.
- The P20 Group was set up during the G20 Presidency of Canada in 2010.
- The P20 Group provides an opportunity to deepen the recognition of G20 member nations’ efforts and methods of international collaboration in related policies by deliberating upon emerging issues faced by the global community.
- The theme of the P20 Summit 2023 was “Parliaments for One Earth, One Family, One Future.” Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It also highlighted the “LiFE is Beautiful” initiative, promoting eco-friendly practices for a sustainable ecosystem.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- P20 is a congregation of Parliamentary Speakers from the Parliaments of G20 nations. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is a meeting that pertains to Speakers and presiding officers of the Parliament from the G20 countries and invitee nations.
- The P20 Group was set up during the G20 Presidency of Canada in 2010.
- The P20 Group provides an opportunity to deepen the recognition of G20 member nations’ efforts and methods of international collaboration in related policies by deliberating upon emerging issues faced by the global community.
- The theme of the P20 Summit 2023 was “Parliaments for One Earth, One Family, One Future.” Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It also highlighted the “LiFE is Beautiful” initiative, promoting eco-friendly practices for a sustainable ecosystem.
-
Question 27 of 35
27. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Avian influenza is a highly contagious bacterial infection that primarily affects wild birds and domestic poultry.
- The Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV) causes serious illness in birds resulting in high death rates in different species of birds.
- India’s approach to controlling Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) follows a “detect and cull” policy.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Avian influenza is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects wild birds and domestic poultry. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV) causes serious illness in birds resulting in high death rates in different species of birds. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- HPAI was first detected in India in the state of Maharashtra in 2006. Since then, India has experienced annual outbreaks of HPAI in different regions, leading to substantial economic losses.
- India’s approach to controlling Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) follows a “detect and cull” policy as outlined in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised – 2021). The policy approach includes:
- The humane destruction of infected and exposed animals, eggs, feed, litter, and other contaminated materials.
- Restricting the movement of poultry and poultry products, disinfection, and clean-up of infected premises. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Avian influenza is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects wild birds and domestic poultry. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV) causes serious illness in birds resulting in high death rates in different species of birds. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- HPAI was first detected in India in the state of Maharashtra in 2006. Since then, India has experienced annual outbreaks of HPAI in different regions, leading to substantial economic losses.
- India’s approach to controlling Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) follows a “detect and cull” policy as outlined in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised – 2021). The policy approach includes:
- The humane destruction of infected and exposed animals, eggs, feed, litter, and other contaminated materials.
- Restricting the movement of poultry and poultry products, disinfection, and clean-up of infected premises. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 28 of 35
28. Question
Consider the following:
Port Name Country - Hanshin
Brazil - Hambantota
Sri Lanka - Santos
Japan - Duqum Port
Oman Which of the given pairs are correctly matched?
Correct
Solution (b)
Port Name Country 1. Hanshin Japan 2. Hambantota Sri Lanka 3. Santos Brazil 4. Duqum Port Oman Hence option b is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Port Name Country 1. Hanshin Japan 2. Hambantota Sri Lanka 3. Santos Brazil 4. Duqum Port Oman Hence option b is correct.
-
Question 29 of 35
29. Question
Consider the following statements about the Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP):
- It is a paradigm shift from the Production Sharing Contract regime to the Revenue Sharing Contract regime based on ease of doing business.
- It provides a single license for exploration and production of conventional as well as non-conventional hydrocarbon resources.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP) is a policy framework. It provides guidelines for the exploration and production of hydrocarbons in India. It aims to make India a global hub for hydrocarbon exploration and production. It simplifies the licensing process. It provides fiscal incentives and promotes investment in the sector.
- The Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP) is a paradigm shift from the Production Sharing Contract regime to the Revenue Sharing Contract regime based on ease of doing business. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It provides for a revenue-sharing model, the government will receive a share of the gross revenue from the sale of oil and gas, etc., and will not be concerned with the cost incurred.
- It provides for a uniform licensing system that will cover all hydrocarbons such as oil, gas, and coal bed methane.
- It provides a single license for exploration and production of conventional as well as non-conventional hydrocarbon resources. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP) is a policy framework. It provides guidelines for the exploration and production of hydrocarbons in India. It aims to make India a global hub for hydrocarbon exploration and production. It simplifies the licensing process. It provides fiscal incentives and promotes investment in the sector.
- The Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy (HELP) is a paradigm shift from the Production Sharing Contract regime to the Revenue Sharing Contract regime based on ease of doing business. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It provides for a revenue-sharing model, the government will receive a share of the gross revenue from the sale of oil and gas, etc., and will not be concerned with the cost incurred.
- It provides for a uniform licensing system that will cover all hydrocarbons such as oil, gas, and coal bed methane.
- It provides a single license for exploration and production of conventional as well as non-conventional hydrocarbon resources. Hence statement 2 is correct.
-
Question 30 of 35
30. Question
Consider the following statements about the World Health Assembly:
- It was founded on the occasion of the 300th anniversary of Berlin’s Charité Hospital.
- It is held annually in Berlin, Germany under the patronage of Germany, France, the European Commission, and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The theme for the World Health Assembly 2023 was “A Defining Year for Global Health Action.”
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The World Health Assembly was founded in 2009 on the occasion of the 300th anniversary of Berlin’s Charité Hospital. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Berlin Charité was founded as a military hospital in 1710 under the Prussian King Friedrich-Wilhelm I.
- It is held annually in Berlin, Germany under the patronage of Germany, France, the European Commission, and the World Health Organization (WHO). Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It aims to set the agenda for a healthier future by inspiring innovative solutions for better health and well-being for all.
- The theme for the World Health Assembly 2023 was “A Defining Year for Global Health Action.” Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The World Health Assembly was founded in 2009 on the occasion of the 300th anniversary of Berlin’s Charité Hospital. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Berlin Charité was founded as a military hospital in 1710 under the Prussian King Friedrich-Wilhelm I.
- It is held annually in Berlin, Germany under the patronage of Germany, France, the European Commission, and the World Health Organization (WHO). Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It aims to set the agenda for a healthier future by inspiring innovative solutions for better health and well-being for all.
- The theme for the World Health Assembly 2023 was “A Defining Year for Global Health Action.” Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 31 of 35
31. Question
A cube of side 16 cm was painted on all faces and divided into 64 smaller equal cubes. How many cubes are painted from 3 sides?
Correct
Solution (b)
Only the corner cubes i.e. the 8 cubes at the corners of the original cube will have three faces painted. Hence the answer will be 8 only. Further, i) In a cube of size nxn (where n>=2) the number of cubes painted with 3 adjacent faces will always be 8 irrespective of the number of cubes
- ii) Number of cubes painted with 2 adjacent faces = (n-2)x12 [here 12 represents 12 edges of the cube]
iii) Number of cubes painted on 1 face = [(n-2)^2 x6] [here 6 represents 6 faces of the cube] iv) Number of cubes having no faces painted = (n-2)^3
In the above question, the cube is of 4×4 size (64/16), hence 3 face painted cubes are 8, 2 face painted cubes are (4-2) x 12 = 24, 1 face painted cubes are (4-2)2 x 6 = 24 and no face painted cubes are (4-2)^3 = 8.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Only the corner cubes i.e. the 8 cubes at the corners of the original cube will have three faces painted. Hence the answer will be 8 only. Further, i) In a cube of size nxn (where n>=2) the number of cubes painted with 3 adjacent faces will always be 8 irrespective of the number of cubes
- ii) Number of cubes painted with 2 adjacent faces = (n-2)x12 [here 12 represents 12 edges of the cube]
iii) Number of cubes painted on 1 face = [(n-2)^2 x6] [here 6 represents 6 faces of the cube] iv) Number of cubes having no faces painted = (n-2)^3
In the above question, the cube is of 4×4 size (64/16), hence 3 face painted cubes are 8, 2 face painted cubes are (4-2) x 12 = 24, 1 face painted cubes are (4-2)2 x 6 = 24 and no face painted cubes are (4-2)^3 = 8.
-
Question 32 of 35
32. Question
From a group of 7 men and 6 women, five persons are to be selected to form a committee so that at least 3 men are there on the committee. In how many ways can it be done?
Correct
Solution (d)
We may have (3 men and 2 women) or (4 men and 1 woman) or (5 men only).
∴ Required number of ways =
(7C3 × 6C2 ) + ( 7C4 × 6C1 ) + ( 7C5 ) = (7×6×5/3×2×1)×(6×5/2×1) + ( 7C3 × 6C1 ) + ( 7C2 )
= 525 + (7×6×5/3×2×1 ×6) + ( 7×6/2×1)
= ( 525 + 210 + 21 ) = 756
Incorrect
Solution (d)
We may have (3 men and 2 women) or (4 men and 1 woman) or (5 men only).
∴ Required number of ways =
(7C3 × 6C2 ) + ( 7C4 × 6C1 ) + ( 7C5 ) = (7×6×5/3×2×1)×(6×5/2×1) + ( 7C3 × 6C1 ) + ( 7C2 )
= 525 + (7×6×5/3×2×1 ×6) + ( 7×6/2×1)
= ( 525 + 210 + 21 ) = 756
-
Question 33 of 35
33. Question
The monthly incomes of A and B are in the ratio of 3:2 and their monthly expenses are in the ratio of 2:1. If each saves Rs. 3000 at the end of the month, what is their combined monthly income?
Correct
Solution (c)
Let incomes of A and B are 3x and 2x, and expenditures are 2y and y
3x-2y=3000 ..(i)
2x-y=3000 …(ii)
After solving equation (i) and (ii) we get x=3000
Thus their combined monthly income is 3x+2x = 5x = 5×3000 = 15000
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Let incomes of A and B are 3x and 2x, and expenditures are 2y and y
3x-2y=3000 ..(i)
2x-y=3000 …(ii)
After solving equation (i) and (ii) we get x=3000
Thus their combined monthly income is 3x+2x = 5x = 5×3000 = 15000
-
Question 34 of 35
34. Question
In a two-digit, if it is known that its unit’s digit exceeds its ten’s digit by 2 and that the product of the given number and the sum of its digits is equal to 144, then the number is
Correct
Solution (c)
Let the ten’s digit be x. Then, unit’s digit = x + 2.
Number = 10x + (x + 2) = 11x + 2.
Sum of digits = x + (x + 2) = 2x + 2.
∴ (11x + 2)(2x + 2) = 144
⇒ 22×2 + 26x – 140 = 0
⇒ 11×2 + 13x – 70 = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(11x + 35) = 0 ⇒ x = 2.
Hence, required number = 11x + 2 = 24.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Let the ten’s digit be x. Then, unit’s digit = x + 2.
Number = 10x + (x + 2) = 11x + 2.
Sum of digits = x + (x + 2) = 2x + 2.
∴ (11x + 2)(2x + 2) = 144
⇒ 22×2 + 26x – 140 = 0
⇒ 11×2 + 13x – 70 = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(11x + 35) = 0 ⇒ x = 2.
Hence, required number = 11x + 2 = 24.
-
Question 35 of 35
35. Question
The sum of the present ages of a mother and her daughter is 60 years. Six years ago, mother’s age was five times the age of the daughter. After 6 years, daughter‘s age will be
Correct
Solution (c)
Method 1:
Let the present ages of daughter and mother be x and (60 -x) years respectively. Six years ago, mother’s age was five times the age of the daughter then
(60 – x) – 6 = 5(x – 6)
54 – x = 5x – 30
6x = 84
x = 14.
Daughter‘s age after 6 years = (x+ 6) = (14+6) = 20 years.
Method 2:
Go by answer options: The sum of present age of mother and daughter = 60
Sum of age of mother and daughter six years ago = 60 – 6 – 6 = 48
In the answer options age of daughter is given which is six years ahead of present age hence the age of daughter six years ago from the present age was (answer option – 12) = let say d Sum of age of mother and daughter six years ago = 5d + d = 48
Six years ago, mother’s age was five times the age of the daughter
Option (d) gives value of d zero i.e. 12 – 12 hence ruled out.
From option (c), we get value of d = 20- 12 =8 which satisfy the equation 5d + d = 48. Hence the answer is option (c).
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Method 1:
Let the present ages of daughter and mother be x and (60 -x) years respectively. Six years ago, mother’s age was five times the age of the daughter then
(60 – x) – 6 = 5(x – 6)
54 – x = 5x – 30
6x = 84
x = 14.
Daughter‘s age after 6 years = (x+ 6) = (14+6) = 20 years.
Method 2:
Go by answer options: The sum of present age of mother and daughter = 60
Sum of age of mother and daughter six years ago = 60 – 6 – 6 = 48
In the answer options age of daughter is given which is six years ahead of present age hence the age of daughter six years ago from the present age was (answer option – 12) = let say d Sum of age of mother and daughter six years ago = 5d + d = 48
Six years ago, mother’s age was five times the age of the daughter
Option (d) gives value of d zero i.e. 12 – 12 hence ruled out.
From option (c), we get value of d = 20- 12 =8 which satisfy the equation 5d + d = 48. Hence the answer is option (c).
All the Best
IASbaba











