IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs April 2016, International, UPSC
Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 29th April, 2016
ECONOMICS
TOPIC: General studies 3
- Indian Economy and issues relating to mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
- Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth
India’s jobless growth
- Census 2011: The average growth rate of the economy was 7.7 per cent per annum, when it was only 1.8 per cent for employment
- The last quarterly survey by the Labour Bureau showed that India has never created so few jobs, since the survey started in 2009, as in 2015: Only 1.35 lakh jobs compared to more than nine lakh in 2011 and 4.19 lakh in 2013 in eight labour-intensive industries (the only ones that are surveyed).
- Economic Survey (last year)— during the last decade (2001-11), the growth rate of the labour force (2.23 per cent) was significantly higher than the growth rate of employment (1.4 per cent), which itself was several-fold less than the growth rate of the economy.
President Pranab Mukherjee— “The Indian economy today needs to generate 115 million non-farm jobs over the next decade to gainfully employ its workforce and reap its demographic dividend.”
All arrows point towards ‘Jobless Growth’—
Largely responsible for demonstrations by young Patels of Gujarat and Jats of Haryana in the name of reservations (fall back on government jobs)
Public sector is shrinking: Government jobs, which were 19.5 million in 1996-97, are about 17 million today (Fewer jobs—badly paid because of the informalisation of the economy)
Factors behind Jobless growth—
India has an employability problem:
- While the services can rather easily recruit skilled white-collar workers (IT engineers, English-speaking people for the call centres, etc.), the industry cannot transform peasants into factory workers so quickly
- Lack of basic skills training (6.8 per cent persons aged 15 years and above are reported to have received/ be receiving vocational training)
- Primary and secondary education (dropout rate remains very high with poor education)
- The minuscule increase in the share of education in the 2015-16 budget—from 3 to 3.1 per cent
Solution: A robust public education system
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs)—
- Employ 40 per cent of the workforce of the country
- Represent about 45 per cent of India’s manufacturing output
- Represents 40
- Labour intensity— four times higher than that of large firms
Make in India programme— Revelation of the jobless growth syndrome (creation of the manufacturing workforce seems unrealistic)
Poor access to credit: approximately 95 per cent of units still require to be brought into banking fold- resulting in them getting a small share of the net credit of India’s domestic banks, whereas these banks are mandated to register at least 20 per cent year-to-year growth in credit to micro and small enterprises
Erosion of state protections: With the positive discrimination going away in the making of furniture, the replacement of carpenters by machines is feared by many since that would mean that highly capitalistic big companies will import from abroad
Big companies being the main beneficiaries of the fiscal policy of the government: The total amount of tax exemptions represent Rs 5,50,000 crore in the 2015-16 budget, including Rs 1,84,764 crore for Central excise duties and Rs 3,01,688 crore for customs duties
Connecting the Dots
- Should a ‘Greece-like’ possibility takes place in India, can the government deal with it proactively. Discuss the steps that should be taken to contain the crisis.
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General studies 2
- India and its neighborhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
India’s challenge in Afghanistan
Why in news?
- Recently India hosted the sixth Heart of Asia (HoA) conference aimed at speeding up reconstruction in war-torn Afghanistan and bringing peace and normalcy to the nation.
Istanbul Process:
- The Istanbul Process provides a new agenda for regional cooperation in the ‘Heart of Asia’ by placing Afghanistan at its center and engaging the ‘Heart of Asia’ countries in sincere and result?oriented cooperation for a peaceful and stable Afghanistan, as well as a secure and prosperous region as a whole.
Sixth Heart of Asia conference:
- The ministerial conference was held at New Delhi and it was attended by the 14 member states namely, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, China, India, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Pakistan, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan and the United Arab Emirates.
Struggling Afghanistan:
- The government in Afghanistan today, is struggling to hold key districts in the south due to increased Taliban presence.
- The government is also struggling to hold overdue parliamentary elections this year amid the worsening security situation.
- American commanders are asking Washington that US troop numbers remain at the current level of 9,800, and not drop to about 5,500 by the end of the year.
India’s policy towards Afghanistan:
- India has been demanding dismantling of safe havens and terror sanctuaries in the region besides pressing for deeper engagement of various stakeholders for Afghanistan’s stability and security.
China factor in Afghanistan:
- China is stepping up its military role in Afghanistan.
- China is making it clear that it wants to have deeper security ties with Afghanistan and there are plans to strengthen counter-terror and intelligence cooperation along with enhancing China’s role in the training of Afghan military and civilian personnel.
- China has become increasingly concerned about its extremists and separatists in Xinjiang, where violence has killed hundreds in recent years, and sees security in Afghanistan as key to stability in China.
Way ahead:
- Till now India’s engagement with Afghanistan was moved by economic cooperation and military engagement.
- Now a time has come for India to evolve a comprehensive policy, which involves all dimensions of power, to preserve its leverage in Afghanistan.
For static part of India Afghanistan relations refer:
http://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/ForeignRelation/Afghnistan_Dec2014.pdf
http://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/ForeignRelation/Afghanistan_2015_07_20.pdf
Connecting the dots:
- To what extent do you think India’s internal stability depends on a stable Afghanistan.
- Do you think china factor plays an important role in India Afghanistan relations. Analyse.
MUST READ
Another missed opportunity : India- Pakistan
Related Articles:
Pakistan has crippled SAARC: time to reassess
Revisiting Pakistan before the window shuts again
The KG basin scam — part II
How to teach Sanskrit
Related Articles:
The trap of personal laws- They may harm rather than preserve religious freedom.
A higher well-being- In this article, we argue that the actual well-being of the household will be higher than what is indicated by the poverty line, if we take into account public expenditure along with private expenditure.
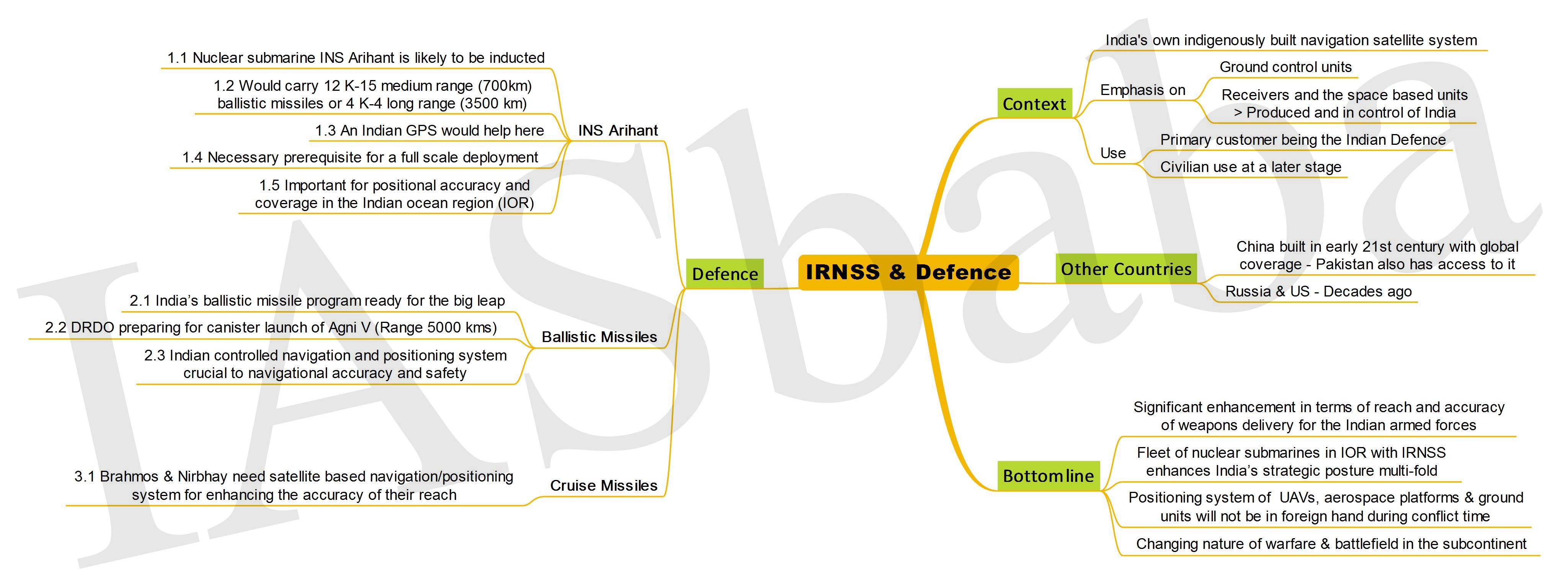
India gets its own GPS with successful launch of 7th navigation satellite- The country will not have to depend on a foreign power for military navigation anymore
A trade policy agenda for India-II
Tribunal to redress PPP disputes faster- A PPP re-negotiation framework would also be evolved to give flexibility to contracts signed with private companies
More women falling ill, but they have lower access to medical treatment-NSSO data shows that more women are falling ill than men and this gender gap in morbidity has increased over the years
MIND MAPS
1. IRNSS and Defence