IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 18th June 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
Highlights of NITI Aayog’s fourth governing council meeting
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Indian Polity and Economy; C-S relations
In news:
- Prime Minister calls for widespread consultation on simultaneous elections in the country, keeping in view aspects such as the resulting financial savings and better utilisation of resources.
- There were no signs of amending Terms of reference (ToR) of 15th Finance Commission
Important value additions
About 15th Finance Commission’s ToR
Terms of reference of 15th Finance Commission – has become a major item which has led to the controversy. It deals with distribution of revenue collected to states.
- The ToR of 15th Finance Commission has drawn protests from many states, especially from southern ones.
- They allege that the ToR was in contradiction to the principles of Federalism enshrined in the Constitution and also would result in revenue loss to performing states.
- They oppose the ToR recommendation to use the 2011 census to calculate population for allocation of union tax revenue in place of 1971 census, which was used by previous Finance Commissions.
Do you know?
- Fifteenth Finance Commission (FCC) is headed by NK Singh.
- Finance Commission is constitutionally-mandated body established once every five years by President to devise a formula for distributing net tax proceeds between centre and states as well as among states and local bodies.
- The recommendations of 15th Finance Commission (FFC) will come into effect from 1 April 2020.
Dhanush a.k.a Desi Bofors
Key points:
- Dhanush – indigenously upgraded artillery gun
- It is ready for induction into the Army
- Developed by the Jabalpur-based Gun Carriage Factory (GCF)
- Dhanush is an upgraded version of the Swedish Bofors gun procured by India in the mid-1980s. (The design is based on Bofors, therefore Dhanush is aka Desi Bofors)
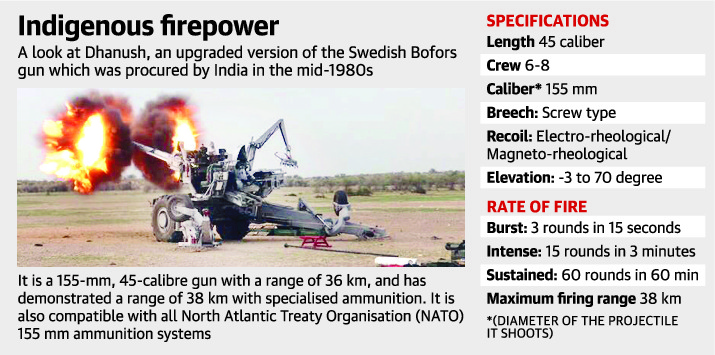
Pic credits: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/18/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_07/b6e1ba4a_2181033_101_mr.jpg
Fast recap:
We had read about
- AH-64 Apache attack helicopters; Chinook heavy-lift helicopters; C-130J Hercules ; Howitzers; Harpoon anti-ship missile system — (India US deal)
- S-400 Triumf; Mi-25 and Mi-35 attack helicopters – (India and Russia)
- SPYDER – (India and Israel)
Article link: Battle ready: Dhanush artillery gun clears final trials
Centre State Relations: Andhra Pradesh versus Centre
Pending issues between Andhra government and the Centre –
- bifurcation-related Special Category Status (SCS)
- construction of a capital city
- Polavaram project
- revenue deficit and
- pull back of ₹350 crore relating to the backward areas development fund.
Other areas of contention
- Establishment of a greenfield crude oil refinery and petrochemical complex
- Railway zone
- Increase of seats in the Assembly
- Resolving anomalies in the taxation matters
- Construction of a steel plant at the YSR Kadapa district
- Establishment of the Vizag-Chennai Industrial Corridor
- the Visakhapatnam and the Vijayawada metro rail,
- the Dugarajapatnam port and
- establishment of a Greyhound Training Centre
Just know the following pointers –
- Polavaram project and Dugarajapatnam port is associated with Andhra Pradesh
- Special Category Status (SCS) is granted by National Development Council (NDC), a NITI Aayog body
- SCS is granted to States that are disadvantaged as compared to the others
- 1st State to be granted the status: Jammu and Kashmir
- Other States having the SCS status: Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Sikkim, Tripura, and Uttarakhand
Set of parameters that determine the decision:
- Hilly and difficult terrain
- Low population density or the presence of sizeable tribal population
- Strategic location along international borders
- Economic and infrastructural backwardness
- Non-viable nature of state finances
Assistance provided to the States with Special Category Status:
- Receive preferential treatment in the form of 30 percent of the Centre’s budget
- Concession on excise duty and other tax breaks to attract industries and investment
- Option to avail benefits of debt swapping and debt relief schemes
- In central government-sponsored schemes and external aid, the states get it as 90 percent grants and 10 percent loans. Other states receive only 30 percent of their funds as grants.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC:General Studies 2:
- India and its neighbourhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Countering China in the Indo-Pacific
Introduction:
Security cooperation between Japan, India, the US and Australia is on the rise.
At the recently concluded Shangri-La Dialogue in Singapore, Prime Minister Narendra Modi and the defence ministers of Japan, the US and Australia reiterated their shared commitment to the Indo-Pacific region. It was closely followed by Japan-India-US Malabar exercises in Guam.
Japan, India, the US and Australia will also join Rimpac (Rim of the Pacific) exercises.
Turning Indo-Pacific security cooperation into a “counter China strategy”:
There are three possible ways-
- Focusing on the link between Indo-China border area and the East China Sea.
If India cooperates with Japan and the US, it will not need to deal with all the Chinese fighter jets at once, because China is likely to keep some of its fighter jets to defend its eastern front. Japan and the US are willing to support India’s efforts to modernize its defence in the Indo-China border area.
The US has already exported transport planes, attack helicopters, heavy-lift helicopter, ultra-light howitzers and carbines for Indian forces. Since 2014, Japan has invested in India’s strategic road project in the North-East region.
There is a high possibility that in the near future India will be the most influential sea power in the Indian Ocean Region. Japan, the US and Australia will then be able to deploy more military force in the East China Sea and South China Sea to maintain the military balance against China.
Therefore, these three countries should share the know-how related with anti-submarine capabilities and enhance India’s military preparedness.
- Developing infrastructure in countries of the region.
Bangladesh has already chosen Japan’s Martabali port project instead of China’s Sonadia port project. If the Trincomalee port project—involving Japanese assistance—in Sri Lanka succeeds, then the importance of China’s Hambantota port will decline. Similarly, the Chabahar port project in Iran can mitigate the importance of the Chinese Gwadar port in Pakistan.
The Asia-Africa Growth Corridor (AAGC), a result of Indo-Japanese cooperation, will also counter China’s growing influence in Africa.
Japan, India, the US and the Australia can collaborate to support South-East Asian countries in the South China Sea.
- The South-East Asian countries need to beef up their military power.
Japanese investment in India’s strategic road project in the latter’s North-East region will help increase India-South-East Asia trade. There is a possibility that growing India-South-East Asia trade could reduce China’s influence in South-East Asia.
Conclusion:
Security cooperation among Japan, India, the US and Australia is increasingly reasonable. The time has come to proactively further this cooperation to ensure prosperity and stability in the whole of Indo-Pacific.
Connecting the dots:
- Security cooperation among Japan, India, the US and Australia can help counter China in the Indo-Pacific region. Comment.
ENVIRONMENT
TOPIC:
General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
General Studies 3:
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment
NITI Aayog ‘Composite Water Management Index’ and Mihir Shah Committee on water management
Introduction:
In earlier article we had read about NITI Aayog report ‘Composite Water Management Index’ (CWMI) dealing with water crisis.
NITI Aayog had released the results of a study warning that India is facing its “worst” water crisis in history, which had implications for the health of the entire population.
Outcome of Composite Water Management Index
- According to the CWMI developed by Niti Aayog, 70% of the water resources are identified as polluted.
- If the water accessible to millions is contaminated, the problem is infinitely worse than that of availability.
- Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Punjab and Telangana have initiated reforms for judicious water use, while populous ones such as Uttar Pradesh and Bihar have failed to respond to the challenge.
- Tamil Nadu, which has a middling score, does well on augmentation of water sources, but is abysmally poor in ensuring sustainable use for farming.
- As per the report, CWMI the crisis is only going to get worse. By 2030, the country’s water demand is projected to be twice the available supply, implying severe water scarcity for hundreds of millions of people and an eventual 6 per cent loss in the country’s GDP.
Indices considered for ratings –
States were rated on the basis of –
- performance in augmenting water resources and watersheds
- investing in infrastructure
- providing rural and urban drinking water
- encouraging efficient agricultural use
Need of the hour:
Two areas that need urgent measures are augmentation of watersheds that can store more good water, for use in agriculture and to serve habitations, and strict pollution control enforcement.
Mihir Shah Committee
- In order to meet the above demands, Committee on Restructuring the Central Water Commission and the Central Ground Water Board (chaired by Mihir Shah) was constituted.
- Mihir Shah Committee has called for a user-centric approach to water management, especially in agriculture.
User-centric approach
- Mihir Shah Committee advocates decentralisation of irrigation commands, offering higher financial flows to well-performing States through a National Irrigation Management Fund.
- It also calls for awarding an index rank, which would help States feel the need to be competitive. It will also foster “competitive and cooperative federalism”.
- The Committee suggests for robust data collection to understand groundwater extraction patterns, as less than 5% of about 12 million wells are now under study.
- The Committee highlights that the growing pace of urbanization calls for a new management paradigm, augmenting sources of clean drinking water supply and treatment technologies that will encourage reuse. Pollution can be curbed by levying suitable costs.
Conclusion:
Therefore, all these forward-looking changes would need revamped national and State institutions, and updated laws. A legal mandate will work better than just competition and cooperation; it would make governments accountable.
Connecting the dots:
- What India needs is not interlinking of rivers but something else to achieve water, agriculture and livelihood security. Critically analyze.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Polavaram Project
- It implements Godavari-Krishna link under National River Linking Project
- It has been accorded national project status by the central government
- The dam is across the Krishna River
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- All of the above
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- The Chairman of the Finance Commission is the Cabinet Secretary
- Setting up of Finance Commission is a Constitutional obligation under Article 280 of the Constitution of India
Select the correct statements
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements with reference to Finance Commission
- It is a quasi-judicial body.
- The chairman of the commission is not eligible for reappointment.
- The qualifications of the members of commission are not specified in the Constitution.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.4) Consider the following and find the correct match
- Dhanush is the surface-to-surface missile and a naval variant of Prithvi missile
- Dhanush is an upgraded version of the Swedish Bofors gun procured by India
Select the correct one
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.5) Fifteenth Finance Commission (FCC) is headed by –
- Preetham Reddy
- Y V Reddy
- NK Singh
- Mihir Shah
Q.6) Committee on Restructuring the Central Water Commission and the Central Ground Water Board is chaired by –
- Preetham Reddy
- Y V Reddy
- NK Singh
- Mihir Shah
MUST READ
India’s Dutch disease
Creating more jobs in India
Wanted, a national rubber policy











