IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan
ARCHIVES
Hello Friends,
The most beloved 60 Days for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019 has finally begun 🙂
Once again the time has come for the battle (Prelims). And who else than your best companion in the last preparatory phase for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019 i.e 60 days plan.
It does not matter how slowly you go as long as you do not stop.
Hope the message given above makes sense to you all.
The productive utilization of this programme demands consistency, honesty, faith and strong determination to be in the process of learning and unlearning. You might not be fully prepared to solve all the questions but the learning and unlearning through these questions will prepare you for the real battle on 2nd June 2019.
You have to unlearn your repetitive mistakes, gut feeling on which you mark doubtful questions. You have to learn new things and also those concepts that you were very sure of but somehow because of traps in the option, got it wrong. You have to learn ‘how to convert knowledge into marks’ (Because most of the times, after ending the exam, you regret making mistakes in known concepts).
Secondly, keep a long distance from following too many things at this point. It will always backfire. Once you are here, put complete faith and follow this initiative along with whatever you were doing. It is very important to consolidate your preparation with many revisions. Simply following many things will leave you in despair. You can cross check this with veterans.
Everything that seems attractive is not productive. You should always go for productivity. Be wise!
Let us pledge to make it a big game changer (better than last year) in the next 60 days of this plan!
Importance of Self – Tracking: Learning from Last Year
Last year, aspirants used to type/post their answers in the comment box on a daily basis. There were huge participation and discussion below the test post. Putting answers in the comment box has been very effective to self-track yourself after updating the score. In the end, you can cross check your performance through Disqus profile.
It was highly effective in the last edition of 60 Days that propelled aspirants to monitor their performance and learn through discussion. Let you solve these questions with full honesty and write your result in the comment box. Interact with peers to know your mistakes.
The importance of this initiative stands time-bound and aggressive reverse engineering to learn the concepts. Many of you must be busy with your own strategy but let us tell you honestly that in the last few months, it is very important to revise and consolidate your learning. Just reading won’t suffice.
So, take out a few hours from your schedule and make it a revision exercise.
How can you make the best use of it?
Be honest to your effort and do not start competing with XYZ aspirants just for the sake of marks. It is more important for you to introspect and check your learning than focusing on others. Try to answer the questions in 25 minutes only.
Do not get into negative feeling that I don’t have enough knowledge to answer these questions. Feel like you are taking the real exam. What would be your response then?
The same will be replicated in the UPSC exam. Here, you get marks only and nothing else matters. So, make effort to know the answers to all questions. Do not cheat 😛
DETAILED MICRO ANALYSIS MATRIX SAMPLE– is given here. You can download this and do an assessment for yourself (the excel sheet must be modified as per this years planning. The provided excel sheet is only for reference). DOWNLOAD
- You can copy paste the same format/modify as per your need in Google Spreadsheet and update it on daily basis.
- Feedback talks about daily test results.
- Follow-up talks about daily target achieved from sources and the number of revisions to do/done and dates. Sources column is to ensure that aspirants do not run behind various sources and follow the same throughout.
Would like to end on this quote:
Either you run the day or the day runs you.
Are you ready? Let’s start!
Important Note
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2019 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
Q.1) The powers and functions of the governor is different from the President, in that Governor has no –
- Diplomatic powers
- Emergency powers
- Financial powers
- Judicial powers
- Military powers
Select the correct code:
Correct
A governor possesses executive, legislative, financial and judicial powers more or less analogous to the President of India. However, he has no diplomatic, military or emergency powers like the president.
Incorrect
A governor possesses executive, legislative, financial and judicial powers more or less analogous to the President of India. However, he has no diplomatic, military or emergency powers like the president.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
Q.2) Which among the following statements are true with regard to Governor?
- He is the chief executive head of the state.
- He acts as an agent of the central government.
- He is appointed by the president by warrant under his hand and seal.
- Even though the office of governor is an employment under the Central government, it is not under its control or it’s subordinate.
Choose the correct statement:
Correct
The governor is the chief executive head of the state. But, like the president, he is a nominal executive head (titular or constitutional head). The governor also acts as an agent of the central government. Therefore, the office of governor has a dual role.
The governor is neither directly elected by the people nor indirectly elected by a specially constituted electoral college as is the case with the president. He is appointed by the president by warrant under his hand and seal. In a way, he is a nominee of the Central government.
The office of governor of a state is not an employment under the Central government. It is an independent constitutional office and is not under the control of or subordinate to the Central government.
Do you know?
- Constitution has assigned a dual role to the office of a governor in the Indian federal system. He is the constitutional head of the state as well as the representative of the Centre (i.e., President).
Incorrect
The governor is the chief executive head of the state. But, like the president, he is a nominal executive head (titular or constitutional head). The governor also acts as an agent of the central government. Therefore, the office of governor has a dual role.
The governor is neither directly elected by the people nor indirectly elected by a specially constituted electoral college as is the case with the president. He is appointed by the president by warrant under his hand and seal. In a way, he is a nominee of the Central government.
The office of governor of a state is not an employment under the Central government. It is an independent constitutional office and is not under the control of or subordinate to the Central government.
Do you know?
- Constitution has assigned a dual role to the office of a governor in the Indian federal system. He is the constitutional head of the state as well as the representative of the Centre (i.e., President).
-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Q.3) The Chief Minister enjoys which of the following powers as head of the state council of ministers?
- He allocates and reshuffles the portfolios among ministers.
- He can make rules for more convenient transaction of the business of a state government and for the allocation among the ministers of the said business.
- He sees that the Annual Financial Statement (state budget) is laid before the state legislature.
Choose the correct answer:
Correct
The Chief Minister allocates and reshuffles the portfolios among ministers. He can ask a minister to resign or advise the governor to dismiss him in case of difference of opinion. He presides over the meetings of the council of ministers and influences its decisions.
The CM guides, directs, controls and coordinates the activities of all the ministers.
However, the power of making rules for more convenient transaction of the business of a state government and for the allocation among the ministers of the said business belong to the executive powers and functions of the Governor and not the Chief Minister.
The financial powers and functions of the governor include that he sees the Annual Financial Statement (state budget) is laid before the state legislature. Therefore, both statement (2) and (3) are powers of the Governor and not the Chief Minister.
Incorrect
The Chief Minister allocates and reshuffles the portfolios among ministers. He can ask a minister to resign or advise the governor to dismiss him in case of difference of opinion. He presides over the meetings of the council of ministers and influences its decisions.
The CM guides, directs, controls and coordinates the activities of all the ministers.
However, the power of making rules for more convenient transaction of the business of a state government and for the allocation among the ministers of the said business belong to the executive powers and functions of the Governor and not the Chief Minister.
The financial powers and functions of the governor include that he sees the Annual Financial Statement (state budget) is laid before the state legislature. Therefore, both statement (2) and (3) are powers of the Governor and not the Chief Minister.
-
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
Q.4) Consider the following statements about the Governor and choose the incorrect statement:
Correct
Usually, there is a governor for each state, but the 7th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1956 facilitated the appointment of the same person as a governor for two or more states.
The Constitution lays down that the Governor is entitled to such emoluments, allowances and privileges as may be determined by Parliament.
It also lays down that when the same person is appointed as the governor of two or more states, the emoluments and allowances payable to him are shared by the states in such proportion as determined by the president.
Incorrect
Usually, there is a governor for each state, but the 7th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1956 facilitated the appointment of the same person as a governor for two or more states.
The Constitution lays down that the Governor is entitled to such emoluments, allowances and privileges as may be determined by Parliament.
It also lays down that when the same person is appointed as the governor of two or more states, the emoluments and allowances payable to him are shared by the states in such proportion as determined by the president.
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Q.5) Which of the statements given above is/are true about the Governor?
- The oath of office to the governor is administered by the President or some person appointed in that behalf by him.
- The term of the governor is not fixed and he holds office during the pleasure of the president.
Choose correct answer:
Correct
The oath of office to the governor is administered by the chief justice of the concerned state high court and in his absence, the senior-most judge of that court available.
Every person discharging the functions of the governor also undertakes the similar oath or affirmation.
A governor holds office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office. However, this term of five years is subject to the pleasure of the President. Further, he can resign at any time by addressing a resignation letter to the President.
Incorrect
The oath of office to the governor is administered by the chief justice of the concerned state high court and in his absence, the senior-most judge of that court available.
Every person discharging the functions of the governor also undertakes the similar oath or affirmation.
A governor holds office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office. However, this term of five years is subject to the pleasure of the President. Further, he can resign at any time by addressing a resignation letter to the President.
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Q.6) Which of the statements given below is/are true with regard to composition of Legislative Council?
- The maximum strength of the council is fixed at one-third of the total strength of the legislative assembly and the minimum strength is fixed at 40.
- 5/6 of the total number of members of a legislative council are indirectly elected and 1/6 are nominated by the governor.
Choose the correct code from below options:
Correct
The maximum strength of the legislative council is fixed at one-third of the total strength of the legislative assembly and the minimum strength is fixed at 40.
Note: The minimum strength fixed at 40 by the Constitution of India is not applicable to Jammu and Kashmir. Its council has 36 members under the provisions of its own state Constitution.
5/6 of the total number of members of a legislative council are indirectly elected and 1/6 are nominated by the governor.
Of the total number of members of a legislative council:
- 1/3 are elected by the members of local bodies in the state like municipalities, district boards, etc.,
- 1/12 are elected by graduates of three years standing and residing within the state,
- 1/12 are elected by teachers of three years standing in the state, not lower in standard than secondary school,
- 1/3 are elected by the members of the legislative assembly of the state from amongst persons who are not members of the assembly, and
- the remainder are nominated by the governor from amongst persons who have a special knowledge or practical experience of literature, science, art, cooperative movement and social service.
Incorrect
The maximum strength of the legislative council is fixed at one-third of the total strength of the legislative assembly and the minimum strength is fixed at 40.
Note: The minimum strength fixed at 40 by the Constitution of India is not applicable to Jammu and Kashmir. Its council has 36 members under the provisions of its own state Constitution.
5/6 of the total number of members of a legislative council are indirectly elected and 1/6 are nominated by the governor.
Of the total number of members of a legislative council:
- 1/3 are elected by the members of local bodies in the state like municipalities, district boards, etc.,
- 1/12 are elected by graduates of three years standing and residing within the state,
- 1/12 are elected by teachers of three years standing in the state, not lower in standard than secondary school,
- 1/3 are elected by the members of the legislative assembly of the state from amongst persons who are not members of the assembly, and
- the remainder are nominated by the governor from amongst persons who have a special knowledge or practical experience of literature, science, art, cooperative movement and social service.
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
Q.7) Consider the following statements about the Chief Minister and choose the incorrect statement:
Correct
All executive actions of the State are formally taken in the name of the Governor (not Chief Minister). Hence, statement (d) is incorrect.
Chief Minister performs the following functions:
- He is the chairman of the State Planning Board.
- He acts as a vice-chairman of the concerned zonal council by rotation, holding office for a period of one year at a time.
- He is a member of the Inter-State Council and the National Development Council, both headed by the prime minister.
- He is the chief spokesman of the state government.
- He is the crisis manager-in-chief at the political level during emergencies.
- As a leader of the state, he meets various sections of the people and receives memoranda from them regarding their problems, and so on.
- He is the political head of the services.
Incorrect
All executive actions of the State are formally taken in the name of the Governor (not Chief Minister). Hence, statement (d) is incorrect.
Chief Minister performs the following functions:
- He is the chairman of the State Planning Board.
- He acts as a vice-chairman of the concerned zonal council by rotation, holding office for a period of one year at a time.
- He is a member of the Inter-State Council and the National Development Council, both headed by the prime minister.
- He is the chief spokesman of the state government.
- He is the crisis manager-in-chief at the political level during emergencies.
- As a leader of the state, he meets various sections of the people and receives memoranda from them regarding their problems, and so on.
- He is the political head of the services.
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
Q.8) When a Money Bill is reserved by the Governor for the consideration of the President, the President can –
- Give his assent to the bill
- Withhold his assent to the bill
- Return a money bill for the reconsideration of the state legislature
- Return a money bill for the reconsideration of the Governor
Choose the appropriate answer:
Correct
When a Money Bill is reserved by the Governor for the consideration of the President, the President has two alternatives:
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an Act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act.
Thus, the President cannot return a money bill for the reconsideration of the state legislature (as in the case of the Parliament).
Incorrect
When a Money Bill is reserved by the Governor for the consideration of the President, the President has two alternatives:
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an Act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act.
Thus, the President cannot return a money bill for the reconsideration of the state legislature (as in the case of the Parliament).
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
Q.9) Consider the below statements with regard to ordinance-making power of the Governor and identify the incorrect statement:
Correct
Governor can promulgate an ordinance only when he is satisfied that circumstances exist which render it necessary for him to take immediate action.
His ordinance-making power is not a discretionary power. This means that he can promulgate or withdraw an ordinance only on the advice of the council of ministers headed by the chief minister.
He cannot make an ordinance without the instructions from the President in three cases: (Hence, statement c is incorrect)
- If a bill containing the same provisions would have required the previous sanction of the President for its introduction into the state legislature.
- If he would have deemed it necessary to re-serve a bill containing the same provisions for the consideration of the President.
- If an act of the state legislature containing the same provisions would have been invalid without receiving the President’s assent.
An ordinance issued by him ceases to operate on the expiry of six weeks from the reassembly of the state legislature. It may cease to operate even earlier than the prescribed six weeks, if a resolution disapproving it is passed by the legislative assembly and is agreed to by the legislative council (in case of a bicameral legislature).
Incorrect
Governor can promulgate an ordinance only when he is satisfied that circumstances exist which render it necessary for him to take immediate action.
His ordinance-making power is not a discretionary power. This means that he can promulgate or withdraw an ordinance only on the advice of the council of ministers headed by the chief minister.
He cannot make an ordinance without the instructions from the President in three cases: (Hence, statement c is incorrect)
- If a bill containing the same provisions would have required the previous sanction of the President for its introduction into the state legislature.
- If he would have deemed it necessary to re-serve a bill containing the same provisions for the consideration of the President.
- If an act of the state legislature containing the same provisions would have been invalid without receiving the President’s assent.
An ordinance issued by him ceases to operate on the expiry of six weeks from the reassembly of the state legislature. It may cease to operate even earlier than the prescribed six weeks, if a resolution disapproving it is passed by the legislative assembly and is agreed to by the legislative council (in case of a bicameral legislature).
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Q.10) Consider the following statements with regard to legislative Council:
- Parliament has the power to create or abolish the legislative Council in various States on the basis of resolutions adopted by two thirds majority in the respective Assembly.
- Article 169 has given power to the States to set up the Council or abolish it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
The legislative Council or the Vidhan Parishad is the Upper Chamber of the State legislature.
Article 169 has given power to the States to set up the Council or abolish it.
The process of creating an Upper House is lengthy. The State Assembly has to pass a resolution for the creation of the Council by a majority of its total membership. Thereafter, Parliament has to enact a law to create it.
In other words, the Union Parliament has the power to create or abolish the legislative Council in various States on the basis of resolutions adopted by two thirds majority in the respective Assembly.
The power of abolition and creation of the State legislative council is vested in Parliament of India as per article 169.
Do you know?
- When a legislative council is created or abolished, the Constitution of India is also changed. However, still, such type of law is not considered a Constitution Amendment Bill. (Article 169).
- In other words, this Act of Parliament is not to be deemed as an amendment of the Constitution for the purposes of Article 368 and is passed like an ordinary piece of legislation (ie, by simple majority).
- The resolution to create and abolish a state legislative council is to be assented by the President also.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/editorial/council-conundrum/article24786733.ece
https://www.dailypioneer.com/2018/state-editions/is-legislative-council-formation-so-easy.html
Incorrect
The legislative Council or the Vidhan Parishad is the Upper Chamber of the State legislature.
Article 169 has given power to the States to set up the Council or abolish it.
The process of creating an Upper House is lengthy. The State Assembly has to pass a resolution for the creation of the Council by a majority of its total membership. Thereafter, Parliament has to enact a law to create it.
In other words, the Union Parliament has the power to create or abolish the legislative Council in various States on the basis of resolutions adopted by two thirds majority in the respective Assembly.
The power of abolition and creation of the State legislative council is vested in Parliament of India as per article 169.
Do you know?
- When a legislative council is created or abolished, the Constitution of India is also changed. However, still, such type of law is not considered a Constitution Amendment Bill. (Article 169).
- In other words, this Act of Parliament is not to be deemed as an amendment of the Constitution for the purposes of Article 368 and is passed like an ordinary piece of legislation (ie, by simple majority).
- The resolution to create and abolish a state legislative council is to be assented by the President also.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/editorial/council-conundrum/article24786733.ece
https://www.dailypioneer.com/2018/state-editions/is-legislative-council-formation-so-easy.html
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
Q.11) Which among the following statements is/are true with regard to Disqualification on Ground of Defection?
- The question of disqualification under the Tenth Schedule is decided by the Chairman, in the case of legislative council and, Speaker, in the case of legislative assembly.
- Supreme Court has ruled that the decision of Chairman/Speaker in this regard is subject to judicial review.
Choose the correct answer:
Correct
Disqualification on Ground of Defection
- The Constitution lays down that a person shall be disqualified for being a member of either House of state legislature if he is so disqualified on the ground of defection under the provisions of the Tenth Schedule.
- The question of disqualification under the Tenth Schedule is decided by the Chairman, in the case of legislative council and, Speaker, in the case of legislative assembly (and not by the governor).
- In 1992, the Supreme Court ruled that the decision of Chairman/Speaker in this regard is subject to judicial review.
Incorrect
Disqualification on Ground of Defection
- The Constitution lays down that a person shall be disqualified for being a member of either House of state legislature if he is so disqualified on the ground of defection under the provisions of the Tenth Schedule.
- The question of disqualification under the Tenth Schedule is decided by the Chairman, in the case of legislative council and, Speaker, in the case of legislative assembly (and not by the governor).
- In 1992, the Supreme Court ruled that the decision of Chairman/Speaker in this regard is subject to judicial review.
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
Q.12) Consider the below statements with respect to legislative procedure in State Legislature:
- The Constitution does not provide for the mechanism of joint sitting of both the Houses to resolve the disagreement between the two Houses over a bill.
- The ultimate power of passing an ordinary bill is vested in the assembly.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Correct
The Constitution does not provide for the mechanism of joint sitting of both the Houses to resolve the disagreement between the two Houses over a bill. On the other hand, there is a provision for joint sitting of the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha to resolve a disagreement between the two over an ordinary bill. Moreover, when a bill, which has originated in the council and was sent to the assembly, is rejected by the assembly, the bill ends and becomes dead.
Thus, the council has been given much lesser significance, position and authority than that of the Rajya Sabha at the Centre.
The ultimate power of passing an ordinary bill is vested in the assembly. At the most, the council can detain or delay the bill for a period of four months—three months in the first instance and one month in the second instance.
Incorrect
The Constitution does not provide for the mechanism of joint sitting of both the Houses to resolve the disagreement between the two Houses over a bill. On the other hand, there is a provision for joint sitting of the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha to resolve a disagreement between the two over an ordinary bill. Moreover, when a bill, which has originated in the council and was sent to the assembly, is rejected by the assembly, the bill ends and becomes dead.
Thus, the council has been given much lesser significance, position and authority than that of the Rajya Sabha at the Centre.
The ultimate power of passing an ordinary bill is vested in the assembly. At the most, the council can detain or delay the bill for a period of four months—three months in the first instance and one month in the second instance.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
Q.13) Legislative council can delay the Money Bill passed by the legislative assembly for a period not exceeding
Correct
After a money bill is passed by the legislative assembly, it is transmitted to the legislative council for its consideration. The legislative council has restricted powers with regard to a money bill. It cannot reject or amend a money bill. It can only make the recommendations. It must return the bill to the legislative assembly within 14 days, whether with or without recommendations.
If the legislative council does not return the bill to the legislative assembly within 14 days, the bill is deemed to have been passed by both the Houses at the expiration of the said period in the form originally passed by the legislative assembly.
Incorrect
After a money bill is passed by the legislative assembly, it is transmitted to the legislative council for its consideration. The legislative council has restricted powers with regard to a money bill. It cannot reject or amend a money bill. It can only make the recommendations. It must return the bill to the legislative assembly within 14 days, whether with or without recommendations.
If the legislative council does not return the bill to the legislative assembly within 14 days, the bill is deemed to have been passed by both the Houses at the expiration of the said period in the form originally passed by the legislative assembly.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
Q.14) Consider the following statements with regard to President’s Rule
- Articles 356 enables the Central Government to intervene in state affairs for the sake of good government of the State concerned.
- The Centre decides on the question of whether there is good government or not in the state.
Choose the correct code from below:
Correct
The Centre is not given any such authority to intervene in state affairs for the sake of good government. Article 356 allows the Centre to intervene only when the government is not carried on in consonance with the provisions laid down for the constitutional governance.
On question on whether there is good government or not in the state is not for the Centre to determine.
Incorrect
The Centre is not given any such authority to intervene in state affairs for the sake of good government. Article 356 allows the Centre to intervene only when the government is not carried on in consonance with the provisions laid down for the constitutional governance.
On question on whether there is good government or not in the state is not for the Centre to determine.
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Q.15) Which of the statements given below is/are correct in regard to Lt. Governor of Delhi?
- The Chief Minister of Delhi is appointed by the Lt. Governor.
- The Council of Ministers headed by the Chief Minister aid and advise the Lt. Governor in the exercise of his functions.
- Lt. Governor is empowered to promulgate ordinances when the assembly is dissolved or suspended or in recess.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Correct
The chief minister of Delhi is appointed by the President (not by the lt. governor). Hence, statement (1) is wrong.
The other ministers are appointed by the president on the advice of the chief minister. The ministers hold office during the pleasure of the president.
The council of ministers headed by the chief minister aid and advise the lt. governor in the exercise of his functions except in so far as he is required to act in his discretion. In the case of difference of opinion between the lt. governor and his ministers, the lt. governor is to refer the matter to the president for decision and act accordingly.
The Lt. governor is empowered to promulgate ordinances during recess of the assembly. An ordinance has the same force as an act of the assembly. Every such ordinance must be approved by the assembly within six weeks from its reassembly. He can also withdraw an ordinance at any time. But, he cannot promulgate an ordinance when the assembly is dissolved or suspended. Hence, statement (3) is wrong.
Further, no such ordinance can be promulgated or withdrawn without the prior permission of the President.
Incorrect
The chief minister of Delhi is appointed by the President (not by the lt. governor). Hence, statement (1) is wrong.
The other ministers are appointed by the president on the advice of the chief minister. The ministers hold office during the pleasure of the president.
The council of ministers headed by the chief minister aid and advise the lt. governor in the exercise of his functions except in so far as he is required to act in his discretion. In the case of difference of opinion between the lt. governor and his ministers, the lt. governor is to refer the matter to the president for decision and act accordingly.
The Lt. governor is empowered to promulgate ordinances during recess of the assembly. An ordinance has the same force as an act of the assembly. Every such ordinance must be approved by the assembly within six weeks from its reassembly. He can also withdraw an ordinance at any time. But, he cannot promulgate an ordinance when the assembly is dissolved or suspended. Hence, statement (3) is wrong.
Further, no such ordinance can be promulgated or withdrawn without the prior permission of the President.
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
Q.16) Consider the following statements with reference to the Ayushman Bharat-National Health Protection Scheme (AB-NHPS)
- The scheme will provide a cover of Rs.5 lakh per family per year.
- Only hospitalization expenses will be a part of the cover.
- It will subsume Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY) and the Senior Citizen Health Insurance Scheme (SCHIS).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Correct
Ayushman Bharat
- PM Modi’s ambitious scheme aims to provide coverage of ₹5 lakh per family annually and benefiting more than 10 crore poor families in the country.
- AB-NHPM will subsume the on-going centrally sponsored schemes — Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY) and the Senior Citizen Health Insurance Scheme (SCHIS).
Salient features of the AB-NHPM scheme:
- This scheme has the benefit cover of Rs. 5 lakh per family per year. The target beneficiaries of the proposed scheme will be more than 10 crore families belonging to poor and vulnerable population based on SECC database.
- The Rs. 5 lakh per family a year cover will take care of almost all secondary care and most of tertiary care procedures. To ensure that nobody is left out (especially women, children and elderly) there will be no cap on family size and age in the scheme.
- The benefit cover will also include pre- and post-hospitalisation expenses.
- All pre-existing conditions will be covered from day one of the policy.
- A defined transport allowance per hospitalisation will also be paid to the beneficiary.
- Also, benefits of the scheme are portable across the country and a beneficiary covered under the scheme will be allowed to take cashless benefits from any public/private empanelled hospital across the country.
- AB-NHPM will be an entitlement based scheme with entitlement decided on the basis of deprivation criteria in the SECC database.
Incorrect
Ayushman Bharat
- PM Modi’s ambitious scheme aims to provide coverage of ₹5 lakh per family annually and benefiting more than 10 crore poor families in the country.
- AB-NHPM will subsume the on-going centrally sponsored schemes — Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY) and the Senior Citizen Health Insurance Scheme (SCHIS).
Salient features of the AB-NHPM scheme:
- This scheme has the benefit cover of Rs. 5 lakh per family per year. The target beneficiaries of the proposed scheme will be more than 10 crore families belonging to poor and vulnerable population based on SECC database.
- The Rs. 5 lakh per family a year cover will take care of almost all secondary care and most of tertiary care procedures. To ensure that nobody is left out (especially women, children and elderly) there will be no cap on family size and age in the scheme.
- The benefit cover will also include pre- and post-hospitalisation expenses.
- All pre-existing conditions will be covered from day one of the policy.
- A defined transport allowance per hospitalisation will also be paid to the beneficiary.
- Also, benefits of the scheme are portable across the country and a beneficiary covered under the scheme will be allowed to take cashless benefits from any public/private empanelled hospital across the country.
- AB-NHPM will be an entitlement based scheme with entitlement decided on the basis of deprivation criteria in the SECC database.
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Q.17) Consider the following statements with regard to National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF):
- It is a competency-based framework that organizes all qualifications according to a series of levels of knowledge, skills and aptitude.
- It shall be mandatory for all training/educational programmes/courses to be NSQF-compliant.
- All training and educational institutions shall define eligibility criteria for admission to various courses in terms of NSQF levels.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF) was introduced in 2013.
- According to NSQF, all qualifications were to be organized according to a series of levels of knowledge, skills and aptitude.
- For each trade/occupation or professional qualification, course content should be prepared that corresponds to higher and higher level of professional knowledge and practical experience.
- The framework was to be implemented by December 27, 2018.
Do you know?
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship is a Ministry of Government of India set up on 9 November 2014 to coordinate all skill development efforts across the country.
- The Ministry mandated that all training/educational programmes/courses be NSQF-compliant by December 27, 2018.
- It also mandated that all training and educational institutions define eligibility criteria for admission to various courses in terms of NSQF levels, by December 27, 2018.
Incorrect
National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF) was introduced in 2013.
- According to NSQF, all qualifications were to be organized according to a series of levels of knowledge, skills and aptitude.
- For each trade/occupation or professional qualification, course content should be prepared that corresponds to higher and higher level of professional knowledge and practical experience.
- The framework was to be implemented by December 27, 2018.
Do you know?
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship is a Ministry of Government of India set up on 9 November 2014 to coordinate all skill development efforts across the country.
- The Ministry mandated that all training/educational programmes/courses be NSQF-compliant by December 27, 2018.
- It also mandated that all training and educational institutions define eligibility criteria for admission to various courses in terms of NSQF levels, by December 27, 2018.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Q.18) With respect to Article 239AA of Constitution Delhi assembly can legislate on all those matters listed in the State List and Concurrent List as are applicable to union territories, excluding which of the following?
- Public Order
- Police
- Land
Select the correct statements
Correct
Sixty-ninth amendment act inserted Article 239AA which confers a special status to Delhi among UTs where it was a provided with a legislative assembly to make laws on state subjects.
As per Article 239AA – Public Order, Police & Land in NCT of Delhi fall within the domain and control of Central Government which shall have the power to make laws on these matters. For remaining matters of State List or Concurrent List, in so far as any such matter is applicable to UTs, the Legislative Assembly shall have power to make laws for NCT of Delhi.
Further, for Offences against laws, Jurisdiction & powers of Courts (except SC) and Fees (except court fees) so far as they relate to Public Order, Police & Land in NCT of Delhi; Central Government would have power to make laws.
Sources:
Incorrect
Sixty-ninth amendment act inserted Article 239AA which confers a special status to Delhi among UTs where it was a provided with a legislative assembly to make laws on state subjects.
As per Article 239AA – Public Order, Police & Land in NCT of Delhi fall within the domain and control of Central Government which shall have the power to make laws on these matters. For remaining matters of State List or Concurrent List, in so far as any such matter is applicable to UTs, the Legislative Assembly shall have power to make laws for NCT of Delhi.
Further, for Offences against laws, Jurisdiction & powers of Courts (except SC) and Fees (except court fees) so far as they relate to Public Order, Police & Land in NCT of Delhi; Central Government would have power to make laws.
Sources:
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
Q.19) Recently, some states are racing to gain special status which confers preferential treatment in the form of central assistance and tax breaks. Which among the following are the conditions to categorize states for special status?
- hilly and difficult terrain
- low population density or sizable share of tribal population
- strategic location along borders with neighboring countries
- economic and infrastructural backwardness
- non-viable nature of state finances
Select the correct code given below:
Correct
The concept of a special category state was first introduced in 1969. The 5th Finance Commission decided to provide certain disadvantaged states with preferential treatment in the form of central assistance and tax breaks. Initially three states Assam, Nagaland and Jammu & Kashmir were granted special status but since then eight more have been included Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Sikkim, Tripura and Uttarakhand.
Recently, states like Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, West Bengal, Bihar, Tamil Nadu are racing for the special status.
Conditions to categorize states for special status :
The special status is given to certain states because of their inherent features; like they might have a low resource base and cannot mobilize resources for development. Some of the features required for special status are:
- hilly and difficult terrain;
- low population density or sizable share of tribal population;
- strategic location along borders with neighboring countries;
- economic and infrastructural backwardness; and
- non-viable nature of state finances.
For further reading: http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/What-is-the-special-category-status/article14553662.ece
Incorrect
The concept of a special category state was first introduced in 1969. The 5th Finance Commission decided to provide certain disadvantaged states with preferential treatment in the form of central assistance and tax breaks. Initially three states Assam, Nagaland and Jammu & Kashmir were granted special status but since then eight more have been included Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Sikkim, Tripura and Uttarakhand.
Recently, states like Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, West Bengal, Bihar, Tamil Nadu are racing for the special status.
Conditions to categorize states for special status :
The special status is given to certain states because of their inherent features; like they might have a low resource base and cannot mobilize resources for development. Some of the features required for special status are:
- hilly and difficult terrain;
- low population density or sizable share of tribal population;
- strategic location along borders with neighboring countries;
- economic and infrastructural backwardness; and
- non-viable nature of state finances.
For further reading: http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/What-is-the-special-category-status/article14553662.ece
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
Q.20) Which one of the following statements correctly describes the Fourth Schedule of the Constitution of India?
Correct
Fourth schedule allocates seats in the Council of States i.e. Rajya Sabha (Upper House of Parliament)
Incorrect
Fourth schedule allocates seats in the Council of States i.e. Rajya Sabha (Upper House of Parliament)
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Q.21) Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Global Platform for Sustainable Cities (GPSC)’
- It is funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF)
- Five Indian Cities are participants in the GPSC
Select the correct statements
Correct
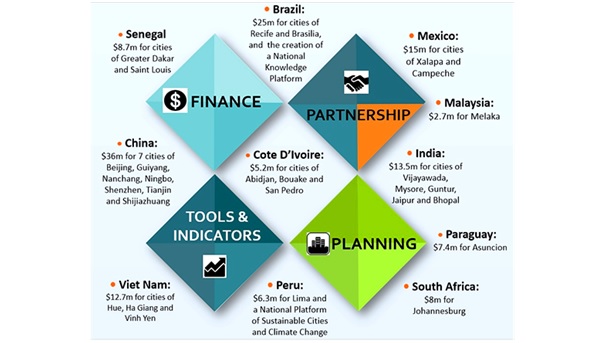
Led by the World Bank, the Global Platform for Sustainable Cities (GPSC) is a forum for knowledge sharing and partnership to achieve urban sustainability.
The GPSC promotes an integrated approach to urban development, focusing on urban sustainability indicators, planning, and financing. Funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the platform currently comprises of 28 cities across 11 countries.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Led by the World Bank, the Global Platform for Sustainable Cities (GPSC) is a forum for knowledge sharing and partnership to achieve urban sustainability.
The GPSC promotes an integrated approach to urban development, focusing on urban sustainability indicators, planning, and financing. Funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the platform currently comprises of 28 cities across 11 countries.

-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Q.22) Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Currency and Gold Revaluation Account (CGRA)’
- It represents the accumulated net balance of unrealised gains and losses arising out of valuation of Foreign Currency Assets (FCA) and gold.
- Increase in gold price and depreciation of the rupee decreases the CGRA fund.
Select the correct statements
Correct
Unrealised gains/losses on valuation of Foreign Currency Assets (FCA) and gold due to movements in the exchange rates and/ or price of gold are not taken to the Profit & Loss Account but instead booked under a balance sheet head named as the Currency and Gold Revaluation Account (CGRA).
Unlike the Contingency Reserve (CR), which is created by apportioning realised gains, the CGRA is not a reserve account as it represents the accumulated net balance of unrealised gains and losses arising out of valuation of FCA and gold.
As CGRA balances mirror the changes in prices of gold and in exchange rate, its balance varies with the size of asset base and volatility in the exchange rate and price of gold.
In the recent past, even though FCA and gold have declined as a percentage of total assets, the CGRA has risen due to sharp depreciation of Indian Rupee against US Dollar. It, thus, acts as a cushion against fluctuations in exchange rates/price of gold which have in the recent times exhibited sharp volatility.
The CGRA shows fund that is available to compensate RBI’s loss in the value of gold and foreign exchange reserve holdings. Gains and losses of the values of Gold and Foreign Currency Assets decreases or increases the CGRA money.
Thus, changes in the market value of gold and forex assets (like the US Government securities where the RBI invested its foreign exchange reserves) is reflected in the CGRA.
CGRA provides a buffer against exchange rate/gold price fluctuations. When CGRA is not enough to fully meet exchange losses, it is replenished from the contingency fund.
Increase in gold price and depreciation of the rupee increases the CGRA fund.
Incorrect
Unrealised gains/losses on valuation of Foreign Currency Assets (FCA) and gold due to movements in the exchange rates and/ or price of gold are not taken to the Profit & Loss Account but instead booked under a balance sheet head named as the Currency and Gold Revaluation Account (CGRA).
Unlike the Contingency Reserve (CR), which is created by apportioning realised gains, the CGRA is not a reserve account as it represents the accumulated net balance of unrealised gains and losses arising out of valuation of FCA and gold.
As CGRA balances mirror the changes in prices of gold and in exchange rate, its balance varies with the size of asset base and volatility in the exchange rate and price of gold.
In the recent past, even though FCA and gold have declined as a percentage of total assets, the CGRA has risen due to sharp depreciation of Indian Rupee against US Dollar. It, thus, acts as a cushion against fluctuations in exchange rates/price of gold which have in the recent times exhibited sharp volatility.
The CGRA shows fund that is available to compensate RBI’s loss in the value of gold and foreign exchange reserve holdings. Gains and losses of the values of Gold and Foreign Currency Assets decreases or increases the CGRA money.
Thus, changes in the market value of gold and forex assets (like the US Government securities where the RBI invested its foreign exchange reserves) is reflected in the CGRA.
CGRA provides a buffer against exchange rate/gold price fluctuations. When CGRA is not enough to fully meet exchange losses, it is replenished from the contingency fund.
Increase in gold price and depreciation of the rupee increases the CGRA fund.
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
Q.23) Consider the following statement with respect to ‘Operation Greens’
- It aims to aid farmers and help control and limit the erratic fluctuations in the prices of all green vegetables
- It is essentially a price fixation scheme that aims to ensure farmers are given the right price for their produce
Select the correct statements
Correct
Operation Greens
- It aims to promote farmer producers organisations, agri-logistics, processing facilities and professional management.
- The operation aims to aid farmers and help control and limit the erratic fluctuations in the prices of onions, potatoes and tomatoes.
- It is essentially a price fixation scheme that aims to ensure farmers are given the right price for their produce.
- It was announced in the Budget speech of 2018-19 with an outlay of Rs 500 crores to stabilize the supply of Tomato, Onion and Potato(TOP) crops and to ensure availability of TOP crops throughout the country round the year without price volatility.
Incorrect
Operation Greens
- It aims to promote farmer producers organisations, agri-logistics, processing facilities and professional management.
- The operation aims to aid farmers and help control and limit the erratic fluctuations in the prices of onions, potatoes and tomatoes.
- It is essentially a price fixation scheme that aims to ensure farmers are given the right price for their produce.
- It was announced in the Budget speech of 2018-19 with an outlay of Rs 500 crores to stabilize the supply of Tomato, Onion and Potato(TOP) crops and to ensure availability of TOP crops throughout the country round the year without price volatility.
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
Q.24) Which of the following statement is/are correct with respect to ‘Doctrine of Double Jeopardy’
- Article 20 (2) of the Constitution mandates that a person cannot be prosecuted or punished twice for the same offence
- If an accused has not been tried at all and convicted or acquitted, the principles of double jeopardy cannot be invoked at all
Select the correct statements
Correct
Double jeopardy
- If an “accused has not been tried at all and convicted or acquitted, the principles of double jeopardy cannot be invoked at all.
- The judgment is based on an appeal filed by the State of Mizoram against an order passed by the Gauhati High Court in August 2015, upholding a Special Court decision to decline to entertain a second chargesheet filed in a corruption case against the accused, Dr. C. Sangnghina, on the ground of double jeopardy.
- Article 20 (2) of the Constitution mandates that a person cannot be prosecuted or punished twice for the same offence.
Read More – https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/no-double-jeopardy-bar-if-there-was-no-trial-supreme-court/article25457534.ece
Incorrect
Double jeopardy
- If an “accused has not been tried at all and convicted or acquitted, the principles of double jeopardy cannot be invoked at all.
- The judgment is based on an appeal filed by the State of Mizoram against an order passed by the Gauhati High Court in August 2015, upholding a Special Court decision to decline to entertain a second chargesheet filed in a corruption case against the accused, Dr. C. Sangnghina, on the ground of double jeopardy.
- Article 20 (2) of the Constitution mandates that a person cannot be prosecuted or punished twice for the same offence.
Read More – https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/no-double-jeopardy-bar-if-there-was-no-trial-supreme-court/article25457534.ece
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
Q.25) Consider the following statements with respect to ‘High-throughput satellite (HTS)’
- It is a classification for communications satellites
- GSAT-29 is India’s first High-throughput satellite
Select the correct statements
Correct
High-throughput satellite (HTS) is a classification for communications satellites that provide at least twice, though usually by a factor of 20 or more, the total throughput of a classic FSS satellite for the same amount of allocated orbital spectrum thus significantly reducing cost-per-bit.
GSAT-19, the first of the series (HTS), was sent up in June 2017 from Sriharikota.
Incorrect
High-throughput satellite (HTS) is a classification for communications satellites that provide at least twice, though usually by a factor of 20 or more, the total throughput of a classic FSS satellite for the same amount of allocated orbital spectrum thus significantly reducing cost-per-bit.
GSAT-19, the first of the series (HTS), was sent up in June 2017 from Sriharikota.
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
Q.26) Purandara Dasa, a saint and chief founding-proponents of the South Indian classical Music (Carnatic Music) was contemporary of:
Correct
Purandara Dāsa was a Haridasa (a devotee – servant of Lord Hari (Vishnu)), great devotee of Lord Krishna (an incarnation of Lord Vishnu) and a saint.
- He was a disciple of the celebrated Madhwa philosopher-saint Vyasatirtha, and a contemporary of yet another great Haridasa, Kanakadasa.
- He was a composer, singer and one of the chief founding-proponents of the South Indian classical Music (Carnatic Music).
- In honor of his significant and legendary contributions to Carnatic Music, he is widely referred to as the Pitamaha (lit, “father” or the “grandfather”) of Carnatic Music.
- He is respected as an avatara (incarnation) of the great sage Narada (a celestial being who is also a singer).
- Purandara Dasa is noted for composing Dasa Sahithya, as a Bhakti movement vocalist, and a music scholar.
- His practice was emulated by his younger contemporary, Kanakadasa. Purandara Dasa’s Carnatic music compositions are mostly in Kannada, while some are in Sanskrit.
- He signed his compositions with the ankita (pen name) “Purandara Vittala” (Vittala is one of the incarnations of the Hindu god Vishnu).
- In the course of his wandering he met the holy sage Vyasatirtha, one of the chief exponents of Madhwa philosophy and the rajaguru of Krishnadevaraya, the emperor of Vijayanagara kingdom.
- Purandara Dasa traveled extensively through the length and breadth of the Vijayanagara empire in Karnataka, Tirupati, Pandharapura composing and rendering soul stirring songs in praise of god.
- He spent his last years in Hampi and also sang in Krishnadevaraya’s durbar.
Incorrect
Purandara Dāsa was a Haridasa (a devotee – servant of Lord Hari (Vishnu)), great devotee of Lord Krishna (an incarnation of Lord Vishnu) and a saint.
- He was a disciple of the celebrated Madhwa philosopher-saint Vyasatirtha, and a contemporary of yet another great Haridasa, Kanakadasa.
- He was a composer, singer and one of the chief founding-proponents of the South Indian classical Music (Carnatic Music).
- In honor of his significant and legendary contributions to Carnatic Music, he is widely referred to as the Pitamaha (lit, “father” or the “grandfather”) of Carnatic Music.
- He is respected as an avatara (incarnation) of the great sage Narada (a celestial being who is also a singer).
- Purandara Dasa is noted for composing Dasa Sahithya, as a Bhakti movement vocalist, and a music scholar.
- His practice was emulated by his younger contemporary, Kanakadasa. Purandara Dasa’s Carnatic music compositions are mostly in Kannada, while some are in Sanskrit.
- He signed his compositions with the ankita (pen name) “Purandara Vittala” (Vittala is one of the incarnations of the Hindu god Vishnu).
- In the course of his wandering he met the holy sage Vyasatirtha, one of the chief exponents of Madhwa philosophy and the rajaguru of Krishnadevaraya, the emperor of Vijayanagara kingdom.
- Purandara Dasa traveled extensively through the length and breadth of the Vijayanagara empire in Karnataka, Tirupati, Pandharapura composing and rendering soul stirring songs in praise of god.
- He spent his last years in Hampi and also sang in Krishnadevaraya’s durbar.
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
Q.27) ‘Jayadeva’ was a Sanskrit poet during the 12th century. He is most known for his epic poem:
Correct
Gita Govinda: is a work composed by the 12th-century Indian poet, Jayadeva. It describes the relationship between Krishna and the gopis (female cow herders) of Vrindavana, and in particular one gopi named Radha.
Incorrect
Gita Govinda: is a work composed by the 12th-century Indian poet, Jayadeva. It describes the relationship between Krishna and the gopis (female cow herders) of Vrindavana, and in particular one gopi named Radha.
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
Q.28) Dakshayagam (The Fire-Sacrifice of Daksha) is related to:
Correct
Dakshayagam (The Fire-Sacrifice of Daksha) is a Kathakali play(Aattakatha) authored by Irayimman Thampi in Malayalam.
Incorrect
Dakshayagam (The Fire-Sacrifice of Daksha) is a Kathakali play(Aattakatha) authored by Irayimman Thampi in Malayalam.
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
Q.29) Consider the following statements regarding ‘Adi Shankara’, an early 8th century Indian philosopher and theologian:
- Shankara’s masterpiece of commentary is the Brahmasutrabhasya, a fundamental text of the Vedanta school of Hinduism.
- He believed that, Hinduism asserts ‘Soul and Self’ whereas Buddhism asserts that there is ‘no Soul, no Self’.
Which of the given statements is/are correct?
Correct
Adi Shankara was an early 8th century Indian philosopher and theologian who consolidated the doctrine of Advaita Vedanta.
- He is credited with unifying and establishing the main currents of thought in Hinduism.
- Adi Shankara is most known for his systematic reviews and commentaries (Bhasyas) on ancient Indian texts. Shankara’s masterpiece of commentary is the Brahmasutrabhasya (literally, commentary on Brahma Sutra), a fundamental text of the Vedanta school of Hinduism.
- His works in Sanskrit discuss the unity of the ātman and Nirguna Brahman “brahman without attributes”.
- He wrote copious commentaries on the Vedic canon (Brahma Sutras, Principal Upanishads and Bhagavad Gita) in support of his thesis.
- His works elaborate on ideas found in the Upanishads. Shankara’s publications criticised the ritually-oriented Mīmāṃsā school of Hinduism.
- He also explained the key difference between Hinduism and Buddhism, stating that Hinduism asserts “Atman (Soul, Self) exists”, while Buddhism asserts that there is “no Soul, no Self”.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/society/faith/hymn-that-enlightens/article25532477.ece
Incorrect
Adi Shankara was an early 8th century Indian philosopher and theologian who consolidated the doctrine of Advaita Vedanta.
- He is credited with unifying and establishing the main currents of thought in Hinduism.
- Adi Shankara is most known for his systematic reviews and commentaries (Bhasyas) on ancient Indian texts. Shankara’s masterpiece of commentary is the Brahmasutrabhasya (literally, commentary on Brahma Sutra), a fundamental text of the Vedanta school of Hinduism.
- His works in Sanskrit discuss the unity of the ātman and Nirguna Brahman “brahman without attributes”.
- He wrote copious commentaries on the Vedic canon (Brahma Sutras, Principal Upanishads and Bhagavad Gita) in support of his thesis.
- His works elaborate on ideas found in the Upanishads. Shankara’s publications criticised the ritually-oriented Mīmāṃsā school of Hinduism.
- He also explained the key difference between Hinduism and Buddhism, stating that Hinduism asserts “Atman (Soul, Self) exists”, while Buddhism asserts that there is “no Soul, no Self”.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/society/faith/hymn-that-enlightens/article25532477.ece
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
Q.30) NASA’s flagship mission, the Chandra X-ray observatory is named after a famous person of Indian origin. Name the person?
Correct
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space observatory launched by NASA on July 23, 1999.
- The telescope is named after the Nobel Prize-winning Indian-American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar.
NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory is a telescope specially designed to detect X-ray emission from very hot regions of the Universe such as exploded stars, clusters of galaxies, and matter around black holes.
Because X-rays are absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, Chandra must orbit above it, up to an altitude of 139,000 km (86,500 mi) in space.
Incorrect
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space observatory launched by NASA on July 23, 1999.
- The telescope is named after the Nobel Prize-winning Indian-American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar.
NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory is a telescope specially designed to detect X-ray emission from very hot regions of the Universe such as exploded stars, clusters of galaxies, and matter around black holes.
Because X-rays are absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, Chandra must orbit above it, up to an altitude of 139,000 km (86,500 mi) in space.











