IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 5th November 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
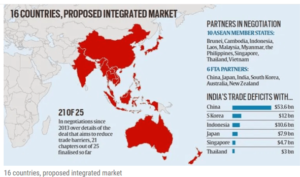
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Affairs
In News
- Seven years after India joined negotiations for the 16-nation ASEAN (Association for South East Asian Nations)-led RCEP India dropped out of the agreement, citing its negative effects on “farmers, MSMEs and the dairy sector”.
- RCEP is a proposed free trade agreement (FTA) between ASEAN and its six FTA partners – China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
- Ten member states of ASEAN areBrunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam
- Without India, RCEP accounts for nearly 1/3rd of global GDP. But they have less than a third of the population.
- Why India opted out?
- The deal requires the gradual elimination of tariffs which may flood Indian markets with Chinese goods and agricultural produce from oceania, harming local producers
- Lack of access to Indian services- allowing Indian labour mobility to other countries for services – in the RCEP countries (Services is India’s strong area and has huge potential to tap into RCEP market)
- Can India join later?
- Yes, if the issues India has with the deal are resolved
SCO joint exercise
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Security
In News
- Pakistan did not participate in the inaugural session of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) joint exercise on urban earthquake and rescue in Delhi.
- Earthquakes have taken more than 2 lakh lives, which account for two-thirds of disaster related mortality in SCO countries. In this background, this joint exercise will be very useful for improving the collective preparedness
- The SCO, in which China plays an influential role, is also comprised of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India and Pakistan. India and Pakistan were admitted into the bloc in 2017.
Do You Know?
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) is a permanent organ of the SCO which serves to promote cooperation of member states against the three evils of terrorism, separatism and extremism. It is headquartered in Tashkent.
- India has launched Geostationary Satellite to improve communication, weather forecasting, etc. among the South Asian countries.
One China Policy
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Federalism
In News
- Vietnam reiterated that it adheres to the one-China policy and expect China to adhere to international law
About One China Policy
- It is a principle whereby China insists Taiwan is an inalienable part of one China to be reunified one day.
- The policy can be traced back to 1949 and the end of the Chinese civil war. The defeated Nationalists, also known as the Kuomintang, retreated to Taiwan and made it their seat of government while the victorious Communists began ruling the mainland as the People’s Republic of China. Both sides said they represented all of China.
- Since then China’s ruling Communist Party has threatened to use force if Taiwan ever formally declares independence, but it has also pursued a softer diplomatic track with the island in recent years.
Mutual logistics agreement
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – International Relations
In News
- India and Russia are expected to conclude a mutual logistics agreement and review the setting up of joint ventures for manufacturing spares for Russian defence platforms in India
- The Agreement on Reciprocal Logistics Support (ARLS) was expected to be signed on the sidelines of the Eastern Economic Forum (EEF) in Vladivostok, but was held back.
- A 50-member industry delegation is accompanying Defence Minister to Russia to explore ways to jointly manufacture spares and components with Russian original equipment manufacturers (OEM) under ‘Make in India’.
- EEF was established by a decree of the President of the Russian Federation, Vladimir Putin, in 2015, with the aim of supporting the economic development of Russia’s Far East, and to expand international cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region
- For more details on EEF, refer:https://iasbaba.com/2019/09/all-india-radio-air-ias-upsc-eastern-economic-forum/
Auto slowdown
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains GS-III – Economy
In News
- One of the key reasons for the slowdown in the automobile sector is the confusion over the policy on electric cars, the government told a parliamentary panel
- NITI Aayog had proposed in August the ban sale of three-wheelers with internal combustion engines by 2023 and two-wheelers with engine capacities less than 150 cc by 2025.
- The 150-cc and below segment forms almost 90% of the two-wheeler market in the country.
- The industry termed the proposed NITI Aayog plan “unrealistic”, while knocking on the Centre’s door pitching for a EV roll-out road map over a “practical” time frame.
- Government clarified at many forums that it did not intend to ban sales of vehicles powered by fossil fuels, but the confusion added to the already low consumer sentiment.
- Some of the reasons attributed to auto slowdown are
- Auto sales were down because of “curtailment” of automobile loans that so far were easily available.
- The sharp increase in road tax in many States added to the problem.
- The switch from BS IV to VI engines for improved emission standards has also led to the slump due to increased cost of production.
Miscellaneous
New species of tree frog
- A new frog species named Polypedates bengalensis has been found in a residential area of West Bengal.
- The new species also named Brown Blotched Bengal Tree was found in two places in West Bengal – Badu, North 24 Parganas District and Khordanahala, South 24 Parganas District.
- It is named Brown Blotched Bengal Tree Frog from the series of six to nine dark brown blotches that extend laterally from behind the frog’s eye to the vent. The frog’s body colour is yellowish-brown to greenish-brown.
Ratnam Pen
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has gifted German Chancellor Angela Merkel an exquisite handloom woollen khadi stole from Ladakh and a Ratnam pen.
- The Ratnam Pen, named after K.V. Ratnam (originally from a family of goldsmiths in Rajahmundry), was made iconic by Mahatma Gandhi.
- The pen was made in 1934 by Ratnam, by using indigenous materials upon Mahatma Gandhi’s request to create a ‘swadeshi’ (locally made) pen. Mahatma Gandhi had written over 31,000 letters in his quest to take India to its freedom. Many of these letters were written using Ratnam Pen.
- It is produced even today in its original form by K.V. Ratnam and Sons — Ratnam Ballpen Works, owned by Ratnam’s descendants. Even today, it has a barrel for filling ink using a dropper and the Genius Iridium Nib from Germany.
(MAINS FOCUS)
GOVERNANCE
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures.
Embracing Digital Governance
Introduction
- Due to the rapid rise of the internet and digitization, Governments all over the world are initiating steps to involve information and communication technology (ICT) in all governmental processes.
- Various government programmes have leveraged ICT on a large scale to transform the public governance ecosystem in the country.
Examples of large-scale digital-led successes
- Transformation brought out in direct and indirect tax regime in the country
- Government procurement reforms driven through Government e-Marketplace
- Roll-out of Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (Ayushman Bharat)
- Participatory governance enabled through MyGov
Importance of ICT for effective governance
- It is a key step towards making the country “Fit for Future”
- administration becomes a swifter and more transparent process
- Makes the whole administrative process convenient, efficient, transparent, fully accountable and responsible
- Improved access to information and better quality of services for citizens
- It would help in bringing government machinery to the doorsteps of the citizens (expanded reach of governance)
- It would increase citizen participation in governance
- Aadhar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Digital Locker, BharatNet etc
India needs to prepare for the next wave of digital governance
- The next wave of digital governance needs to align itself with the perspective of digitally empowered citizens, businesses and government alike
- India to become true ‘Digital India’, a paradigm shift in e-governance approach is needed
- There is a need for shift in approach from the traditional ‘department-centric’ view of service provisioning to a ‘stakeholder-centric’ view driven by their personas (persona-based approach for delivering services)
- In other words, there is a need to create the next generation service delivery framework, where the governments across all levels reach out to each individual proactively for delivery of services and benefits, and in local language of his/her choice. (creating an unbroken value chain)
- The data collected from various e-governance initiatives should be used to reduce redundancy in information sought from the businesses and citizens across the value chain, identify trends, improve delivery mechanisms and for better policy planning.
- India needs a larger framework where the individual’s privacy is respected and data security is ensured.
Conclusion
Today, India is making rapid strides in adoption of emerging concepts such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, cloud computing, drones, microservices etc, which have a huge potential in transforming governance.
Several initiatives are being taken by the government to enhance existing governance mechanisms by leveraging advancements in technology.
Such efforts and initiatives are bound to intensify, given the growing challenges in governance and availability of technology in the country.
The need is now to converge such efforts and align them with a futuristic governance framework, a framework that has a ‘human-need centric design’.
Connecting the dots:
- India should work towards creating an unbroken value chain to prepare for the next wave of digital governance. Elucidate.
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership
Context:
- India decided to hold the signing off of Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) until “significant outstanding issues” were resolved, when all other 15 countries involved in the negotiations stated that they were ready to sign the mega trade deal in 2020.
PM narendra modi’s statement:
“When I measure the RCEP Agreement with respect to the interests of all Indians, I do not get a positive answer. Therefore, neither the Talisman of Gandhiji nor my own conscience permit me to join RCEP,” .
Reasons for not joining:
- Unsatisfactory negotiations pertaining to India’s trade with China — India has an over $50 billion trade deficit
- “Inadequate” protection against surges in imports.
- Industry has voiced fears that cheaper products from China would “flood” the market.
- India has not received any assurances on its demand for more market access,
- India’s concerns over non-tariff barriers is not addressed
- A “possible circumvention” of rules of origin ,the criteria used to determine the national source of a product were not addressed which allow countries like China to pump in more products.
- India has pushed for other countries to allow greater movement of labour and services for a long , which is not addressed
- Concerns over unsustainable trade deficits is also not addressed.
- India already have , bilateral FTAs with most RCEP nations, but it has recorded trade deficits with these countries
- Domestic industries like dairy industry was expected to face stiff competition from Australia and New Zealand.
Way forward:
- An auto-trigger mechanism that would allow India to raise tariffs on products in instances where imports cross a certain threshold.
- Lowering and eliminating tariffs on several products from the India which It has expressed
- Opening the vast Indian market must be matched by openings in some areas where our businesses can also benefit
- India to safeguard the interests of its domestic industry suggested measures like seeking a 2014 base year for tariff reductions instead of 2013, Using a base year before 2014 would mean a drastic drop in the import duties on these products. This measure must be accepted by RCEP
RCEP’s Statement:
“All RCEP Participating Countries will work together to resolve these outstanding issues in a mutually satisfactory way. India’s final decision will depend on satisfactory resolution of these issues,” the joint statement by RCEP members said.
Connecting the dots :
- India believes that the RCEP trade deal doesn’t provide adequate protection against possible surges of imported goods. Justify.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Eastern Economic Forum’
- It is an initiative of the ‘ASEAN + 6’ countries.
- It is an initiative for the purpose of encouraging foreign investment
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Eastern Economic Forum
- EEF is an international forum established by Russia in 1991 to support the economic development of Russia’s Far East
- The Russian Far East comprises the eastern Russian territory between Lake Baikal in eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Ratnam Pen
- The pen was made in 1934 by Ratnam, by using indigenous materials upon Mahatma Gandhi’s request to create a ‘swadeshi’ (locally made) pen
- It is produced even today in its original form which has a barrel for filling ink using a dropper and the Genius Iridium Nib from Germany.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Which of the following countries are members of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- India
- China
- Pakistan
- Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan
Select the correct answer from the codes given below
- 1,2 and 3only
- 1,2,3 and 4 only
- 1,2,3 and 5 only
- All of the above
Q.5) Which of the following are considered as the reasons for automobile slowdown observed in early 2019
- The sharp increase in road tax in many States
- The switch from BS IV to VI engines for improved emission standards
- Falling rural demand due to stagnation in agricultural growth
Select the correct answer from the codes given below
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- All of the above
MUST READ
A rights-based framework to theorise poverty
Fusing traditional medicine with the modern
Kerala’s modernity and its discontents
Stack and blueprint — Building digital infrastructure for national health database
As Delhi chokes on its air, the lessons Gabon, a West African country offers











