IASbaba's Press Information Bureau
Press Information Bureau (PIB) IAS UPSC – 28th October to 4th November, 2019
GS-2
Release of 15 point Reform Charter – New Political normal to enable effective functioning of the Parliament and State Legislatures
(Topic: Functioning of the Parliament)
- Poor attendance in the legislatures and the quality of debates: To ensure attendance of at least 50% of their legislators all through the proceedings of the Houses by adopting a roster system. This suggestion came in the context of Parliament being forced to be adjourned due to lack of quorum of the required presence of 10% of the strength of the Houses.
- A thorough review of the Anti-Defection Law to rectify the grey areas like incentivising legislators to resort to actions inviting expulsion from the party besides providing for time bound disposal of defection cases by the Presiding Officer.
- Building consensus on simultaneous polls to let unfettered governance
- Enacting for reservation of women in legislatures
- Making rules that automatically take effect against erring members in case of interruptions and disruptions
- Regular publication of reports by the Secretariats of Legislatures on the attendance of Members and their participation in debates
- Doing away with the winnability as the sole criterion for selecting contestants by the parties to address the concern of rising number of legislators with criminal record
Frequent disruptions, Points of Order without a point, Adjournment Motions and interruptions betray political immaturity, exhibitionism, excessive fondness for the limelight and inadequate appreciation of the need to utilise the opportunity of serving the public interest.
National Digital Health Blueprint (NDHB)
(Topic: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation)
Government of India is committed to ensuring high quality healthcare, accessible to all upto the last mile. The digital health interventions are accelerating this transformation and have a huge potential for supporting Universal Health care.
The need of the hour is to create an ecosystem which can integrate theexisting disparate health information systems and show clear path for upcoming programmes. There is a need to ensure convergence across these IT systems to monitor and provide health services in a robust and efficient manner.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has initiated efforts in the direction of a comprehensive, nationwide integrated e-Health system under National Digital Health Blueprint. NDHB will help in providing a common platform for integration of existing applications in health domain and data which has existed in silos, either in public health facility, or, in private healthcare facility, in India.
It was also updated that building on the initial document of “National Health Stack” (NHS) by NitiAayog, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has defined clear timelines, targets and the resources required for this digital convergence of Healthcare programmes in India.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) at Uzbekistan
(Topic: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
- India called upon the member countries of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) to strengthen and implement all existing international laws and mechanisms, without exceptions or double standards, to combat terrorism and its enablers.
- Terrorism continues to disrupt our societies and undermine our developmental endeavors.It is important for SCO countries to come together to deal with this menace
- The process of globalisation has opened up immense opportunities for the growth of SCO members, but also brought to the fore multidimensional, complex and transnationalthreats affecting developing countries. All members needs to work together in defeating challenges liketerrorism, climate change, endemic poverty, under development, pandemics and inequality.
- India voiced the Government’s resolve of providing an enabling economic ecosystem for partner countries to invest and do business in India. He listed out various initiatives taken by the Government in this regard including relaxing FDI reforms, allowing 100 per cent foreign investment in coal mining and contract manufacturing, easing sourcing norms for single-brand retailers and approving 26 per cent overseas investment in digital media.
- We strongly support the initiative to facilitate cooperation among small and medium-sized enterprises within the SCO.Food industry is another potential area of collaboration. SCO members can work together for technology and investment support to food processing and put in a supporting logistics chain
- India is ready to share its experience and expertise in skill development and capacity building in areas such as telemedicine, medical tourism, resource mapping, launching of satellites, agricultural education and effective and affordable pharmaceuticals. Finance, hospitality and tourism services also present significant opportunities.
- Reiterated the Government’s commitment to a transparent, rules-based, open, inclusive and non-discriminatory multilateral trading system with the World Trade Organisation at its centre.
- Invited SCO Member states to join the ‘Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure’. India has taken the initiative of launching the coalition to assist countries in upgrading their capacities for developing resilient infrastructure. It will address the loss reduction targets under the Sendai Framework, besides contributing to climate change adaptation. India would be holding Joint Urban Earthquake Search and Rescue exercise of SCO member States along with SCO Expert level meeting on disaster prevention
About SCO:
SCO: Formerly the Sanghai Five and formed in 1996, the SCO has eight members today including India and Pakistan, which became part of it in 2017.
- After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the then security and economic architecture in the Eurasian region dissolved and new structures had to come up.
- The original Shanghai Five were China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan.
- The SCO was formed in 2001, with Uzbekistan included. It expanded in 2017 to include India and Pakistan.
Since its formation, the SCO has focused on regional non-traditional security, with counter-terrorism as a priority: The fight against the “three evils” of terrorism, separatism and extremism has become its mantra. Today, areas of cooperation include themes such as economics and culture.
How does membership of the SCO help India?
In a world riven by geopolitical contestations, SCO membership provides India a vital counter to some of the other groupings it is a part of, balancing out its stated policy of pursuing “multi-alignments”. It is a platform also for alignments on issues such as energy security, connectivity and trade. With India indicating that it sees little use for SAARC, the SCO provides the only multilateral platform for it to deal in close proximity with Pakistan and Afghanistan.
For India, two important objectives are counter-terrorism and connectivity. These sit well with the SCO’s main objective of working cooperatively against the “three evils”.
- India wants access to intelligence and information from SCO’s counter-terrorism body, the Tashkent-based Regional Anti-Terror Structure (RATS).
- A stable Afghanistan too is in India’s interest, and RATS provides access to non-Pakistan-centred counter-terrorism information there.
- Connectivity is important for India’s Connect Central Asia policy.
- Energy cooperation dominates its interest – and it’s in China’s neighbourhood. But India will also have to deal with an assertive China, which will push its Belt and Road Initiative during the summit.
- SCO membership also bolsters India’s status as a major pan-Asian player, which is boxed in the South Asian paradigm.
8th Indo German Energy Forum (IGEF) 2019
(Topic: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests)
The Forum took note of the ongoing cooperation under the following four sub-groups:
Sub Group-I: Flexibilization in Thermal Power Plants.
Sub Group-II: Renewable Energies
Sub Group-III: Demand side energy efficiency and low carbon growth strategies
Sub Group-IV: Green Energy Corridors
The Forum also finalized the roadmap for future collaboration between the two countries which, inter-alia, include Flexibilisation of existing coal fired power plants, promoting niche markets for Solar Energy, promotion of energy efficiency in buildings through ECBC, building materials and credit lines for financing corresponding measures and RE evacuation through state-of-the-art intra-state and inter-state transmission grid infrastructure.
Prelims oriented News
Next Chief Justice of India: Shri Justice Sharad Arvind Bobde
New President of Argentina: Alberto Fernández
Shri Girish Chandra Murmu: Sworn in as first Lieutenant Governor of Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir
Shri Radha Krishna Mathur: Sworn in as first Lieutenant Governor of Ladakh
ICEDASH: Ease of Doing Business monitoring dashboard of the Indian Customs helping public see the daily Customs clearance times of import cargo
ATITHI: Easy to use mobile app for international travelers to file the Customs declaration in advance
National Research Institute of Unani Medicine for Skin Disorders: Erragadda, Hyderabad
UNESCO has designated Mumbai as a member of UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) in the field of FILM and Hyderabad in the field of GASTRONOMY
UCCN, created in 2004, is a network of cities which are thriving, active centres of cultural activities in their respective countries. The UNESCO Creative Cities Network now counts a total of 246 cities.
The member cities that form part of the Network come from all continents and regions with different income levels and populations. They work together towards a common mission: placing creativity and the creative economy at the core of their urban development plans to make cities safe, resilient, inclusive and sustainable, in line with the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
The 7 categories for recognition under UCCN are as follows-
- Crafts and Folk Arts
- Design
- Film
- Gastronomy
- Music
- Media Arts
- Literature
Previously, 3 Indian cities were recognized as members of UCCN, namely-
Jaipur- Crafts and Folk Arts (2015)
Varanasi- Creative city of Music (2015)
Chennai- Creative city of Music (2017)
Ministry of Culture is the nodal Ministry of Government of India for all matters in UNESCO relating to culture.
Dustlik 2019
- The first-ever India-Uzbekistan Joint Exercise at Tashkent in Uzbekistan
- “Terrorism is a global problem. There are many examples where some countries have adopted terrorism as their state policy. The need of the hour is to condemn and isolate such countries,” said Shri Rajnath Singh.
- Raksha Mantri affirmed
- India’s commitment of developing a state-of-the-art IT complex in Armed Forces Academy of Uzbekistan for the benefit of their soldiers.
- India’s enhanced support to Uzbekistan in Military Medicine
Science Facts:
- In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
- Communication link set up through Infrared signals – Wireless infrared communications refers to the use of free-space propagation of light waves in the near infrared band as a transmission medium for communication. This attempt is dedicated to Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman and Satyendra Nath Bose.
- Like all other electromagnetic waves, radio waves travel at the speed of light in vacuum. They are generated by electric charges undergoing acceleration, such as time varying electric currents. Radio waves are generated artificially by transmitters and received by radio receivers, using antennas. This attempt is dedicated to Jagadish Chandra Bose.
India International Science Festival – IISF, organized jointly by Science & Technology -related Ministries and Departments of the Government of India and Vijnana Bharati (Vibha), is an annual festival to celebrate the achievements of India’s scientific and technological advancements with students, innovators, craftsmen, farmers, scientists and technocrats from India and abroad.
India’s first global Mega Science Exhibition: ‘Vigyan Samagam’ in Kolkata; The Exhibition will highlight India’s contribution to the world’s science, technology and innovation, and researches in the areas of high energy physics, nuclear physics, astronomy and astrophysics, nuclear energy etc. It will also showcase that DAE not only works on nuclear technologies, but also works on fundamental science and research; and the wide-ranging connectivity of DST across institutional and disciplinary barriers across the country.
The Kung Fu Nuns of the Drukpa Order: Some of the Himalayas’ most prominent human rights advocates, recently received the Asia Society’s prestigious Game Changer Award in New York on 30th October 2019 for their path-breaking work to empower women and dismantle gender stereotypes in the Himalayas.
- The Nuns use Jigme as their first name and the meaning of Jigme is ‘fearless’.
- The Kung Fu Nuns represent a new generation of Buddhists who use their teachings to take real action and effect meaningful change in the world by promoting gender equality and environmentalism.
- With this recognition, the Kung Fu Nuns join the likes of iconic Indian leaders Indra Nooyi, Mukesh Ambani, and Dev Patel, who have also been honored by the Asia Society in previous years for breaking the glass ceiling with their courage and inspiring their fellow citizens.
- The Gyalwang Drukpa, the spiritual leader and founder of the Drukpa order, encouraged his nuns to train in Kung Fu to build confidence as leaders. In doing so, he flouted centuries of Buddhist tradition that barred nuns from physical exercise. They are the only Buddhist nuns in the world to practice Kung Fu. The nuns use their martial arts expertise to challenge gender roles in India’s conservative culture.
National Corporate Social Responsibility Awards: The NCSRA has been instituted by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs to recognize outstanding contribution in the field of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
Six priority pillars of blue economy:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture
- Renewable Ocean Energy
- Seaports and Shipping
- Offshore Hydrocarbons
- Seabed Minerals
- Marine Biotechnology
Blue economy includes intangible economic benefits such as carbon sequestration, coastal protection, cultural values and biodiversity. Oceans already account for significant trade, commerce and offshore oil and gas, fishing, under sea-cables and tourism, emerging industries such as aquaculture, marine biotechnology, ocean energy and sea-bed mining have the potential to create jobs and spur worldwide economic growth.
There is a need to give a strong thrust to research activities and innovation in the areas of ocean energy, marine biology and bio technology for India to become a leader in those sectors.
India’s exports of marine products to China has tripled and touched almost USD 800 million, in the first nine months of 2019, as per the data released by China’s customs authority recently. India’s marine exports are expected to cross USD 1 billion mark by the end of this year. Embassy of India has been promoting various products such as Indian grapes, sugar, rice, pharmaceuticals, tea, oil meals, IT and ITeS in which India has proven global strength but little market share in China.
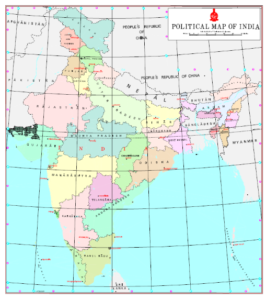
Maps of newly formed Union Territories of Jammu Kashmir and Ladakh, with the map of India Released
Press Information Bureau (PIB) IAS UPSC – 28th October to 4th November, 2019
Personality in News
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
The birthday of India`s Iron Man is being observed as Rashtriya Ekta Diwas or National Unity Day since the year 2014.
- First Deputy Prime Minister of India
- Widely considered to be the architect of modern India, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel played an important role in the integration of all the princely states (especially Hyderabad, Junagadh and Kashmir) into the Indian Union after the British left India in 1947.
- Provided good governance as an able administrator in diverse fields like modern farming and empowerment of tribal communities
- Organised peasants from Kheda, Borsad, and Bardoli in Gujarat in non-violent civil disobedience against the British Raj, becoming one of the most influential leaders in Gujarat.
- He earned the title of “Sardar” after spearheading a no-tax campaign by peasants at Bardoli in Gujarat.
- He also led the relief and rehabilitation operations when Gujarat was ravaged by floods and worked tirelessly during a plague outbreak in Ahmedabad.
- He is also remembered as the “patron saint of India’s civil servants” for having established the modern all-India services system. “A civil servant cannot afford to, and must not, take part in politics. Nor must he involve himself in communal wrangles. To depart from the path of rectitude in either of these respects is to debase public service and to lower its dignity,” he had cautioned them on April 21, 1947.
Acknowledging the monumental contribution of Patel in nation building, Jawaharlal Nehru said, “History will call him the builder and consolidator of new India.”
The remarks Patel made during the Quit India Movement are also relevant today. He said: “We have to shed mutual bickering, shed the difference of being high or low and develop the sense of equality and banish untouchability. We have to live like the children of the same father”.
Unification:
After independence, Sardar Patel become India’s first deputy prime minister and first home minister and placed a very significant role in unification of country.
- Accession of princely states into Indian Union
- Operation Polo
- Referendum in case of Junagarh
- Effort to settle refugees fleeing Pakistan
- Safeguarding and strengthen Civil services
Connecting the Dots
- ‘Statue of Unity’ is as tall as the person it is dedicated to. Describe the contribution of Sardar Vallabh bhai Patel in the Independence Struggle of India and its unification.
- With great skill and masterful diplomacy and using both persuasion and pressure, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel succeeded in integrating hundreds of princely states with the Indian Union. Discuss.
- The strong man of India who made Idea of India possible was Sardar Patel—‘the Bismarck and architect of modern India’. Substantiate











