IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 26th December 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Locust invasion in Gujarat
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Environment, Agriculture
In News
- According to the Agriculture Ministry’s Locust Warning Organisation (LWO) in Jodhpur, locusts (species of grasshoppers) are flying in from Pakistan’s Sindh province and spreading in villages in Rajasthan and Gujarat where south western monsoon was prolonged this year.
- Originally, the locusts emerged in February this year from Sudan and Eritrea on Africa’s Red Sea Coast and travelled through Saudi Arabia and Iran to enter Pakistan.
- Locust invasions usually occurs in areas that receive less than 200 mm of rain annually. This is about 16 million sq km consisting of about 30 countries.
- The insects fly in during the day and settle on the farms at night, making it difficult to ward them off negatively impacting farm output.
- The last major upsurge in India occurred in 1993 which saw the incursion of 172 locust swarms. India has only one locust breeding season- from July to October
- How to tackle?
- Government also explored the possibility of sprinkling pesticides and chemicals through choppers in affected areas.
National Strategy for Suicide Prevention under discussion
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I- Society
In News
- India continues to have the dubious distinction of recording the highest number, or 34% of all suicides in the world.
- According to provision of Section 309 of the IPC attempted suicide continues to be a criminal offence. It says that suicide attempt is punishable with simple imprisonment, which may extend up to one year.
- However, Section 115 of the MCHA, 2017 states that “any person who attempts to commit suicide shall be presumed, unless proved otherwise, to have severe stress and shall not be tried and punished under the said Code (Section 309 of IPC).”
- After the Mental Healthcare Act (MCHA), 2017, the Section has become “redundant” but still remains in law books.
- Therefore, once National strategy of prepared, it is expected to remove confusion surrounding inconsistencies between IPC and MCHA
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ATAL JAL)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Governance; GS-III- Environment Conservation
In News
- The Central Sector scheme aims to improve ground water management through community participation in identified priority areas in seven States, viz. Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
- The Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti is the implementing agency for the scheme.
- Out of the total outlay of Rs. 6000 crore, 50% shall be in the form of World Bank loan, and remaining 50% shall be through Central Assistance from regular budgetary support. The entire amount shall be passed on to the States as Grants.
- ATAL JAL has two major components:
- Institutional Strengthening and Capacity Building for sustainable ground water management in the States including improving monitoring networks, capacity building, strengthening of Water User Associations, etc.
- Incentivising the States for achievements in improved groundwater management practices namely, data dissemination, preparation of water security plans etc.
Do You know?
- Out of 17.87 Crore rural households in the country, about 14.6 Crore which accounts for 81.67% are yet to have household water tap connections.
- Government’s Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) aims to provide Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) to every rural household by 2024.
Intersex Person: Call for National ban on unnecessary medical surgeries
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I- Society
In News
- The term intersex is confused with transgender, the two in-fact have very different meanings.
- Individuals who identify as transgender or transsexual have a gender that is different from the one traditionally associated with the sex they were assigned at birth.
- Intersex refers to people born with biological or physical characteristics that are more diverse than stereotypical male or female bodies.
- Intersex individuals and rights organisations have sought a national ban on unnecessary medical surgeries conducted on children with intersex traits and appealed to the Union government to protect their human rights.
- Call for nation-wide ban comes after the Tamil Nadu government banned normative surgeries on infants and children except in life-threatening situations after a historic judgment of the Madras High Court on April 22, 2019
- WHO and the UN Human Rights Council have called upon Member States to end invasive and irreversible medical surgeries and other medical treatment on intersex children.
- If adopted nationally, India could become only the third country after Malta and Taiwan, to have a legal regime which protects the rights of intersex children.
Saptamatrikas: Earliest Epigraphic evidence for the cult found
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains I- Art & Culture
In News
- The Epigraphy Branch of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has discovered the earliest epigraphic evidence so far for the Saptamatrika cult.
- It is also the earliest Sanskrit inscription to have been discovered in South India as on date.
- Saptamatrikas are a group of seven female deities worshipped in Hinduism as personifying the energy of their respective consorts.
- The inscription is in Sanskrit and in Brahmi characters and was issued by Satavahana king Vijaya in 207 A.D. It was discovered in Chebrolu village in Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh.
- So far the Nagarjunakonda inscription of Ikshavaku king Ehavala Chantamula issued during 4th century A.D. was considered the earliest Sanskrit inscription in South India
Bharatnet Project: Free WiFi to all villages
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains III- Infrastructure (Digital)
In News
- To promote uptake of the Internet in rural areas, government promised free Wi-Fi to about 48,000 villages, which are connected through the government’s flagship Bharatnet project
- With the BharatNet initiative, the Centre aims to connect all 2.5 lakh gram panchayats through optical fibre.
- Digital Village, which was conceptualised by the Common Service Centre (CSC) SPV under the Ministry of Electronics and IT, is a village where citizens can avail various e-services of the central and the State governments, as well as of private players.
- These services include banking, insurance, tele-medicine, pension and e-governance services. Such villages are also equipped with LED bulb assembly unit, sanitary napkin unit, and rural-Wifi infrastructure.
- There were about 3.6 lakh CSCs in the country covering 2.25 lakh gram panchayats.
(MAINS FOCUS)
ENVIRONMENT
TOPIC: General Studies 3:
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment
Desertification: Another 30% of the India’s land is undergoing degradation
Context:
- Every year during the monsoon, Hemant Waman Chowre faces a peculiar situation. On the one hand, he hopes for good rainfall to water his crops but on the other, he is scared, for even a mild shower can destroy his saplings.
- These are clear signs of desertification which, as per the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), is degrading 12 million ha of productive land across the world every year. This is over 80 times the size of Delhi and is enough to grow 20 million tonnes of grain.
- Dry lands affected by desertification not only lose their ability to support plant life, but also their ability to offer ecosystem services, such as management of water systems and storage of carbon use in global warming.
- Desertification has occurred throughout history. But what’s alarming is that its pace has accelerated 30 to 35 times the historical rate in the recent decades. With changing climate, prolonged droughts and increasing incidences of floods, landslides and frost heaving are in any case reducing the amount of productive land.
- The World Atlas of Desertification, 1997, shows overgrazing is responsible for 90 per cent of dryland degradation in Australia and 60 per cent in Africa. Deforestation has caused 40 per cent dryland degradation in South America and Europe and 30 per cent in Asia.
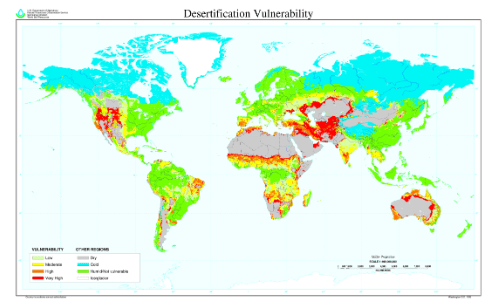
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 26th December 2019
SRC: U.S. Department of Agriculture map from 1998
“According to Desertification and Land Degradation of Selected Districts of India, an atlas published by the Indian Space Research Organisation’s Space Application Centre (SAC), Ahmedabad in 2018, some 96.40 million ha, or about 30 per cent of the country’s total area, is undergoing degradation”
- SAC mapped India’s 76 drought-prone districts and two sub-basins in Ladakh to prepare the atlas and found that in drylands, which span 228.3 million ha, or 70 per cent of the country’s total land, 82.64 million ha is under desertification.
- TERI’s conservative estimate shows land degradation costs $48.8 billion to the country’s exchequer annually.
- This is almost 2.08 per cent of India’s GDP in 2014-15 and over 13 per cent of gross value added from agriculture and forestry that year.
- The economic cost of forest degradation accounts for 55 per cent of the total loss. There has been a consistent increase in the area under water erosion, said the report.
State-wise plight:
- In Maharashtra, the timber mafia was eating into already thin forests, leading to soil erosion. More than a million trees were felled between 2005 and 2014, using permits issued by the state’s forest department every year. Another 0.26 million were cut illegally.
- Excessive mining in Jharkhand has triggered soil erosion and aggravated water scarcity in the state. Data with the Central Ground Water Board shows that water table in the entire block has lowered from 8 m below the ground level in 2013 to about 10 m in 2017.
- Rampant mining and expanding urbanisation has taken a toll on Goa. Lack of planning could, further, degrade land in the state.
- In Nagaland, shifting cultivation (where people slash trees and burn them to prepare the land for farming), deforestation and rising population are to blame for desertification. The rapidly vanishing vegetation cover has intensified soil erosion in the state.
- In Andhra Pradesh, low rainfall and increased dependence on borewells have led to soil aridity, while less snow and more rainfall has deepened the desertification crisis in Himachal Pradesh.
- Overgrazing and encroachment of grassland for agricultural activities have affected Gujarat.
- On the other hand, in Rajasthan, canals, tubewell irrigation and shelterbelts have led to an increase in the green cover.
Various schemes by the Government of India which are helping to reduce land degradation:
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- Soil Health Card Scheme
- Soil Health Management Scheme
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojna (PKSY)
- Per Drop More Crop
Launch of a flagship project on enhancing capacity on forest landscape restoration (FLR) and Bonn Challenge in India, through a pilot phase of 3.5 years implemented in the States of Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Nagaland and Karnataka. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) in partnership with The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), through this flagship project aims to develop and adapt best practices and monitoring protocols for the Indian states and build capacity within the five pilot states on FLR and Bonn Challenge. This will be eventually scaled up across the country through subsequent phases of the project.
Connecting the dots:
- Discuss the problem of desertification. Which parts of the world are suffering from this phenomenon?
POLITY
TOPIC: General Studies 2:
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
Three Capital of Andhra Pradesh : there was nothing wrong in having the capital at three places says CM
Context:
- Chief Minister Y.S. Jagan Mohan Reddy hinted in the Legislative Assembly recently that there was nothing wrong in having the capital at three places, similar to the South African model.
- He hinted that the High Court could be based in Kurnool, Amaravati could continue to be the Legislative capital and Visakhapatnam the Executive capital.
History of the formation of Andhra Pradesh State:
- The first reference of decentralisation was made in the Sri Bagh pact, which was signed by the then political leaders from Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema on November 16, 1937.
- According to the pact, for a balanced decentralisation, it was decided to continue with Andhra University in Visakhapatnam and the High Court and the capital be divided between the two regions.
- Visakhapatnam has all the settings to become a good living space. Even after Amaravati was carved out, most of the bureaucrats did not shift their families and they continued to stay in Hyderabad.
Sri Krishna panel:
- The advantages and qualities of Visakhapatnam to become the capital was discussed not only in the Sri Bagh pact but was also elaborately deliberated by the Sri Krishna Committee.
- The Sri Krishna Committee primarily took up three things for consideration — creation of single city or super city in Greenfield location, expanding existing cities and distributed development.
- The Committee however did not consider a single large capital city as a feasible option available to Andhra Pradesh as of then. But the State government had pushed the VGTM (Vijayawada, Guntur, Tenali, Mangalagiri) area for development.
- Visakhapatnam was in the radar, as it was felt that it has all the requirement.
Cosmopolitan:
- Rapid industrialisation, the presence of Eastern Naval Command and a number of public sector units, Visakhapatnam only city in the State that wears a cosmopolitan fabric.
- the presence of such culture lends peace and gives readymade quality manpower,
Decentralisation:
- Decentralisation was elaborately described in the Sri Bagh pact.
- The pact clearly defined decentralisation, for the benefit of all three main regions such as Coastal AP, Godavari and Krishna districts and Rayalaseema.
Land:
- There is about 10,000 acres of government land.
- Land is not an issue, as the requirement to set up a few new offices and quarters will not exceed 2,000 to 3,000 acres.
Conclusion:
- Decision is a win-win situation both for the government and the city
Connecting the dots:
- Do you think there is nothing wrong in 3 capitals ?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Saptamatrikas
- They are a group of seven female deities worshipped in Hinduism as personifying the energy of their respective consorts
- The earliest epigraphic evidence so far for the Saptamatrika cult was recently discovered in Haryana which is also the earliest Sanskrit inscription of North India
Which of the above statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Locust Invasion
- Locust invasions usually occurs in wet areas that receive more than 300 mm of rain annually
- India has only one locust breeding season- from July to October
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about Bharatnet Project
- It is being implemented by Prime Minister’s Office in collaboration with NITI Aayog
- It aims to connect all 2.5 lakh gram panchayats through optical fibre.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Consider the following statements about Atal Bhujal Yojana
- It aims to improve ground water management through community participation in all states & UT of India
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme whereby 70% of the project cost shall be through Central Assistance and the remaining 30% through State funding.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 25 DEC 2019 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | C |
| 5 | C |
MUST READ
Dangerous doublespeak: On government’s NPR-NRC talk
Double trouble: On uneven inflation and sluggish growth
Mind the gap: On gender gap
The right count
Towards jointness
A move to end coal imports, finally!
Indian research quality lags quantity
Indian agriculture is under an invisible emergency
















