UPSC Articles
Gender Inequality Index
Part of: GS Prelims and GS Mains II – Development
In News
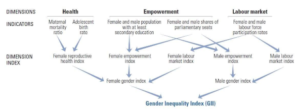
- The GII is an inequality indexreleased by UNDP. It measures gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development—
- reproductive Health, measured by maternal mortality ratio and adolescent birth rates;
- Empowerment, measured by proportion of parliamentary seats occupied by females and proportion of adult females and males aged 25 years and older with at least some secondary education; and
- Economic status, expressed as labour market participation and measured by labour force participation rate of female and male populations aged 15 years and older.
- The GII is built on the same framework as the IHDI—to better expose differences in the distribution of achievements between women and men.
- It measures the human development costs of gender inequality. Thus the higher the GII value the more disparities between females and males and the more loss to human development.
- In the Gender Inequality Index (GII), India is at 122 out of 162 countries. Neighbours China (39), Sri Lanka (86), Bhutan (99), Myanmar (106) were placed above India.
- The report forecasts that it may take 202 years to close the gender gap in economic opportunity
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 10th December 2019











