IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
This is a part of our recently launched, NEW INITIATIVE IASbaba’s INTEGRATED REVISION PLAN (IRP) 2020 – Road Map for the next 100 Days! FREE INITIATIVE!
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about the Initiative -> CLICK HERE
SCHEDULE/DETAILED PLAN – > CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
Consider the following statements:
- The Government of India launched the First National Protocol on Snow Leopard Population Assessment in 2019
- IUCN Red List Status of Common Leopard is Vulnerable
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Common Leopard (Panthera pardus)
- It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in small parts of Western and Central Asia, on the Indian subcontinent to Southeast and East Asia.
- The Indian leopard (Panthera pardus fusca) is a leopard widely distributed on the Indian subcontinent.
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching for the illegal trade of skins and body parts, and persecution due to conflict situations
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Key takeaways:
- A recent study by TRAFFIC India on the seizure and mortality of ‘common leopards’ (Panthera pardus fusca) revealed that of the total of 747 leopard deaths between 2015-2019 in India, 596 were linked to illegal wildlife trade and activities related to poaching.
- The Government of India launched the First National Protocol on Snow Leopard Population Assessment in 2019, to mark the occasion of International Snow Leopard Day (23rd October).
- In 2014, a national census of leopards around tiger habitats was carried out in India except for the northeast. 7,910 individuals were estimated in surveyed areas and a national total of 12,000-14,000 estimated.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Common Leopard (Panthera pardus)
- It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in small parts of Western and Central Asia, on the Indian subcontinent to Southeast and East Asia.
- The Indian leopard (Panthera pardus fusca) is a leopard widely distributed on the Indian subcontinent.
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching for the illegal trade of skins and body parts, and persecution due to conflict situations
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Key takeaways:
- A recent study by TRAFFIC India on the seizure and mortality of ‘common leopards’ (Panthera pardus fusca) revealed that of the total of 747 leopard deaths between 2015-2019 in India, 596 were linked to illegal wildlife trade and activities related to poaching.
- The Government of India launched the First National Protocol on Snow Leopard Population Assessment in 2019, to mark the occasion of International Snow Leopard Day (23rd October).
- In 2014, a national census of leopards around tiger habitats was carried out in India except for the northeast. 7,910 individuals were estimated in surveyed areas and a national total of 12,000-14,000 estimated.
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to AMRUT mission:
- It is under the Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs
- AMRUT is a centrally sponsored scheme
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) Mission is launched in June 2015
- Concerned Ministry: Housing and Urban Affairs
- AMRUT is aimed at transforming 500 cities and towns into efficient urban living spaces over a period of five years.
- AMRUT is a centrally sponsored scheme with 80% budgetary support from the Centre.
Purpose:
- To ensure that every household has access to a tap with the assured supply of water and a sewerage connection.
- The Priority zone of the Mission is water supply followed by sewerage.
- To increase the amenity value of cities by developing greenery and well maintained open spaces (e.g. parks).
- To reduce pollution by switching to public transport or constructing facilities for non-motorized transport (e.g. walking and cycling).
- AMRUT provides for basic civic amenities like water supply, sewerage, urban transport, parks as to improve the quality of life for all, especially the poor and the disadvantaged.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) Mission is launched in June 2015
- Concerned Ministry: Housing and Urban Affairs
- AMRUT is aimed at transforming 500 cities and towns into efficient urban living spaces over a period of five years.
- AMRUT is a centrally sponsored scheme with 80% budgetary support from the Centre.
Purpose:
- To ensure that every household has access to a tap with the assured supply of water and a sewerage connection.
- The Priority zone of the Mission is water supply followed by sewerage.
- To increase the amenity value of cities by developing greenery and well maintained open spaces (e.g. parks).
- To reduce pollution by switching to public transport or constructing facilities for non-motorized transport (e.g. walking and cycling).
- AMRUT provides for basic civic amenities like water supply, sewerage, urban transport, parks as to improve the quality of life for all, especially the poor and the disadvantaged.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
The term Aquaponics was recently in news it refers to which of the following?
Correct
Solution (b)
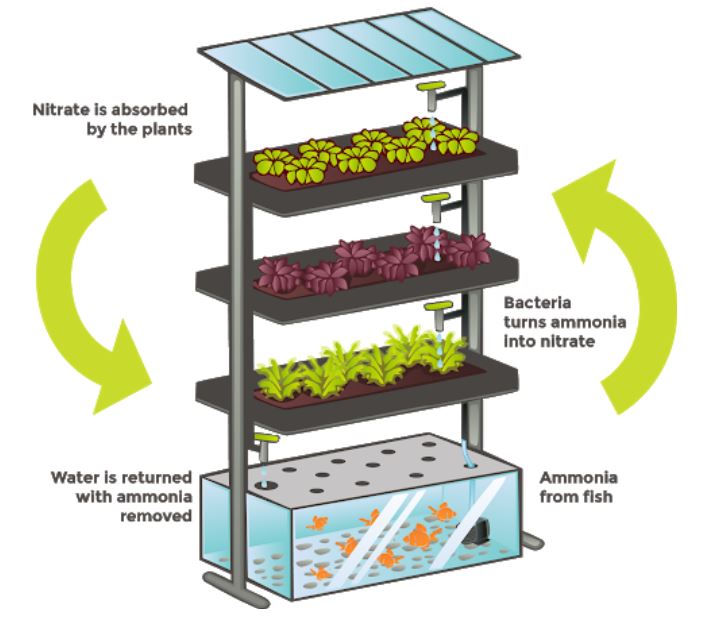
- Aquaponics is a system that combines hydroponics, soil-less agriculture, and aquaculture within a closed system.
- Hydroponics: It is a method of growing plants in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution.
- Hydroponics does not use soil, instead, the root system is supported using an inert medium such as clay pellets.
- The basic premise behind hydroponics is to allow the plant’s roots to come in direct contact with the nutrient solution, while also having access to oxygen, which is essential for proper growth.
- Aquaculture: Breeding, raising, and harvesting fish, and aquatic plants.
- There are three biological components in the aquaponics process: fish, plants, and bacteria (for cycling of nutrients- ammonia to nitrate conversion).
Process:
- With aquaponics, the farmer combines the aquaculture with hydroponic vegetables – the fish waste provides fertilizer for growing plants.
- The plants absorb nutrients and filter the water. This filtered water is used to replenish the fish tank. This is an environment friendly technique.
- The result is value-added, local production of both fish and vegetables together, using the same water.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Aquaponics is a system that combines hydroponics, soil-less agriculture, and aquaculture within a closed system.
- Hydroponics: It is a method of growing plants in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution.
- Hydroponics does not use soil, instead, the root system is supported using an inert medium such as clay pellets.
- The basic premise behind hydroponics is to allow the plant’s roots to come in direct contact with the nutrient solution, while also having access to oxygen, which is essential for proper growth.
- Aquaculture: Breeding, raising, and harvesting fish, and aquatic plants.
- There are three biological components in the aquaponics process: fish, plants, and bacteria (for cycling of nutrients- ammonia to nitrate conversion).
Process:
- With aquaponics, the farmer combines the aquaculture with hydroponic vegetables – the fish waste provides fertilizer for growing plants.
- The plants absorb nutrients and filter the water. This filtered water is used to replenish the fish tank. This is an environment friendly technique.
- The result is value-added, local production of both fish and vegetables together, using the same water.

-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Program for International Student Assessment:
- It is an international assessment that measures 15-year-old students’ reading, mathematics, and science literacy every three years.
- PISA was introduced in 2000 by the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
- Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) is an international assessment that measures 15-year-old students’ reading, mathematics, and science literacy every three years.
- First conducted in 2000, the major domain of study rotates between reading, mathematics, and science in each cycle.
- PISA also includes measures of general or cross-curricular competencies, such as collaborative problem solving.
- PISA was introduced in 2000 by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- PISA is coordinated by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), an intergovernmental organization of industrialized countries, and is conducted in the United States by NCES.
- India stayed away from PISA in 2012 and 2015 on account of its dismal performance in 2009, when it was placed 72nd among the 74 participating countries. The government decided to end the boycott in 2019.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) is an international assessment that measures 15-year-old students’ reading, mathematics, and science literacy every three years.
- First conducted in 2000, the major domain of study rotates between reading, mathematics, and science in each cycle.
- PISA also includes measures of general or cross-curricular competencies, such as collaborative problem solving.
- PISA was introduced in 2000 by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- PISA is coordinated by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), an intergovernmental organization of industrialized countries, and is conducted in the United States by NCES.
- India stayed away from PISA in 2012 and 2015 on account of its dismal performance in 2009, when it was placed 72nd among the 74 participating countries. The government decided to end the boycott in 2019.
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
Consider the following statements:
- India is presently serving as member in the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC)
- The members of United Nations Human Rights Council are elected for a period of ten years, with a maximum of two consecutive terms.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC)
- It was established in 2006.
- Headquarter: Geneva, Switzerland
- Aim: Promoting and protecting human rights around the globe, as well as investigating alleged human rights violations.
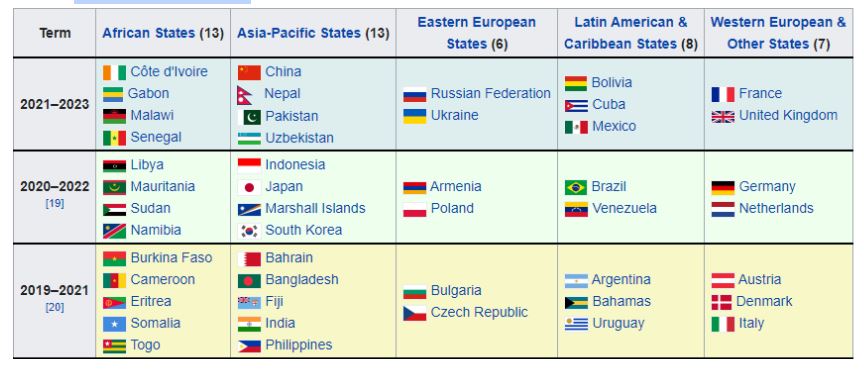
- Features: The UNHRC has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis from 5 groups.
- Membership: To become a member, a country must receive the votes of at least 96 of the 191 states of the UN General Assembly (an absolute majority).
- According to Resolution 60/251, which created the council, members are elected directly by secret ballot by the majority of the UN General Assembly. Membership has to be equally distributed geographically.
- Five regional groups for membership: Africa, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, Western Europe and Eastern Europe.
- The members are elected for a period of three years, with a maximum of two consecutive terms.
- Sessions: The UNHRC holds regular sessions three times a year, in March, June, and September.
- The council also carries out the Universal Periodic Review of all UN member states, which allows civil society groups to bring accusations of human rights violations in member states to the attention of the UN.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (a)
United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC)
- It was established in 2006.
- Headquarter: Geneva, Switzerland
- Aim: Promoting and protecting human rights around the globe, as well as investigating alleged human rights violations.
- Features: The UNHRC has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis from 5 groups.
- Membership: To become a member, a country must receive the votes of at least 96 of the 191 states of the UN General Assembly (an absolute majority).
- According to Resolution 60/251, which created the council, members are elected directly by secret ballot by the majority of the UN General Assembly. Membership has to be equally distributed geographically.
- Five regional groups for membership: Africa, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, Western Europe and Eastern Europe.
- The members are elected for a period of three years, with a maximum of two consecutive terms.
- Sessions: The UNHRC holds regular sessions three times a year, in March, June, and September.
- The council also carries out the Universal Periodic Review of all UN member states, which allows civil society groups to bring accusations of human rights violations in member states to the attention of the UN.













