IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
This is a part of our recently launched, NEW INITIATIVE IASbaba’s INTEGRATED REVISION PLAN (IRP) 2020 – Road Map for the next 100 Days! FREE INITIATIVE!
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about the Initiative -> CLICK HERE
SCHEDULE/DETAILED PLAN – > CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to National Nutrition Mission:
- The progress report on National Nutrition Mission is released by Ministry of Health
- Its aim is to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anemia and low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- National Nutrition Mission launched in 2018, it is the Government of India’s flagship programme to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- It is backed by a National Nutrition Strategy prepared by the NITI Aayog with the goal of attaining “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat” or malnutrition-free India, by 2022.
- Aims:
- To reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively.
- To address the problem of malnutrition in a mission-mode.
- 50% of the total budget comes from the World Bank or other multilateral development banks and the rest of the 50% is through Centre’s budgetary support.
-
- The Centre’s budgetary support is further divided into 60:40 between the Centre and the States, 90:10 for the north-eastern region and the Himalayan States and 100% for the Union Territories (UTs) without legislature.
- NITI Aayog recently released “Accelerating Progress on nutrition in India: What Will It Take”, the third progress report on the National Nutrition Mission or the Poshan Abhiyaan.
- The third progress report (October 2019-April 2020) takes stock of the roll-out status on the ground and implementation challenges encountered at various levels through large scale datasets.
- The initial Reports I and II, focused majorly on the mission’s preparedness and implementation by States and UTs, respectively.
- The review report was drafted in March 2020 and does not factor worsening poverty and hunger levels since then, which are expected to have gone down further due to the Covid-19.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- National Nutrition Mission launched in 2018, it is the Government of India’s flagship programme to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- It is backed by a National Nutrition Strategy prepared by the NITI Aayog with the goal of attaining “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat” or malnutrition-free India, by 2022.
- Aims:
- To reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively.
- To address the problem of malnutrition in a mission-mode.
- 50% of the total budget comes from the World Bank or other multilateral development banks and the rest of the 50% is through Centre’s budgetary support.
-
- The Centre’s budgetary support is further divided into 60:40 between the Centre and the States, 90:10 for the north-eastern region and the Himalayan States and 100% for the Union Territories (UTs) without legislature.
- NITI Aayog recently released “Accelerating Progress on nutrition in India: What Will It Take”, the third progress report on the National Nutrition Mission or the Poshan Abhiyaan.
- The third progress report (October 2019-April 2020) takes stock of the roll-out status on the ground and implementation challenges encountered at various levels through large scale datasets.
- The initial Reports I and II, focused majorly on the mission’s preparedness and implementation by States and UTs, respectively.
- The review report was drafted in March 2020 and does not factor worsening poverty and hunger levels since then, which are expected to have gone down further due to the Covid-19.
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Chang’e-5 mission was recently launched to bring back lunar rocks, the first attempt by any nation to retrieve samples from the Moon by which of the following country?
Correct
Solution (c)
- China has launched an unmanned spacecraft to bring back lunar rocks, the first attempt by any nation to retrieve samples from the Moon in four decades.
- Upon entering the moon’s orbit, the spacecraft is intended to deploy a pair of vehicles to the lunar surface, a lander and an ascender.
- A lander will drill into the ground, then transfer its soil and rock samples to an ascender that will lift off and dock with an orbiting module.
- There will be an attempt to collect 2 kg of samples in a previously unvisited area in a massive lava plain known as Oceanus Procellarum, or “Ocean of Storms”.
- Area of the moon where the spacecraft is due to land is 1-2 billion years old.
- If this is successful, the samples will be transferred to a return capsule that will return them to Earth, with a landing in China’s Inner Mongolia region.
- The entire mission is scheduled to take around 23 days.
- If the mission is completed as planned, it would make China only the third country to have retrieved lunar samples, joining the United States and the Soviet Union.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- China has launched an unmanned spacecraft to bring back lunar rocks, the first attempt by any nation to retrieve samples from the Moon in four decades.
- Upon entering the moon’s orbit, the spacecraft is intended to deploy a pair of vehicles to the lunar surface, a lander and an ascender.
- A lander will drill into the ground, then transfer its soil and rock samples to an ascender that will lift off and dock with an orbiting module.
- There will be an attempt to collect 2 kg of samples in a previously unvisited area in a massive lava plain known as Oceanus Procellarum, or “Ocean of Storms”.
- Area of the moon where the spacecraft is due to land is 1-2 billion years old.
- If this is successful, the samples will be transferred to a return capsule that will return them to Earth, with a landing in China’s Inner Mongolia region.
- The entire mission is scheduled to take around 23 days.
- If the mission is completed as planned, it would make China only the third country to have retrieved lunar samples, joining the United States and the Soviet Union.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Consider the following statements:
- The IMO is the United Nations specialised agency responsible for the safety and security of shipping.
- India has become the second country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system recognised by the IMO.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
- The Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) of the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) has recognised the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) as a component of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) during its 102nd session held virtually.
- The IMO is the United Nations specialised agency responsible for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine and atmospheric pollution by ships.
- India has become the fourth country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system recognised by the IMO as a part of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS).
- The other three countries that have its navigation systems recognised by the IMO are the USA, Russia and China.
- The IMO has accepted IRNSS as an alternative navigation module in Indian waters. It was in use only on a pilot basis earlier but now all merchant vessels are authorised to use it, even small fishing vessels.
- The navigation system can now replace GPS in the Indian Ocean waters upto 1500 km from the Indian boundary.
- IRNSS is a regional and not a global navigation system.
- With the recognition as a component of the WWRNS, the Indian navigation system is similarly placed as Global Positioning System (GPS – USA), most commonly used by marine shipping vessels across the world or the Russian Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS).
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- The Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) of the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) has recognised the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) as a component of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) during its 102nd session held virtually.
- The IMO is the United Nations specialised agency responsible for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine and atmospheric pollution by ships.
- India has become the fourth country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system recognised by the IMO as a part of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS).
- The other three countries that have its navigation systems recognised by the IMO are the USA, Russia and China.
- The IMO has accepted IRNSS as an alternative navigation module in Indian waters. It was in use only on a pilot basis earlier but now all merchant vessels are authorised to use it, even small fishing vessels.
- The navigation system can now replace GPS in the Indian Ocean waters upto 1500 km from the Indian boundary.
- IRNSS is a regional and not a global navigation system.
- With the recognition as a component of the WWRNS, the Indian navigation system is similarly placed as Global Positioning System (GPS – USA), most commonly used by marine shipping vessels across the world or the Russian Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS).
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to BrahMos supersonic cruise missile:
- It is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile which can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft or land.
- It is the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- The range of the land-attack version of the BrahMos missile has been extended to 400 km from the original 290 km but its speed has been maintained at 2.8 Mach or almost three times the speed of sound.
- The test was done in a “top-attack” configuration.
- In top attack mode, the missile is required to climb sharply after launch, travel at a certain altitude and then fall on top of the target.
- An amalgamation of the names of Brahmaputra river and Moskva river (Russia), BrahMos missiles are designed, developed and produced by BrahMos Aerospace. BrahMos Aerospace is a joint venture company set up by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Mashinostroyenia of Russia.
- It is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile which can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft or land.
- Cruise missiles are defined as “an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target.”
- It is the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile, as well as the fastest anti-ship cruise missile in operation.
- It operates on the “Fire and Forget” principle, i.e it does not require further guidance after launch.
- The missile has a flight range upto 290-km. However, India’s entry into the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) has extended the range of the BrahMos missile to reach 450-600 km.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- The range of the land-attack version of the BrahMos missile has been extended to 400 km from the original 290 km but its speed has been maintained at 2.8 Mach or almost three times the speed of sound.
- The test was done in a “top-attack” configuration.
- In top attack mode, the missile is required to climb sharply after launch, travel at a certain altitude and then fall on top of the target.
- An amalgamation of the names of Brahmaputra river and Moskva river (Russia), BrahMos missiles are designed, developed and produced by BrahMos Aerospace. BrahMos Aerospace is a joint venture company set up by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Mashinostroyenia of Russia.
- It is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile which can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft or land.
- Cruise missiles are defined as “an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target.”
- It is the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile, as well as the fastest anti-ship cruise missile in operation.
- It operates on the “Fire and Forget” principle, i.e it does not require further guidance after launch.
- The missile has a flight range upto 290-km. However, India’s entry into the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) has extended the range of the BrahMos missile to reach 450-600 km.
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
Katchal Island was recently in news, is located in which of the following country?
Correct
Solution (c)
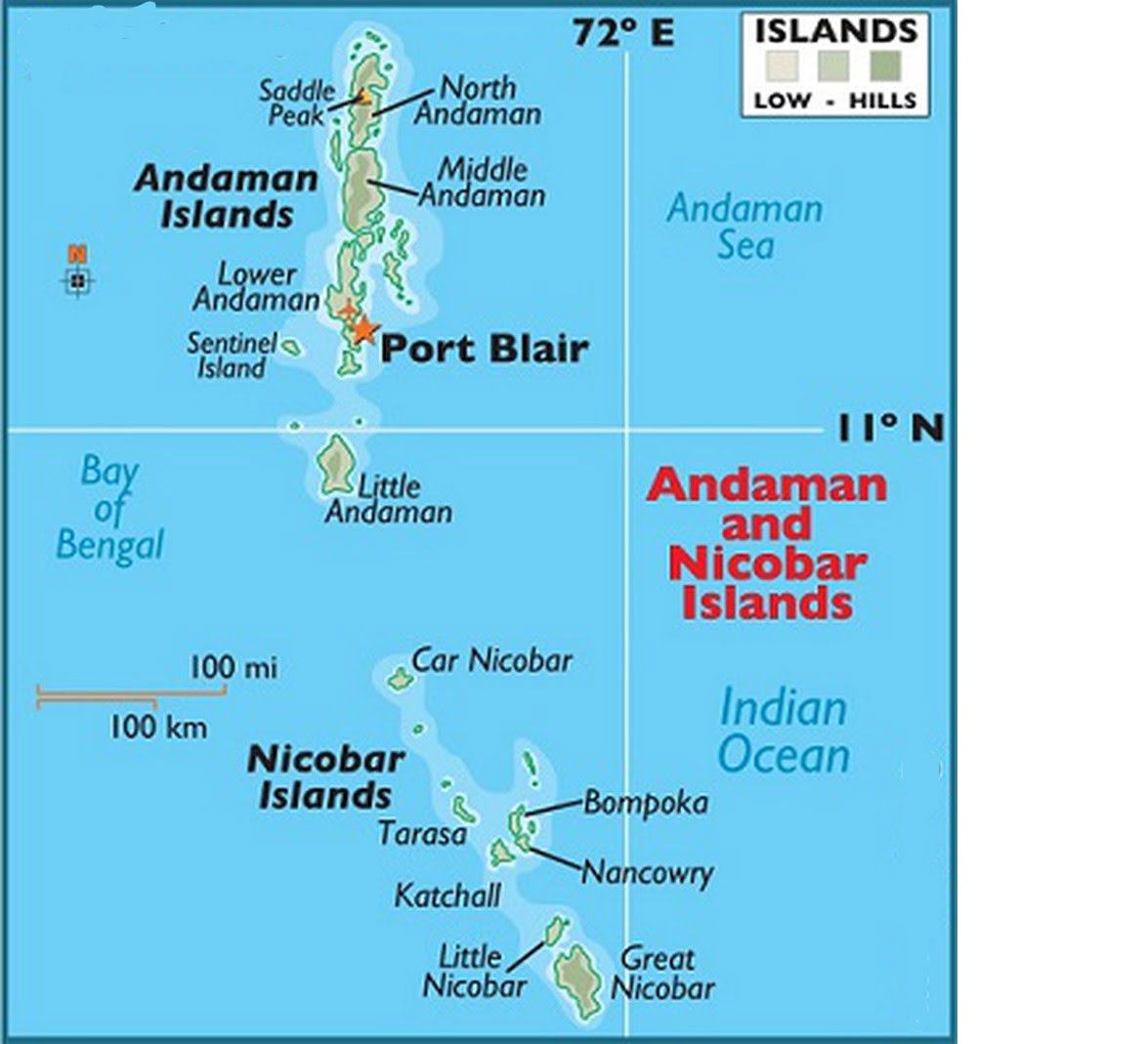 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (c)












