IASbaba Daily Prelims Quiz
For Previous Daily Quiz (ARCHIVES) – CLICK HERE
The Current Affairs questions are based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, which are very important sources for UPSC Prelims Exam. The questions are focused on both the concepts and facts. The topics covered here are generally different from what is being covered under ‘Daily Current Affairs/Daily News Analysis (DNA) and Daily Static Quiz’ to avoid duplication. The questions would be published from Monday to Saturday before 2 PM. One should not spend more than 10 minutes on this initiative.
This is a part of our recently launched, NEW INITIATIVE IASbaba’s INTEGRATED REVISION PLAN (IRP) 2020 – Road Map for the next 100 Days! FREE INITIATIVE!
We will make sure, in the next 4 months not a single day is wasted. All your energies are channelized in the right direction. Trust us! This will make a huge difference in your results this time, provided that you follow this plan sincerely every day without fail.
Gear up and Make the Best Use of this initiative.
Do remember that, “the difference between Ordinary and EXTRA-Ordinary is PRACTICE!!”
To Know More about the Initiative -> CLICK HERE
SCHEDULE/DETAILED PLAN – > CLICK HERE
Important Note:
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- After completing the 5 questions, click on ‘View Questions’ to check your score, time taken and solutions.
Test-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
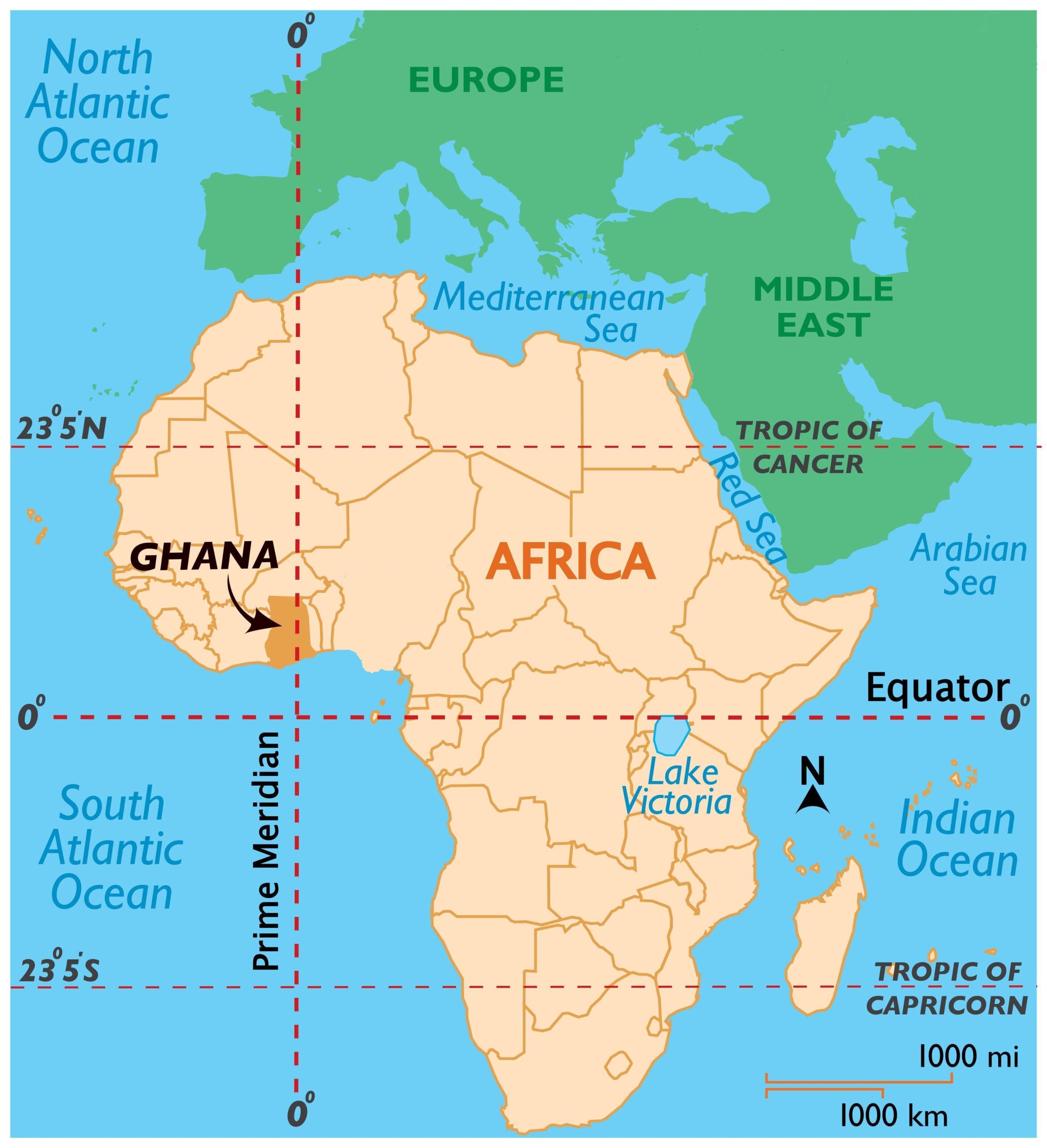
Consider the following statements with respect to Ghana:
- It is the only country in the world in which both prime meridian and equator intersects.
- Lake Victoria is the major lake of this country.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (d)

-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Transfer of judges from one High Court to any other High Court is provided under Article 222 of the Constitution
- The power of transferring High court judges lies only in the hands of CJI.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Procedure of transfer of HC judge:
- Article 222 of the Constitution makes provision for the transfer of a Judge (including Chief Justice) from one High Court to any other High Court.
- The initiation of the proposal for the transfer of a Judge should be made by the Chief Justice of India(CJI).
- The opinion of the CJI “is determinative”.
- Consent of the Judge for his first or subsequent transfer would not be required.
- CJI is expected to take into account the views of the Chief Justice of the High Court from which the Judge is to be transferred and Chief Justice of the High Court to which the transfer is to be effected.
- The views of one or more Supreme Court Judges who are in a position to offer his/their views are also taken into account.
- In the case of transfer of a Chief Justice, only the views of one or more knowledgeable Supreme Court Judges need to be taken into account.
- The views on the proposed transfer of a Judge or a Chief Justice of the High Court should be expressed in writing and should be considered by the CJI and the four senior most Judges of the Supreme Court.
- The proposal once referred to the Government, the Union Minister of Law, Justice and Company Affairs would submit a recommendation to the Prime Minister who will then advise the President as to the transfer of the Judge concerned.
- After the President approves the transfer, the notification will be gazetted and the judge remains transferred.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Procedure of transfer of HC judge:
- Article 222 of the Constitution makes provision for the transfer of a Judge (including Chief Justice) from one High Court to any other High Court.
- The initiation of the proposal for the transfer of a Judge should be made by the Chief Justice of India(CJI).
- The opinion of the CJI “is determinative”.
- Consent of the Judge for his first or subsequent transfer would not be required.
- CJI is expected to take into account the views of the Chief Justice of the High Court from which the Judge is to be transferred and Chief Justice of the High Court to which the transfer is to be effected.
- The views of one or more Supreme Court Judges who are in a position to offer his/their views are also taken into account.
- In the case of transfer of a Chief Justice, only the views of one or more knowledgeable Supreme Court Judges need to be taken into account.
- The views on the proposed transfer of a Judge or a Chief Justice of the High Court should be expressed in writing and should be considered by the CJI and the four senior most Judges of the Supreme Court.
- The proposal once referred to the Government, the Union Minister of Law, Justice and Company Affairs would submit a recommendation to the Prime Minister who will then advise the President as to the transfer of the Judge concerned.
- After the President approves the transfer, the notification will be gazetted and the judge remains transferred.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to Gaur:
- It has been categorised as ‘Vulnerable’ in the IUCN status.
- It is endemic to only India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
- In news: An Indian Bison, or Gaur, in Pune’s urban landscape died due to human-animal conflict.
- It is mainly found in South and Southeast Asia.
- In India, the Gaur is mainly found in Western Ghats, the forests of central India and forest patches in the Northeast.
- It has been listed as ‘Vulnerable’ since 1986 on the Red List of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- It is listed in Appendix I of the CITES.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
- In news: An Indian Bison, or Gaur, in Pune’s urban landscape died due to human-animal conflict.
- It is mainly found in South and Southeast Asia.
- In India, the Gaur is mainly found in Western Ghats, the forests of central India and forest patches in the Northeast.
- It has been listed as ‘Vulnerable’ since 1986 on the Red List of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- It is listed in Appendix I of the CITES.
-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
Kerala state was recently in news because of pink phenomenon which was caused by Cabomba plant. Which of the statements given below is/are correct with regard to this plant?
- It is an invasive species that belongs to Central and South America.
- It requires a huge amount of oxygen to grow and that could badly affect freshwater biodiversity.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Correct
Solution (d)
- In news: In Avalapandi, a village in Kerala, an aquatic plant forked fanwort has painted the water bodies pink, which led to the ‘pink phenomenon’.
- Cabomba is a submerged perennial aquatic plant that grows in stagnant to slow-flowing freshwater.
- This plant comes from the family of Red Cabomba (Cabomba furcata).
- It is an invasive species that belongs to Central and South America.
- It requires a huge amount of oxygen to grow and that could badly affect freshwater biodiversity.
- It has a high natural dispersal potential due to its ability to readily fragment and spread.
Invasive Species
- Invasive alien species are any biological species that are introduced outside their natural range.
- They would negatively impact the native biodiversity, ecosystem function, health and human welfare.
- They could reproduce rapidly and out-compete the native species for food, water and space.
- They are the second-biggest cause for biodiversity loss, next to habitat destruction.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
- In news: In Avalapandi, a village in Kerala, an aquatic plant forked fanwort has painted the water bodies pink, which led to the ‘pink phenomenon’.
- Cabomba is a submerged perennial aquatic plant that grows in stagnant to slow-flowing freshwater.
- This plant comes from the family of Red Cabomba (Cabomba furcata).
- It is an invasive species that belongs to Central and South America.
- It requires a huge amount of oxygen to grow and that could badly affect freshwater biodiversity.
- It has a high natural dispersal potential due to its ability to readily fragment and spread.
Invasive Species
- Invasive alien species are any biological species that are introduced outside their natural range.
- They would negatively impact the native biodiversity, ecosystem function, health and human welfare.
- They could reproduce rapidly and out-compete the native species for food, water and space.
- They are the second-biggest cause for biodiversity loss, next to habitat destruction.
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
If the animal is protected under the Schedule II of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, it says which of the following?
Correct
Solution (c)
Salient Features of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- The Act provides for the protection of a listed species of animals, birds, and plants, and also for the establishment of a network of ecologically-important protected areas in the country.
- The Act provides for the formation of wildlife advisory boards, wildlife wardens, specifies their powers and duties, etc.
- The Act prohibited the hunting of endangered species.
- The Act provides for licenses for the sale, transfer, and possession of some wildlife species.
- Its provisions paved the way for the formation of the Central Zoo Authority. This is the central body responsible for the oversight of zoos in India.
- The Act created six schedules which gave varying degrees of protection to classes of flora and fauna.
- Schedule I and Schedule II (Part II) get absolute protection, and offences under these schedules attract the maximum penalties.
- The schedules also include species that may be hunted.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Salient Features of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- The Act provides for the protection of a listed species of animals, birds, and plants, and also for the establishment of a network of ecologically-important protected areas in the country.
- The Act provides for the formation of wildlife advisory boards, wildlife wardens, specifies their powers and duties, etc.
- The Act prohibited the hunting of endangered species.
- The Act provides for licenses for the sale, transfer, and possession of some wildlife species.
- Its provisions paved the way for the formation of the Central Zoo Authority. This is the central body responsible for the oversight of zoos in India.
- The Act created six schedules which gave varying degrees of protection to classes of flora and fauna.
- Schedule I and Schedule II (Part II) get absolute protection, and offences under these schedules attract the maximum penalties.
- The schedules also include species that may be hunted.











