UPSC Articles
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-3: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers,
LIDAR
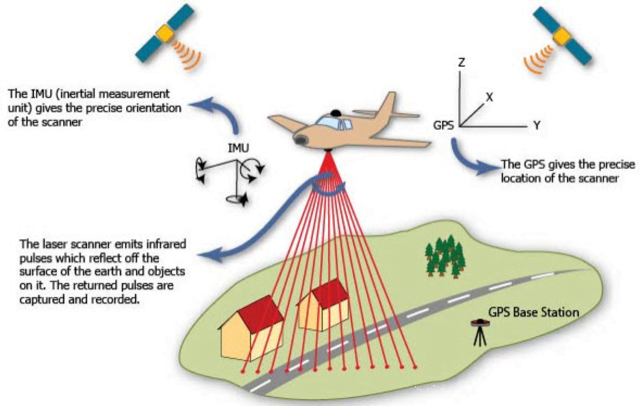
Light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges to the Earth.
- LiDAR uses a pulsed laser to calculate an object’s variable distances from the earth surface.
- LiDAR follows a simple principle — throw laser light at an object on the earth surface and calculate the time it takes to return to the LiDAR source. Given the speed at which the light travels (approximately 186,000 miles per second), the process of measuring the exact distance through LiDAR appears to be incredibly fast.
- These light pulses — put together with the information collected by the airborne system — generate accurate 3D information about the earth surface and the target object.
- There are three primary components of a LiDAR instrument — the scanner, laser and GPS receiver. Other elements that play a vital role in the data collection and analysis are the photodetector and optics.
- Two Types: Airborne LiDAR installed on a helicopter or drone for collecting data and Terrestrial LiDAR systems installed on moving vehicles or tripods on the earth surface for collecting accurate data points.
Applications of LiDAR
- Oceanography: LiDAR technology is used to map the land and is used to measure seafloor and riverbed elevations. LiDAR is also used for calculating phytoplankton fluorescence and biomass in the ocean surface, which otherwise is very challenging.
- Digital Elevation or Terrain Model: Terrain elevations play a crucial role during the construction of roads, large buildings and bridges. LiDAR technology has x, y and z coordinates, which makes it incredibly easy to produce the 3D representation of elevations to ensure that concerned parties can draw necessary conclusions more easily.
- Agriculture: Typical applications of LiDAR technology in the agriculture sector include analysis of yield rates, crop scouting and seed dispersions. Besides this, it is also used for campaign planning, mapping under the forest canopy, and more.
- Security: LiDAR is used by military for carrying out various security operations near the national borders.
- Rescue Missions: When the authorities want to know the exact depth of the ocean’s surface to locate any object in the case of a maritime accident or for research purposes, they use LiDAR technology to accomplish their mission
Advantages of using LiDAR
- Data can be collected quickly and with high accuracy: LiDAR is an airborne sensing technology which makes data collection fast and comes with extremely high accuracy as a result of the positional advantage.
- Surface Data has a higher sample density: LiDAR gives a much higher surface density compared to other methods of data collection such as photogrammetry. This improves results for some kinds of applications such as flood plain delineation.
- Capable of collecting elevation data in a dense forest: LiDAR technology is capable of collecting elevation data from a densely populated forest thanks to the high penetrative abilities. This means it can map even the densely forested areas.
- Can be used day and night: LiDAR technology can be used day and night thanks to the active illumination sensor. It is not affected by light variations such as darkness and light. This improves its efficiency.
- It is not affected by extreme weather: LiDAR technology is independent of extreme weather conditions such as extreme sunlight and other weather scenarios. This means that data can still be collected under these conditions and sent for analysis.
- Does not have any geometry distortions
- It can be integrated with other data sources
- It has minimum human dependence
- Surface data has a higher sample density
- Can be used to map inaccessible and featureless areas
Disadvantages of LiDAR
- High operating costs in some applications
- Ineffective during heavy rain or low hanging clouds because of the effects of refraction. However, the data collected can still be used for analysis.
- Degraded at high sun angles and reflections
- Unreliable for turbulent breaking waves as it will affect the reflection of pulses
- No International protocols
- Very large data sets which are difficult to interpret.
- The laser beams may affect human eye in cases where the beam is powerful
- Requires skilled data analysis techniques
- Low operating altitude of between 500-2000m











