UPSC Articles
Children and Digital Dumpsites Report released by WHO
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – E-waste
In news
- The World Health Organization (WHO) in its recent report “Children and Digital Dumpsites” has highlighted the risk that children working in informal processing are facing due to discarded electronic devices or e-waste.
- It is the first ever WHO report on electronic waste and child health.
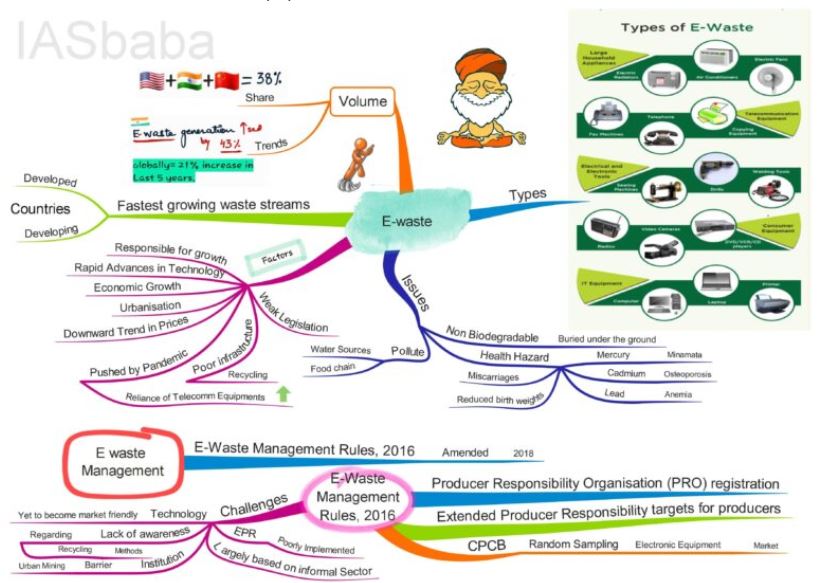
- E waste refers to old, end-of-life or discarded electronic items and their parts.
Key highlights of the report
- Around 12.9 million women are working in informal waste sector exposing them to toxic e-waste (like Nickel, lead and Mercury) and put them and their unborn children at risk.
- Children exposed to e waste are particularly vulnerable to the toxic chemicals they contain due to their smaller size, less developed organs and rapid rate of growth and Development.
Suggestions
- Environmentally sound disposal of e-waste and safety of workers.
- Monitor e waste exposure and health outcomes.
- Facilitate better use of e waste
Do you know?
- According to UN Global e waste monitor 2020 53.6 million metric tonnes of e waste was generated worldwide in 2009.
- Out of this, only 17.4% of e waste was collected and recycled.
- India is the third largest electronic waste generator after China and USA.
- In 2016 India enacted E waste (Management) Rules under which e Waste is categorised under two broad categories: Information technology and Telecommunications equipment and consumer electrical and electronic.
Pic courtesy: Iasbaba











