UPSC Articles
Russia’s gamble with Gas Supplies
Context: Russian energy company Gazprom has stopped gas supplies to Bulgaria and Poland citing their failure to pay in roubles.
- Poland and Bulgaria have accused Russia of breach of contract, according to which payments were to be made in euros and dollars only.
- Towards the end of March, Russian President Vladimir Putin had signed a decree that from April 1, “unfriendly foreign buyers” would have to pay for gas supplies in roubles. He had also added that defaults would result in the suspension of contracts.
How will the stoppage of gas supplies affect Poland and Bulgaria?
- The gas cuts do not immediately put the two countries in any dire trouble.
- Russian gas deliveries to both Poland and Bulgaria were anyway expected to end later this year.
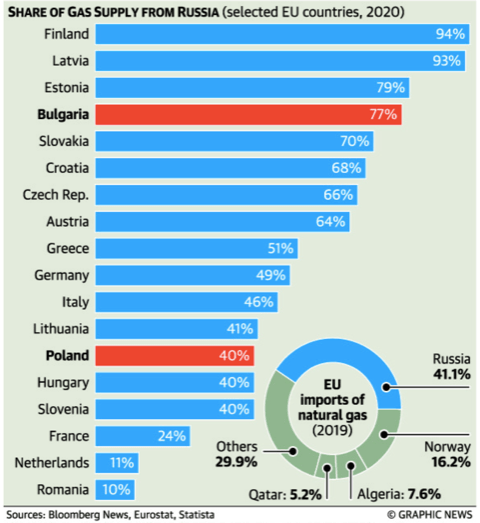
- Poland, which gets 40% of its natural gas from Russia, has been working on alternatives for many years.
- In the immediate scenario, however, it will lose out on the five billion cubic metres of gas it was set to get from Gazprom(Russia). It will likely make up for it with supplies from Germany.
- Bulgaria, which gets 77% of its natural gas from Russia, has a bigger problem. While it is said that the country has enough reserves for another month, it needs to urgently look for alternatives, with additional supplies via pipelines from Greece being a distinct possibility.
Why has Russia targeted Poland and Bulgaria with this move?
- Poland has been a major gateway for supply of military hardware to Ukraine. It also confirmed recently that it will be sending tanks to Ukraine.
- Just hours before Gazprom’s action, it had announced a fresh set of sanctions against the company and other Russian businesses and oligarchs.
- As for Bulgaria, after a new liberal government took office last year, it has cut many of its old ties to Russia. Not only has it supported the West’s sanctions against Russia, it has also hosted Western fighter jets at a new NATO outpost on its Black Sea coast.
- Bulgaria is also a major producer of non-NATO weapons that it’s considering sending to Ukraine.
Will other countries be hit with similar stoppages?
- Russia supplies gas via pipelines to 23 countries in Europe.
- Among EU members, so far, only Hungary has officially agreed to make rouble payments, with the rest rejecting the demand.
- However, even if no other country agrees to Russia’s rouble payment mechanism, there won’t be any further cuts in supplies at least until the second half of May, which is when the next tranche of payments are due.
- Meanwhile, four European buyers have already started making gas payments in roubles, while 10 European companies have opened accounts with Gazprombank to make rouble payments.
How have the EU, Poland, and Bulgaria reacted to the gas supply suspension?
- The 27-member European Union has described Russia’s decision as “blackmail” and accused Moscow of trying to divide the West over its support for Ukraine.
What could happen if Russia shuts gas supplies to more countries?
- Europe’s natural gas comes from only three sources:
- Russia
- Norway
- Algeria
- Until the Ukraine invasion, Russia accounted for almost 40% of Europe’s gas imports.
- While the dependence on Russian gas varies from country to country — ranging from 94% for Finland to 11% for the Netherlands — there is little doubt that disruption in supplies would fuel inflation and damage economic activity, with strong possibilities of energy rationing and even a major recession in the continent’s industrial powerhouse, Germany.
What has been the EU’s strategy to reduce dependence on Russian gas?
- Europe’s energy mix comprises of oil (43%), natural gas (24%), nuclear energy (14%), and hydroelectric (4%), with renewables such as wind and solar making up the rest.
- With climate change a major political issue in Europe, coal — of which there are abundant reserves on the continent — is off the table, and given public hostility to nuclear energy, EU is left with natural gas as the cleanest source of energy.
- So, for the short-term, the EU is preparing for the heating requirements of the coming winter by tanking up on its gas storage facilities at 80-90% capacity and substituting Russian supplies, as much as possible, with piped gas from Norway and North Africa.
- But these won’t be adequate to reduce Russian dependence to zero.
- So, the longer-term strategy is centred on importing liquefied natural gas (LNG) from the U.S. and the Middle East.
Will it be feasible for Europe to transition from Russian natural gas to LNG?
- It will be tough challenge, primarily because it is easier and cheaper to transport natural gas via pipeline.
- LNG requires massive facilities and container ships that require huge capital investments. And yet, over the past decade, the EU has beefed up its LNG infrastructure, building several large terminals.
- Nonetheless, LNG transported from the U.S. by container ships would be much more expensive than Russian gas received via pipeline.
- Achieving strategic autonomy, as it were, by replacing Russian gas with American LNG would mean higher prices for the average European consumer, who is currently the primary beneficiary of cheap Russian gas.
How will the gas suspension impact Russia?
- Western analysts believe that Russia has taken a gamble by cutting off supplies to Poland and Bulgaria.
- The Russian economy is heavily dependent on gas exports, deriving 40% of its revenue coming from it.
- If the move forces more EU countries to pay for gas in roubles, it will help shore up its currency and offer some relief for its sanction-hit economy.
- But at the same time, it could also backfire, if it ends up accelerating the decoupling of the energy ‘partnership’ between Europe and Russia.
- Since it is difficult to reroute piped natural gas to different markets, Russia, which doesn’t have elaborate storage infrastructure, may well find itself desperate for buyers.
Connecting the dots:











