IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan, Rapid Revision Series (RaRe)
Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
1. Daily RaRe Series (RRS) Videos on High Probable Topics (Monday – Saturday)
- In video discussions, special focus is given to topics which have high probability to appear in UPSC Prelims Question Paper.
- Each session will be of 20 mins to 30 mins, which would cover rapid revision of 15 high probable topics (both static and current affairs) important for Prelims Exam this year according to the schedule.
Note – The Videos will be available only in English.
2. Rapid Revision (RaRe) Notes
- Right material plays important role in clearing the exam and Rapid Revision (RaRe) Notes will have Prelims specific subject-wise refined notes.
- The main objective is to help students revise most important topics and that too within a very short limited time frame.
Note – PDFs of Daily Tests & Solution and ‘Daily Notes’ will be updated in PDF Format which are downloadable in both English & हिंदी.
3. Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule and in the RaRe videos.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
4. Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
5. Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Saturday)
- CSAT has been an achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 5 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (30 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis in Both English and हिंदी.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
Download 60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
Download 60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Notes & Solutions DAY 46– CLICK HERE
Note –
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
Important Note
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2022 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Import Substitution:
- Import Substitution seeks to eliminate the import of the commodity and allows for its production in the domestic market.
- The Import Substitution Industrialization strategy in India was based on the model of growth as propounded by Mahalanobis.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Import Substitution (IS) generally refers to a policy that eliminates the importation of the commodity and allows for the production in the domestic market.
The policy of import substitution is achieved through discrimination of capital goods against consumer goods by tariffs, quotas, exchange control barriers, exchange rate policies, and fiscal and credit policies.
India adopted the strategy of import substitution industrialization strategy in the fifties. From the Second Five Year Plan, there was determined thrust towards the substitution of basic and capital goods industries. The ISI strategy was based on the model of growth as propounded by Mahalanobis.
The State was to play an active role in building a self-reliant economy, discriminating structure of protection was evolved to acquire foreign technology and for policies towards foreign investment.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Import Substitution (IS) generally refers to a policy that eliminates the importation of the commodity and allows for the production in the domestic market.
The policy of import substitution is achieved through discrimination of capital goods against consumer goods by tariffs, quotas, exchange control barriers, exchange rate policies, and fiscal and credit policies.
India adopted the strategy of import substitution industrialization strategy in the fifties. From the Second Five Year Plan, there was determined thrust towards the substitution of basic and capital goods industries. The ISI strategy was based on the model of growth as propounded by Mahalanobis.
The State was to play an active role in building a self-reliant economy, discriminating structure of protection was evolved to acquire foreign technology and for policies towards foreign investment.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
With reference to the International trade, what does the term “de minimis” refer to?
Correct
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Under the WTO Agreement on Agriculture (AoA), domestic agri-subsidies are classified into three categories: green, blue and amber.
Under WTO principles, “amber box” subsidies create trade distortions because they encourage excessive production through farm subsidies to fertilizers, seeds, electricity, and irrigation.
They are also called as Aggregate Measure of Support.
As per the WTO norms, the AMS can be given up to 10 % of a country’s agricultural GDP (at 1986-88 prices) in the case of developing countries. On the other hand, the limit is 5% for a developed economy. This limit is called the de minimis level of support.
It is thus minimal amounts of domestic support that are allowed even though they distort trade; up to 5% of the value of production for developed countries, 10% for developing countries.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Under the WTO Agreement on Agriculture (AoA), domestic agri-subsidies are classified into three categories: green, blue and amber.
Under WTO principles, “amber box” subsidies create trade distortions because they encourage excessive production through farm subsidies to fertilizers, seeds, electricity, and irrigation.
They are also called as Aggregate Measure of Support.
As per the WTO norms, the AMS can be given up to 10 % of a country’s agricultural GDP (at 1986-88 prices) in the case of developing countries. On the other hand, the limit is 5% for a developed economy. This limit is called the de minimis level of support.
It is thus minimal amounts of domestic support that are allowed even though they distort trade; up to 5% of the value of production for developed countries, 10% for developing countries.
-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to foreign investments in India:
- FII increases capital availability in general, whereas FDI simply targets specific enterprises.
- FII helps bring better management skills and technology, while FDI only brings in the capital.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Foreign Direct Investment is an investment that a parent company makes in a foreign nation. Foreign Direct Investment simply targets an exact enterprise. Whereas, Foreign Institutional Investor is an investment prepared by an investor in the stock markets of a foreign country.
In FII, the companies just require to get registered in the stock exchange to make investments.
FDI is more favored to the FII as FDI is considered to be more stable than FII. FDI not just brings in the capital but also assists in high-quality governance practices and improved management skills and even technology transfer.
RBI via the Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of Security by a Person Resident outside India) Regulations, 2000 (FEMA 20) has allowed startups to issue convertible notes to foreign investors apart from FDI in startups by foreign venture capital investors through subscribing to equity or equity linked instruments or debt instruments.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Foreign Direct Investment is an investment that a parent company makes in a foreign nation. Foreign Direct Investment simply targets an exact enterprise. Whereas, Foreign Institutional Investor is an investment prepared by an investor in the stock markets of a foreign country.
In FII, the companies just require to get registered in the stock exchange to make investments.
FDI is more favored to the FII as FDI is considered to be more stable than FII. FDI not just brings in the capital but also assists in high-quality governance practices and improved management skills and even technology transfer.
RBI via the Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of Security by a Person Resident outside India) Regulations, 2000 (FEMA 20) has allowed startups to issue convertible notes to foreign investors apart from FDI in startups by foreign venture capital investors through subscribing to equity or equity linked instruments or debt instruments.
-
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
Consider the following statements regarding floating exchange rates:
- If the demand for foreign exchange goes up, the domestic currency depreciates.
- A rise in the interest rates at home often leads to an appreciation of the domestic currency which will lead to increase in the exchange rate of the domestic currency.
- If a country’s imports grow faster than its exports, then the domestic currency tends to depreciate.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
In flexible exchange rates (also known as floating exchange rates), the exchange rate is determined by the forces of market demand and supply. If the demand for foreign exchange goes up, the domestic currency (rupee) depreciates since it has become less expensive in terms of foreign currency. By contrast, the currency appreciates when it becomes more expensive in terms of foreign currency.
Interest rate differential is important in determining exchange rate movements. There are huge funds owned by banks, multinational corporations and wealthy individuals who move around the world in search of the highest interest rates. If we assume that government bonds in country A pay 8 percent rate of interest whereas equally safe bonds in country B yield 10 percent, the interest rate differential is 2 percent.
Investors from country A will be attracted by the high-interest rates in country B and will buy the currency of country B selling their own currency.
At the same time, investors in country B will also find investing in their own country more attractive and will, therefore, demand less of country A’s currency. This means that the demand for country A’s currency will decrease while that of country B’s currency will increase.
Therefore, country A’s currency depreciates whereas that of country B’s currency appreciates. Thus, a rise in the interest rates at home often leads to an appreciation of the domestic currency which will lead to increase in the exchange rate of the domestic currency.
If a country’s imports grow faster than exports, the capital inflows from exports will not be sufficient to pay for the imports. This will lead to an increase in demand for foreign currency. Therefore the domestic currency depreciates.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
In flexible exchange rates (also known as floating exchange rates), the exchange rate is determined by the forces of market demand and supply. If the demand for foreign exchange goes up, the domestic currency (rupee) depreciates since it has become less expensive in terms of foreign currency. By contrast, the currency appreciates when it becomes more expensive in terms of foreign currency.
Interest rate differential is important in determining exchange rate movements. There are huge funds owned by banks, multinational corporations and wealthy individuals who move around the world in search of the highest interest rates. If we assume that government bonds in country A pay 8 percent rate of interest whereas equally safe bonds in country B yield 10 percent, the interest rate differential is 2 percent.
Investors from country A will be attracted by the high-interest rates in country B and will buy the currency of country B selling their own currency.
At the same time, investors in country B will also find investing in their own country more attractive and will, therefore, demand less of country A’s currency. This means that the demand for country A’s currency will decrease while that of country B’s currency will increase.
Therefore, country A’s currency depreciates whereas that of country B’s currency appreciates. Thus, a rise in the interest rates at home often leads to an appreciation of the domestic currency which will lead to increase in the exchange rate of the domestic currency.
If a country’s imports grow faster than exports, the capital inflows from exports will not be sufficient to pay for the imports. This will lead to an increase in demand for foreign currency. Therefore the domestic currency depreciates.
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Which among the following can widen the Current Account Deficit of India?
- Imposing import quota.
- Reduction in the export subsidy.
- Indian companies raising money from External Commercial Borrowings.
Select from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
The current account records exports and imports in goods and services and transfer payments. Trade-in services denoted as invisible trade includes both factor income (payment for inputs-investment income, that is, the interest, profits and dividends on our assets abroad minus the income foreigners earn on assets they own in India) and non-factor income (shipping, banking, insurance, tourism, software services, etc.)
Transfer payments are receipts which the residents of a country receive for free, without having to make any present or future payments in return. They consist of remittances, gifts, and grants.
CAD rises/widens when the value of goods and services a country imports exceeds the value of goods and services it exports.
Reducing export subsidy can hamper the growth of exports and thus widen the current account deficit.
One of the objectives of enforcing import quota is to reduce the balance of payments deficit by restricting imports. That portion of national income going into imports can be utilised for investment in the import substitution or export industries. The expansion in exports, coupled with the restriction of imports is likely to bring about improvement in the balance of payments position of the country.
India is one of the biggest importers of crude oil. A rise in crude oil prices indicates rising imports and thus CAD widens.
ECBs are borrowings raised by permitted resident entities from recognized non-resident entities. Therefore, ECBs would lead to capital inflow which would in turn reduce CAD.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
The current account records exports and imports in goods and services and transfer payments. Trade-in services denoted as invisible trade includes both factor income (payment for inputs-investment income, that is, the interest, profits and dividends on our assets abroad minus the income foreigners earn on assets they own in India) and non-factor income (shipping, banking, insurance, tourism, software services, etc.)
Transfer payments are receipts which the residents of a country receive for free, without having to make any present or future payments in return. They consist of remittances, gifts, and grants.
CAD rises/widens when the value of goods and services a country imports exceeds the value of goods and services it exports.
Reducing export subsidy can hamper the growth of exports and thus widen the current account deficit.
One of the objectives of enforcing import quota is to reduce the balance of payments deficit by restricting imports. That portion of national income going into imports can be utilised for investment in the import substitution or export industries. The expansion in exports, coupled with the restriction of imports is likely to bring about improvement in the balance of payments position of the country.
India is one of the biggest importers of crude oil. A rise in crude oil prices indicates rising imports and thus CAD widens.
ECBs are borrowings raised by permitted resident entities from recognized non-resident entities. Therefore, ECBs would lead to capital inflow which would in turn reduce CAD.
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Which of the following are the possible impacts of the devaluation of a currency in a
country?- It may lead to reduction in aggregate demand for domestically produced goods.
- It may lead to an improvement in the current account balance.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Devaluating a currency is decided by the government issuing the currency, and unlike depreciation, is not a result of non-governmental activities.
Impacts:
Increased Aggregate Demand (AD) : Exports become cheaper and more competitive to foreign buyers. Higher exports relative to imports can increase aggregate demand as increased consumer spending on domestic goods and services.
Inflation is more likely to occur because imports are more expensive causing cost-push inflation, AD increases causing demand-pull inflation and with exports becoming, cheaper manufacturers may have less incentive to cut costs and become more efficient. Therefore over time, costs may increase.
Improvement in the current account balance: With exports more competitive and imports more expensive, we may see higher exports and lower imports, which will reduce the current account deficit.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Devaluating a currency is decided by the government issuing the currency, and unlike depreciation, is not a result of non-governmental activities.
Impacts:
Increased Aggregate Demand (AD) : Exports become cheaper and more competitive to foreign buyers. Higher exports relative to imports can increase aggregate demand as increased consumer spending on domestic goods and services.
Inflation is more likely to occur because imports are more expensive causing cost-push inflation, AD increases causing demand-pull inflation and with exports becoming, cheaper manufacturers may have less incentive to cut costs and become more efficient. Therefore over time, costs may increase.
Improvement in the current account balance: With exports more competitive and imports more expensive, we may see higher exports and lower imports, which will reduce the current account deficit.
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
With reference to Balance of Payments, consider the following statements:
- The balance of payments is said to be in surplus if autonomous receipts are greater than autonomous payments.
- Accommodating transactions are determined by the net consequences of the autonomous items.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Balance of Payments can be divided under the following components:
Autonomous:
- International economic transactions are called autonomous when transactions are made independently of the state of the BoP (for instance due to profit motive).
- These items are called ‘above the line’ items in the BoP. The balance of payments is said to be in surplus / deficit if autonomous receipts are greater / less than autonomous payments.
Accommodating transactions:
- These are termed ‘below the line’ items. These are determined by the net consequences of the autonomous items, that is, whether the BoP is in surplus or deficit.
- The official reserve transactions are seen as the accommodating item in the BoP (all others being autonomous).
Errors and Omissions:
These constitute the third element in the BoP (apart from the current and capital accounts) which is the ‘balancing item’ reflecting our inability to record all international transactions accurately.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Balance of Payments can be divided under the following components:
Autonomous:
- International economic transactions are called autonomous when transactions are made independently of the state of the BoP (for instance due to profit motive).
- These items are called ‘above the line’ items in the BoP. The balance of payments is said to be in surplus / deficit if autonomous receipts are greater / less than autonomous payments.
Accommodating transactions:
- These are termed ‘below the line’ items. These are determined by the net consequences of the autonomous items, that is, whether the BoP is in surplus or deficit.
- The official reserve transactions are seen as the accommodating item in the BoP (all others being autonomous).
Errors and Omissions:
These constitute the third element in the BoP (apart from the current and capital accounts) which is the ‘balancing item’ reflecting our inability to record all international transactions accurately.
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
Which of the following measures can help in tackling rupee appreciation?
- Buying of foreign currency by the Central Bank.
- Lowering interest rates in commercial banks.
- Purchase of Government securities from the public by the Central Bank.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Currency appreciation is an increase in the value of one currency in relation to another currency. A strong currency makes imports cheaper and can improve living standards.
However, it can also make exports less competitive and lead to lower economic growth. So, to stabilise the currency, various measures are adopted to increase the quantum of domestic currency and reduce the volume of foreign currency.
All the options given above lead to an infusion of domestic currency among the public and reduces the foreign currency in the market. Thus it helps in tackling rupee appreciation.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Currency appreciation is an increase in the value of one currency in relation to another currency. A strong currency makes imports cheaper and can improve living standards.
However, it can also make exports less competitive and lead to lower economic growth. So, to stabilise the currency, various measures are adopted to increase the quantum of domestic currency and reduce the volume of foreign currency.
All the options given above lead to an infusion of domestic currency among the public and reduces the foreign currency in the market. Thus it helps in tackling rupee appreciation.
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
With reference to eligibility conditions for Qualified Foreign Investors (QFI), which of the following statements is/are true?
- QFI is a resident of a country that is a member of the Financial Action Task Force.
- A QFI can neither be a person resident in India nor can be registered with the SEBI
as a Foreign Institutional Investor.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Qualified Foreign Investor (QFI) is sub-category of Foreign Portfolio Investor and refers to any foreign individuals, groups or associations, or resident, however, restricted to resident from a country that is a member of Financial Action Task Force (FATF) or a country that is a member of a group (the Gulf Cooperation Council /the European Commission) which is a member of FATF and a country that is a signatory to International Organization of Securities Commission’s (IOSCO) Multilateral Memorandum of Understanding (MMOU).
As per the guidelines issued by the Securities & Exchange Board of India, other eligibilities
for QFIs (which shall include individuals, groups or associations) are:A QFI should neither be a person resident in India nor should be registered with the SEBI as a Foreign Institutional Investor (‘FII’), sub-account or Foreign Venture Capital Investor.
A QFI should be set up with a SEBI – registered Qualified Depository Participant (QDP)
to commence activities. The QDP shall provide inter alia custody services.Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The Qualified Foreign Investor (QFI) is sub-category of Foreign Portfolio Investor and refers to any foreign individuals, groups or associations, or resident, however, restricted to resident from a country that is a member of Financial Action Task Force (FATF) or a country that is a member of a group (the Gulf Cooperation Council /the European Commission) which is a member of FATF and a country that is a signatory to International Organization of Securities Commission’s (IOSCO) Multilateral Memorandum of Understanding (MMOU).
As per the guidelines issued by the Securities & Exchange Board of India, other eligibilities
for QFIs (which shall include individuals, groups or associations) are:A QFI should neither be a person resident in India nor should be registered with the SEBI as a Foreign Institutional Investor (‘FII’), sub-account or Foreign Venture Capital Investor.
A QFI should be set up with a SEBI – registered Qualified Depository Participant (QDP)
to commence activities. The QDP shall provide inter alia custody services. -
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to purchasing power parity (PPP):
- PPP exchange rates are calculated by the prices of the different basket of goods and services, based on domestic demands, in different countries.
- India stands third in the world in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), behind China and USA.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) exchange rates are calculated by the prices of the same basket of goods and services in different countries.
India stands third in the world in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), behind the US and China.
PPP is a popular macroeconomic analysis metric to compare economic productivity and standards of living between countries. PPP is an economic theory that compares different countries’ currencies through a “basket of goods” approach. It measures prices at different locations using a common good or goods to contrast the real purchasing power between different currencies.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) exchange rates are calculated by the prices of the same basket of goods and services in different countries.
India stands third in the world in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), behind the US and China.
PPP is a popular macroeconomic analysis metric to compare economic productivity and standards of living between countries. PPP is an economic theory that compares different countries’ currencies through a “basket of goods” approach. It measures prices at different locations using a common good or goods to contrast the real purchasing power between different currencies.
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
Which of the following reasons led to the slowing down of global trade growth?
- Volatility in financial markets
- Weaker global economic growth
- Introduction of new and retaliatory tariff measures
- Persistent inflation.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
Introduction of new and retaliatory tariff measures, Heightened US-China trade tensions, weaker global economic growth, Volatility in financial markets.
Introduction of a new and retaliatory tariff imposed by countries are the effects of ongoing trade wars between USA and China, which negatively impacts investor sentiments and is one of the primary reasons for the slowdown in global trade growth
Weaker economic growth reinstates weaker global trade growth creating a downward spiral of growth.
Such a weak global scenario also creates a bearish market and drop in the stock market. Added to this, crude oil price volatility also creates uncertainty in financial markets.
Trade growth in 2022 is likely to be lower than expected, given the macroeconomic trends like persistent inflation in the United States and concerns related to China’s real estate sector.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
Introduction of new and retaliatory tariff measures, Heightened US-China trade tensions, weaker global economic growth, Volatility in financial markets.
Introduction of a new and retaliatory tariff imposed by countries are the effects of ongoing trade wars between USA and China, which negatively impacts investor sentiments and is one of the primary reasons for the slowdown in global trade growth
Weaker economic growth reinstates weaker global trade growth creating a downward spiral of growth.
Such a weak global scenario also creates a bearish market and drop in the stock market. Added to this, crude oil price volatility also creates uncertainty in financial markets.
Trade growth in 2022 is likely to be lower than expected, given the macroeconomic trends like persistent inflation in the United States and concerns related to China’s real estate sector.
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
With reference to Elasticity of Demand, consider the following statements:
- Elasticity is defined as the ratio of one variable’s percent change to another variable’s percent change.
- Lower demand elasticity for an economic variable indicates that the customers are more conscious of changes in this variable.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Elasticity is defined as the ratio of one variable’s percent change to another variable’s percent change. It is denoted as follows:
The elasticity of demand describes how sensitive a good’s demand is to changes in other economic variables like prices and consumer benefits.
Higher demand elasticity for an economic variable indicates that the customers are more conscious of changes in this variable.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
Elasticity is defined as the ratio of one variable’s percent change to another variable’s percent change. It is denoted as follows:
The elasticity of demand describes how sensitive a good’s demand is to changes in other economic variables like prices and consumer benefits.
Higher demand elasticity for an economic variable indicates that the customers are more conscious of changes in this variable.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
Consider the following statements regarding J curve in economic theory:
- The J Curve states that, under certain assumptions, a country’s trade deficit will initially worsen after the depreciation of its currency.
- This theory can be applied to areas including private equity, medical field, and politics.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The J Curve is an economic theory which states that, under certain assumptions, a country’s trade deficit will initially worsen after the depreciation of its currency.
It is often used to observe the effects of a weaker currency on trade balances. The pattern is as follow:
- Immediately after a nation’s currency is devalued, imports get more expensive and exports get cheaper, creating a worsening trade deficit (or at least a smaller trade surplus).
- Shortly thereafter, the sales volume of the nation’s exports begins to rise steadily, thanks to their relatively cheap prices.
- At the same time, consumers at home begin to buy more locally-produced goods because they are relatively affordable compared to imports.
- Over time, the trade balance between the nation and its partners bounces back and even exceeds pre-devaluation times.
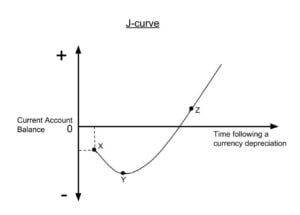
The J Curve theory can be applied to other areas besides trade deficits, including in private equity, the medical field, and politics.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
The J Curve is an economic theory which states that, under certain assumptions, a country’s trade deficit will initially worsen after the depreciation of its currency.
It is often used to observe the effects of a weaker currency on trade balances. The pattern is as follow:
- Immediately after a nation’s currency is devalued, imports get more expensive and exports get cheaper, creating a worsening trade deficit (or at least a smaller trade surplus).
- Shortly thereafter, the sales volume of the nation’s exports begins to rise steadily, thanks to their relatively cheap prices.
- At the same time, consumers at home begin to buy more locally-produced goods because they are relatively affordable compared to imports.
- Over time, the trade balance between the nation and its partners bounces back and even exceeds pre-devaluation times.

The J Curve theory can be applied to other areas besides trade deficits, including in private equity, the medical field, and politics.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
With respect to international trade, consider the following statements:
- A country has an absolute advantage in producing a good if it can produce that good
at lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. - A country has a comparative advantage in producing a good if it can produce that
good at lower marginal cost and opportunity cost than its trading partner.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Marginal cost is the cost added by producing one additional unit of a product or service while opportunity cost is the loss of other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
Absolute Advantage is the inherent ability of a country that allows that country to produce
specific goods efficiently and effectively at a relatively lower marginal cost. A country has
an absolute advantage in producing a good if it can produce that good at lower marginal
cost, lesser workforce, lesser time and lesser cost without compromising the quality.Comparative Advantage refers to the country’s capability of producing the specific good at
lower marginal cost and opportunity cost in comparison to other countries. In absolute
advantage, whereas the emphasis is only on marginal cost, comparative advantage takes
into account both marginal and opportunity cost.Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Marginal cost is the cost added by producing one additional unit of a product or service while opportunity cost is the loss of other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
Absolute Advantage is the inherent ability of a country that allows that country to produce
specific goods efficiently and effectively at a relatively lower marginal cost. A country has
an absolute advantage in producing a good if it can produce that good at lower marginal
cost, lesser workforce, lesser time and lesser cost without compromising the quality.Comparative Advantage refers to the country’s capability of producing the specific good at
lower marginal cost and opportunity cost in comparison to other countries. In absolute
advantage, whereas the emphasis is only on marginal cost, comparative advantage takes
into account both marginal and opportunity cost. - A country has an absolute advantage in producing a good if it can produce that good
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Consider the following statements regarding an Escrow Account:
- It is an arrangement for safeguarding the seller against its buyer from the payment risk for the goods or services sold by the former to the latter
- In India, escrow account is widely used in public-private partnership projects in infrastructure.
- RBI has permitted Banks to open escrow accounts on behalf of Non-Resident corporates for acquisition/transfer of shares/ convertible shares of an Indian company.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Escrow Account:
- An escrow account in simple terms is a third party account.
- It is a separate bank account to hold money which belongs to others and where the money parked will be released only under the fulfillment of certain conditions of a contract.
- An escrow account is an arrangement for safeguarding the seller against its buyer from the payment risk for the goods or services sold by the former to the latter
How it operates:
- This is done by removing the control over cash flows from the hands of the buyer to an independent agent.
- The independent agent, i.e, the holder of the escrow account would ensure that the appropriation of cash flows is as per the agreed terms and conditions between the transacting parties.
- In India, escrow account is widely used in public-private partnership projects in infrastructure.
- RBI has also permitted Banks (Authorised Dealer Category I) to open escrow accounts on behalf of Non-Resident corporates for acquisition/transfer of shares/ convertible shares of an Indian company
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Escrow Account:
- An escrow account in simple terms is a third party account.
- It is a separate bank account to hold money which belongs to others and where the money parked will be released only under the fulfillment of certain conditions of a contract.
- An escrow account is an arrangement for safeguarding the seller against its buyer from the payment risk for the goods or services sold by the former to the latter
How it operates:
- This is done by removing the control over cash flows from the hands of the buyer to an independent agent.
- The independent agent, i.e, the holder of the escrow account would ensure that the appropriation of cash flows is as per the agreed terms and conditions between the transacting parties.
- In India, escrow account is widely used in public-private partnership projects in infrastructure.
- RBI has also permitted Banks (Authorised Dealer Category I) to open escrow accounts on behalf of Non-Resident corporates for acquisition/transfer of shares/ convertible shares of an Indian company
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
Which of the following fall within the purview of Capital account under the Balance of Payments?
- Foreign institutional investment
- Remittances, gifts and grants
- Global Depository Receipts
Select from the codes given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
There are two main accounts in the Balance of Payments: Current account and the Capital account.
Current account:
It records exports and imports in goods and services and transfer payments. Trade in services denoted as invisible trade (because they are not seen to cross national borders) includes both factor income (payment for inputs-investment income, that is, the interest, profits and dividends on our assets abroad minus the income foreigners earn on assets they own in India) and non-factor income (shipping, banking, insurance, tourism, software services, etc.).
Transfer payments are receipts which the residents of a country receive for free, without having to make any present or future payments in return. They consist of remittances, gifts and grants. They could be official or private.
Capital Account:
It includes sales of assets such as money, stocks, bonds, etc. The main components of the capital account include foreign investment, loans and banking capital. Foreign investment, comprising Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Portfolio Investment consisting of Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) investment, American Depository Receipts/Global Depository Receipts (ADRs/GDRs) represents non-debt liabilities, while loans (external assistance, external commercial borrowings and trade credit) and banking capital, including non-resident Indian (NRI) deposit are debt liabilities.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Basic Info:
There are two main accounts in the Balance of Payments: Current account and the Capital account.
Current account:
It records exports and imports in goods and services and transfer payments. Trade in services denoted as invisible trade (because they are not seen to cross national borders) includes both factor income (payment for inputs-investment income, that is, the interest, profits and dividends on our assets abroad minus the income foreigners earn on assets they own in India) and non-factor income (shipping, banking, insurance, tourism, software services, etc.).
Transfer payments are receipts which the residents of a country receive for free, without having to make any present or future payments in return. They consist of remittances, gifts and grants. They could be official or private.
Capital Account:
It includes sales of assets such as money, stocks, bonds, etc. The main components of the capital account include foreign investment, loans and banking capital. Foreign investment, comprising Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Portfolio Investment consisting of Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) investment, American Depository Receipts/Global Depository Receipts (ADRs/GDRs) represents non-debt liabilities, while loans (external assistance, external commercial borrowings and trade credit) and banking capital, including non-resident Indian (NRI) deposit are debt liabilities.
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
With reference to Dumping, consider the following statements:
- It refers to a practice when the export price of a product is less than the cost of
production in the home country. - Ministry of Corporate Affairs is the nodal agency responsible for investigating the
cases of dumping in India.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
When goods are exported to another country at a price which is less than what it is sold for in the home country or when the export price is less than the cost of production in the home
country, then those goods have been dumped.Home Market Price – Export Sales Price = Margin of dumping
The Department of Commerce in the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry has a dedicated unit, called the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping & Allied Duties which investigates cases where the domestic industry (domestic producers) provide evidence that dumping has taken place by producers abroad. They also defend cases where allegations of dumping are brought
against Indian exporters by foreign governments.There is a well-established process which is followed where questionnaires are sent to all stakeholders and evidence is collected in a time-bound fashion to either prove or disprove that dumping has taken place.
If the good is alleged to be dumped from a non-market country (a country where there are considerable distortions to the market through government subsidies) then the Anti-dumping cell will calculate what the ―normal price of the product should be in the home market. The normal price will reflect the market price of the product had it been produced in the exporting country without these subsidies.
If necessary, the price of such a commodity in a similar market (say a neighbouring country at the same level of development as the exporting country) will be considered as the normal price.
If there is evidence of dumping then the Government of India will levy anti-dumping duty on that commodity.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Basic Info:
When goods are exported to another country at a price which is less than what it is sold for in the home country or when the export price is less than the cost of production in the home
country, then those goods have been dumped.Home Market Price – Export Sales Price = Margin of dumping
The Department of Commerce in the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry has a dedicated unit, called the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping & Allied Duties which investigates cases where the domestic industry (domestic producers) provide evidence that dumping has taken place by producers abroad. They also defend cases where allegations of dumping are brought
against Indian exporters by foreign governments.There is a well-established process which is followed where questionnaires are sent to all stakeholders and evidence is collected in a time-bound fashion to either prove or disprove that dumping has taken place.
If the good is alleged to be dumped from a non-market country (a country where there are considerable distortions to the market through government subsidies) then the Anti-dumping cell will calculate what the ―normal price of the product should be in the home market. The normal price will reflect the market price of the product had it been produced in the exporting country without these subsidies.
If necessary, the price of such a commodity in a similar market (say a neighbouring country at the same level of development as the exporting country) will be considered as the normal price.
If there is evidence of dumping then the Government of India will levy anti-dumping duty on that commodity.
- It refers to a practice when the export price of a product is less than the cost of
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Deemed Exports Benefit Scheme:
- Deemed Exports refers to those transactions in which goods supplied do not leave the country but the payment for such supplies is received only in foreign exchange.
- The scheme is applicable to the units in Petroleum refinery and Nuclear Power Projects.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Deemed Exports refers to those transactions in which goods supplied do not leave the country, and payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in foreign exchange.
Deemed benefit export scheme has been in operation for more than two decades. The benefits under the scheme include a rebate on duty chargeable on imports or excisable material used in the manufacture of goods which are supplied to the eligible projects.
The policy aims to create a level playing field for the domestic industry vis-a-vis direct import by providing duty-free inputs or exemption/refund of duty paid on goods manufactured in India. Thus, it is an instrument for import substitution. It helps in creating manufacturing capability, value addition and employment opportunities in the country.
Deemed Export Benefit Scheme benefits are availed of by units in Power, Petroleum refinery, fertilizer, and Nuclear Power Projects. They are also availed by the supply of goods to projects financed by multilateral or bilateral agencies.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Deemed Exports refers to those transactions in which goods supplied do not leave the country, and payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in foreign exchange.
Deemed benefit export scheme has been in operation for more than two decades. The benefits under the scheme include a rebate on duty chargeable on imports or excisable material used in the manufacture of goods which are supplied to the eligible projects.
The policy aims to create a level playing field for the domestic industry vis-a-vis direct import by providing duty-free inputs or exemption/refund of duty paid on goods manufactured in India. Thus, it is an instrument for import substitution. It helps in creating manufacturing capability, value addition and employment opportunities in the country.
Deemed Export Benefit Scheme benefits are availed of by units in Power, Petroleum refinery, fertilizer, and Nuclear Power Projects. They are also availed by the supply of goods to projects financed by multilateral or bilateral agencies.
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
Consider the following statements:
- A Customs Union is characterized by the free movement of factors of production
among member countries. - In a free trade agreement, the member countries maintain a common external tariff for exports and imports from non members.
- A common market is where the movement of factors of production is relatively free amongst member countries.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Free Trade Agreement (FTA): A free trade agreement is a preferential arrangement in which members reduce tariffs on trade among themselves, while maintaining their own tariff rates for trade with non members.
Customs Union (CU): A customs union (CU) is a free-trade agreement in which members apply a
common external tariff (CET) schedule to imports from non-members.Common Market (CM): A common market is a customs union where the movement of factors of production is relatively free amongst member countries.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Basic Info:
Free Trade Agreement (FTA): A free trade agreement is a preferential arrangement in which members reduce tariffs on trade among themselves, while maintaining their own tariff rates for trade with non members.
Customs Union (CU): A customs union (CU) is a free-trade agreement in which members apply a
common external tariff (CET) schedule to imports from non-members.Common Market (CM): A common market is a customs union where the movement of factors of production is relatively free amongst member countries.
- A Customs Union is characterized by the free movement of factors of production
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) generally covers negotiation on trade tariff and Tariff Rate Quotas rates only.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) looks into the regulatory aspect of trade and encompasses an agreement covering the regulatory issues.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement:
- It is a kind of free trade pact that covers negotiation on the trade in services and investment, and other areas of economic partnership.
- It may even consider negotiation in areas such as trade facilitation and customs cooperation, competition, and IPR.
- Partnership agreements or cooperation agreements are more comprehensive than Free Trade Agreements.
- CEPA also looks into the regulatory aspect of trade and encompasses an agreement covering the regulatory issues.
- India has signed CEPAs with South Korea and Japan.
Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA):
- CECA generally covers negotiation on trade tariff and TRQ (Tariff Rate Quotas) rates only. It is not as comprehensive as CEPA. India has signed CECA with Malaysia.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Basic Info:
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement:
- It is a kind of free trade pact that covers negotiation on the trade in services and investment, and other areas of economic partnership.
- It may even consider negotiation in areas such as trade facilitation and customs cooperation, competition, and IPR.
- Partnership agreements or cooperation agreements are more comprehensive than Free Trade Agreements.
- CEPA also looks into the regulatory aspect of trade and encompasses an agreement covering the regulatory issues.
- India has signed CEPAs with South Korea and Japan.
Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA):
- CECA generally covers negotiation on trade tariff and TRQ (Tariff Rate Quotas) rates only. It is not as comprehensive as CEPA. India has signed CECA with Malaysia.
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Consider the following statements
- India is a member of the Arctic Council
- India established a research base in the Arctic named IndArc in 2008
- Ministry of Earth Sciences recently released India’s Arctic Policy
Choose the correct answer using the code given below
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Incorrect Correct India has been an Observer nation since 2013 India established a research base named Himadri in Arctic region in 2008. IndArc was deployed in 2014 The Ministry of Earth Science (MoES) released the India’s Arctic policy titled ‘India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development’ Context – Arctic policy was released.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Incorrect Correct India has been an Observer nation since 2013 India established a research base named Himadri in Arctic region in 2008. IndArc was deployed in 2014 The Ministry of Earth Science (MoES) released the India’s Arctic policy titled ‘India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development’ Context – Arctic policy was released.
-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Prompt Corrective Action Framework’
- Ministry of Finance initiated the scheme but it is implemented by Reserve Bank of India
- Capital to risk weighted assets ratio, Net non-performing assets, Return on assets are the parameters assessed
- Primary responsibility of recapitalisation of Domestically-Systemically Important banks(D-SIB’S) often devolves on the Government
Select the correct answer using the code given below
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Incorrect Incorrect Reserve Bank of India initiated the scheme in 2002 and implements it PCA contains three parameters. They are Capital to risk weighted assets ratio, Net non-performing assets, Return on assets Primary responsibility of recapitalisation of PSBs often devolves on the Government, which is the majority shareholder in these banks. Context – Centre has announced to recapitalise weak Public Sector Banks (PSB)
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Incorrect Incorrect Incorrect Reserve Bank of India initiated the scheme in 2002 and implements it PCA contains three parameters. They are Capital to risk weighted assets ratio, Net non-performing assets, Return on assets Primary responsibility of recapitalisation of PSBs often devolves on the Government, which is the majority shareholder in these banks. Context – Centre has announced to recapitalise weak Public Sector Banks (PSB)
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
With reference to ‘Palladium’, consider the following statements
- It is a rare metal used in the manufacture of catalytic converters and fuel cells
- Russia accounts for more than half of world production in Palladium
Choose the correct statements
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Palladium is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into harmless substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is a key component of fuel cells, which react hydrogen with oxygen to produce electricity, heat, and water Russia accounted for 40% of world production of Palladium. It is also found in South Africa, Canada and the U.S.A. Context – It was in news due to ongoing Russia-Ukraine War.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Palladium is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into harmless substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is a key component of fuel cells, which react hydrogen with oxygen to produce electricity, heat, and water Russia accounted for 40% of world production of Palladium. It is also found in South Africa, Canada and the U.S.A. Context – It was in news due to ongoing Russia-Ukraine War.
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
World Energy Transition Outlook is released by
Correct
Solution (b)
World Energy transition Outlook 2022 was launched by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) at the Berlin Energy Transition Dialogue. It sets out priority areas and actions based on available technologies that must be realised by 2030 to achieve net zero emissions by midcentury.
Context – It was launched recently
Incorrect
Solution (b)
World Energy transition Outlook 2022 was launched by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) at the Berlin Energy Transition Dialogue. It sets out priority areas and actions based on available technologies that must be realised by 2030 to achieve net zero emissions by midcentury.
Context – It was launched recently
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
Consider the following statements
- Thermobaric bombs are non-precision weapons that are designed to injure or kill human beings indiscriminately over a large area
- Thermobaric bombs are not prohibited by any international law or agreement presently
Select the correct statement(s)
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Cluster munitions are non-precision weapons that are designed to injure or kill human beings indiscriminately over a large area, and to destroy vehicles and infrastructure. Thermobaric bombs are not prohibited by any international law or agreement presently Context – Russia was accused of using thermobaric bombs
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement Analysis:
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Cluster munitions are non-precision weapons that are designed to injure or kill human beings indiscriminately over a large area, and to destroy vehicles and infrastructure. Thermobaric bombs are not prohibited by any international law or agreement presently Context – Russia was accused of using thermobaric bombs
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
Consider the following statements
- Some cats are rats.
- All bats are tables
- All rats are bats
Conclusions:
- Some cats are bats
- All bats are rats
- All tables are cats
- All bats are cats
Which of the conclusions given above follow?
Correct
Solution (d)
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (d)

-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
Consider the following statements:
Statements
- All clocks are watches.
- Some clocks are alarms
Conclusion:
- Some alarms are watches.
- All watches are alarms
Which of the conclusions given above follow?
Correct
Solution (a)
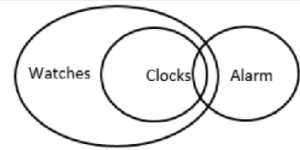 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (a)

-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
Consider the following statements:
- No cities are countries.
- No countries are villages.
Conclusions:
- Some countries are city.
- No villages are city.
Which of the conclusions given above follow(s)?
Correct
Solution (d)
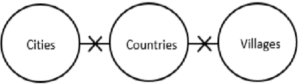
Some countries are city – False, it is not a definite case.
No villages are city – False, it is not a definite case.
So, neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows.
Incorrect
Solution (d)

Some countries are city – False, it is not a definite case.
No villages are city – False, it is not a definite case.
So, neither conclusion I nor conclusion II follows.
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
Consider the following statements
- In a one day cricket match, the total runs made by a team were 300.
- Out of these 240 runs were made by spinners.
Conclusions:
- 80% of the team consists of spinners.
- The opening batsmen were spinners.
Which of the conclusions given above follow(s)?
Correct
Solution (d)
According to the statement,
80% of the total runs were made by spinners. So, (I) does not follow.
Nothing about the opening batsmen is mentioned in the statement. So, (II) also does not follow.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
According to the statement,
80% of the total runs were made by spinners. So, (I) does not follow.
Nothing about the opening batsmen is mentioned in the statement. So, (II) also does not follow.
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow each passage. Your answer to these questions should be based on passage only.
Technology will shape the way we educate students in the next decade. A user is not simply a person who uses. For the student, being a user should involve using the latest technology in a free and autonomous manner. This new-found freedom will allow the student to become an active participant in his/her education instead of a passive passenger. In our current technological society, being a user also means being tracked. Tracking a student means having the ability to target education towards weaknesses and strengths. The ability to accurately customize to the individual has been the holy grail of educational philosophy for many years. This golden age of technological development may soon enable this dream to become a reality.
Q.30) What does the author mean by the term “tracking a student”?
Correct
Solution (a)
Refer to, “Tracking a student means having the ability to target education towards weaknesses and strengths. The ability to accurately customize to the individual….”
It can be clearly inferred from the above two sentences given in the passage that by the term ‘tracking a student’ the author meant analysing the performance of a student and designing an educational syllabus accordingly
Hence, option a is the correct answer.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Refer to, “Tracking a student means having the ability to target education towards weaknesses and strengths. The ability to accurately customize to the individual….”
It can be clearly inferred from the above two sentences given in the passage that by the term ‘tracking a student’ the author meant analysing the performance of a student and designing an educational syllabus accordingly
Hence, option a is the correct answer.
All the Best
IASbaba











