Science and Technology
In News: Recently, the Indian Council of Medical Research (IMCR) released guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment, and management for type-1 diabetes.
- This is the first time the ICMR has issued guidelines specifically for type 1 diabetes, which is rarer than type 2 — only 2% of all hospital cases of diabetes in the country are type 1 — but which is being diagnosed more frequently in recent years.
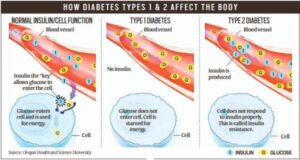
- Type 1 diabetes is a condition where the pancreas completely stops producing insulin, the hormone responsible for controlling the level of glucose in blood by increasing or decreasing absorption to the liver, fat, and other cells of the body.
- Type 1 diabetes is predominantly diagnosed in children and adolescents.
- Although the prevalence is less, it is much more severe than type 2.
- Unlike type 2 diabetes where the body produces some insulin and which can be managed using various pills, if a person with type 1 diabetes stops taking their insulin, they die within weeks. The body produces zero insulin
How rare is it?
- There are over 10 lakh children and adolescents living with type 1 diabetes in the world, with India accounting for the highest numbers.
- Of the 5 lakh people living with type 1 diabetes in India, 90,000 to 1 lakh are under the age of 14 years. For context, the total number of people in India living with diabetes was 7.7 crore in 2019
Who is at risk of type 1 diabetes?
- The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is thought to be an auto-immune condition where the body’s immune system destroys the islets cells on the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Genetic factors play a role in determining whether a person will get type-1 diabetes.
- The presence of certain genes is also strongly associated with the disease.
- For example, the prevalence of genes called DR3-DQ2 and DR4-DQ8 is 30-40% in patients with type 1 diabetes as compared to 2.4% in the general population.
What are the guidelines?
- The guidelines provide details on diet and exercise, insulin monitoring, and prevention and treatment of complications such as retinopathy, kidney disease, and nerve disease.
Source: Indian Express











