Science and Technology
In News: In recent months, automakers have launched hybrid electric vehicles in India, offering car buyers more choices in the nascent electric vehicle market.
- These new hybrid electric vehicles from different automakers, are relying on hybrid technology and its advantages over conventional internal combustion engine (ICE)-powered vehicles to change car buyers’ minds.
What is a hybrid electric vehicle?
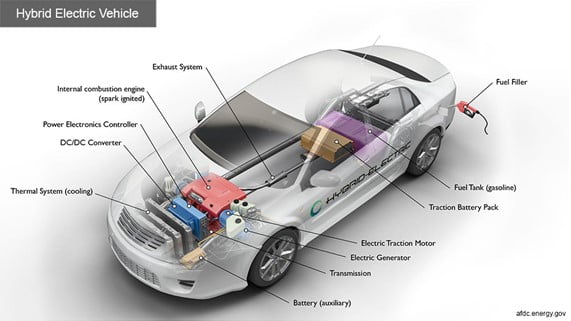
- A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) uses an ICE (a petrol/diesel engine) and one or more electric motors to run.
- It is powered by the electric motor alone, which uses energy stored in batteries, by the ICE, or both.
- The powertrain of the HEV is more complex than a regular ICE-powered car as it has EV components and a conventional ICE.
- That means a typical HEV will have a low-voltage auxiliary battery, a traction battery pack to store electricity for the electric motor, an electric generator, an AC/DC converter, a power electronics controller, a thermal system to maintain working temperature, an ICE, a fuel tank, fuel filler, a transmission and an exhaust system.
How do HEV powertrains work?
- HEV powertrains are designed to power cars in a series, parallel or series-parallel (power split) methods.
- A series HEV uses only the electric motor to drive the wheels, while the ICE powers the generator, which in turn recharges the battery.
- A parallel HEV, based on the driving condition, uses the best power source to power the vehicle. It will alternate between the electric motor and the ICE to keep the car moving.
- A series-parallel HEV offers a combination of both models and allows to split power, wherein power is routed from the ICE alone or from the battery to the electric motor to drive the vehicle.
- Moreover, in all three designs, the battery is charged through regenerative braking technology.
Regenerative braking
- Regenerative braking recovers some of the kinetic energy that would otherwise turn into heat and instead converts it into electricity.
- Regenerative braking is a way of taking the wasted energy from the process of slowing down a car and using it to recharge the car’s batteries. On a normal car, braking simply wastes energy – but with regenerative braking, some of the energy is able to be reused.
How does regenerative braking work?
- A regenerative braking system (RBS) used in automotive applications has several advantages like better braking efficiency in stop-and-go traffic which enhances fuel economy and also helps in reducing carbon emissions.
- Besides, RBS also helps in energy optimisation resulting in minimum energy wastage.
- The efficiency of HEVs and EVs will in large part be determined by their ability to recover as much energy as possible while braking, with a higher degree of energy recovery lowering fuel consumption.
- The adoption of regenerative braking technology in the auto industry is increasing on account of the operating efficiency of vehicles through reduced fuel consumption and the extended range of batteries.
- The technology is also used in electric railways.
- Rail transit can be described as frequent acceleration and braking of trains across many stations.
- This increases the potential for braking energy recovery using energy storage systems, which can recuperate and reuse braking energy from metro cars, further enhancing energy efficiency.
What are the different types of HEVs?
The HEVs can be categorised into micro, mild and full hybrid vehicles, based on the degree of hybridisation.
- A full HEV will have a larger battery and a more powerful electric motor compared with a mild HEV. As a result, a full HEV can power the vehicle for longer distances using just electric mode,
- A mild HEV cannot drive using only the electric motor and uses the battery at traffic lights or in stop-and-go traffic to support the ICE.
- Micro hybrids do not offer electric torque assistance as they lack an electric motor, but they have an idle stop-start system and energy management functions.
- There are plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) that are just like full HEVs, but they can be charged using a wall outlet, as they have an onboard charger and a charging port.
- PHEVs generally use the electric motor until the battery is almost drained, and then automatically switch to the ICE.
What are the main advantages of using hybrid technology?
- Most vehicles with hybrid technology offer better fuel efficiency, more power, and minimum emissions.
- The design of hybrid vehicles for reduced engine size and car weight as compared to ICE vehicles, translates into increased mileage to favour the demand for these vehicles.
- Moreover, with the increase in total power and torque, HEVs can deliver instant torque and provide high torque even at low speeds.
What are some challenges of hybrid technology?
- In a price-sensitive market like India, one of the major challenges for HEVs is the high vehicle cost.
- Battery, a vital component of an HEV, increases the cost of the vehicle, making it pricier than vehicles powered only by an ICE. The RBS also adds to the higher cost of an HEV.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2021)
- Digital security infrastructure
- Food security infrastructure
- Health care and education infrastructure
- Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure














