Economics
In News: Fundraising via Basel III-compliant and infrastructure bonds seen continuing over next few months, say analysts.
What is the Basel Framework:
- The Basel Framework are capital regulations developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the financial crisis of 2007–08.
- Objective: To improve the banking sector’s ability to absorb shocks arising from financial and economic stress, to reduce the risk of spill over from the financial sector to the real economy, to raise capital standard and to implement strong international compensation standards aimed at ending practices that lead to excessive risk-taking
- They were first enforced in the G-10 countries in 1992.
Evolution:
Basel I
- Adopted in 1999
- It defined capital and structure of risk weights for banks and focussed on credit risk
- Minimum capital requirement fixed at 8% of risk-weighted assets (RWA)
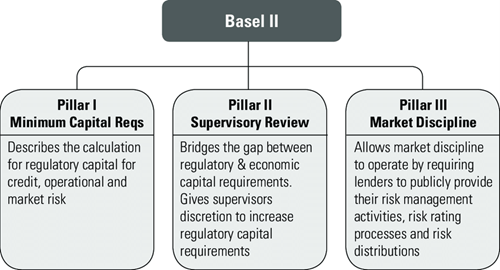
Basel II
- Adopted in 2004
- It defined three types of risk as – operational risk, market risk, capital risk
- Its 3 pillars were as follows:
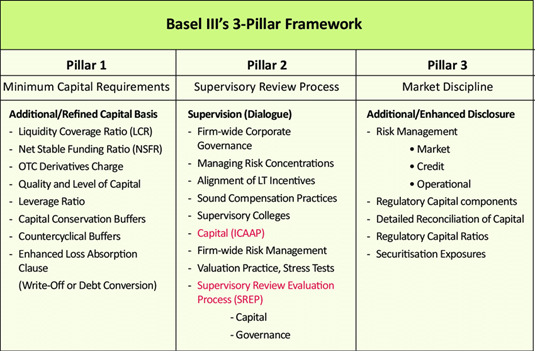
About Basel III norms:
- The new standards will come into effect on January 2023
- Risk-based capital requirements (RWAs) and interest rate risk were introduced for the first time.
- The new standards aim at increasing capital requirements, it introduces requirements on liquid asset holdings and funding stability
- Key difference between the Basel II and Basel III: Basel III framework prescribes more of common equity, creation of capital buffer, introduction of Leverage Ratio, Introduction of Liquidity coverage Ratio (LCR) and Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR).
- Leverage Ratio: The leverage ratio is calculated by dividing Tier 1 capital by the bank’s average total consolidated assets. Banks are expected to maintain a leverage ratio in excess of 3% under Basel III
- Liquidity Coverage Ratio: The liquidity coverage ratio (LCR) denotes to highly liquid assets held by financial institutions to meet short-term obligations. The LCR is a requirement under Basel III for a bank to hold high-quality liquid assets (HQLAs) sufficient to cover 100% of its stressed net cash requirements over 30 days. The LCR is calculated as: LCR = HQLAs / Net cash outflows.
- Net stable funding (NSF): The net stable funding is to ensure that banks maintain a stable funding profile in relation to the composition of their assets and off-balance sheet activities.
About Basel III compliant Bonds:
- The bonds qualify as tier II capital of the bank, and has a face value of Rs 10 lakh each, bearing a coupon rate of 6.24 per cent per annum payable annually for a tenor of 10 years.
- There is a call option after 5 years and on anniversary thereafter.
- Call option means the issuer of the bonds can call back the bonds before the maturity date by paying back the principal amount to investors.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) ‘Basel III Accord’ or simply ‘Basel III’, often seen in the news, seeks to: (2015)
- develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity
- improve banking sector’s ability to deal with financial and economic stress and improve risk management
- reduce the greenhouse gas emissions but places a heavier burden on developed countries
- transfer technology from developed countries to poor countries to enable them to replace the use of chlorofluorocarbons in refrigeration with harmless chemicals














