Governance
In News: The Kushiyara river water agreement signed between India and Bangladesh on September 6 2022 is the first major water sharing accord between the two friendly neighbours since the Ganga water treaty in 1996.
- The India-Bangladesh joint river commission met in New Delhi last month after 12 years and agreed on several vital initiatives.
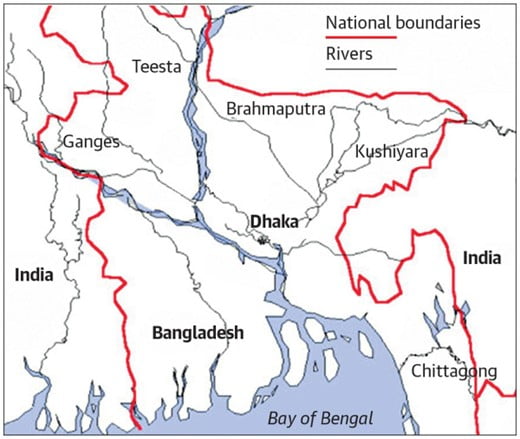
- Kushiyara river is a distributary of the Barak River which originates in the uplands of Assam and flows through it, and then on to Bangladesh.
- Barak River rises in Manipur and is part of Surma-Meghna River System.
- The agreement is aimed to benefit the southern areas of Assam in India and the Sylhet region in Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh will be able to withdraw 153 cusecs (cubic feet per second) of water from the Kushiyara out of the approximately 2,500 cusecs of water that is there in the river during the winter season.
- The water of Kushiyara will be channelled through the Rahimpur Canal project in Sylhet.
Geographical insight:
- Bangladesh and India share a 4,096-kilometre-long (2,545 mi) international border, which is the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- The countries share over 50 rivers such as the main branch of the Ganges known as the Padma River
- Hence, water management remains a contentious issue between the two countries.
Significance
- Help in addressing the major issue of changing nature of the river which unleashes floods in Bangladesh during the monsoon and goes dry during the winter when demand of water goes up because of a crop cycle in Sylhet.
- Benefit to approximately 10,000 hectares of land and millions of people from the water that will flow through a network of canals in Sylhet benefiting the farmers involved in Boro rice – the rice cultivated during the dry season of December to February and harvested in early summer.
- To ensure steady supply of water for irrigation of agriculture fields and orchards of the subdivisions of Sylhet.
- Greater cooperation in flood control
- Strengthening mutual cooperation in combating pollution of common river
- Regular sharing of water-stock data
- Extension of the Ganga treaty beyond its expiry date of 2026
Concerns expressed:
- India objection to the to the Rahimpur Canal of Sylhet which was built to help the farmers access Kushiyara’s water – and claimed that the dyke and other infrastructure interfered in border security.
- Similar pact for Teesta River – which is a tributary of the Brahmaputra, originates in the Teesta Kangse glacier and flows through the state of Sikkim and West Bengal before entering Bangladesh; has been in the works for around a decade and is currently disputed.
- Impact of climate change on South Asian rivers that can affect communities and trigger migration.
- Bangladesh has cited low water flow in its rivers during the winter months as a matter of concern as it affects its agriculture sector
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim
- River Ranjeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3











