Science and Technology
In News: The World Health Organisation (WHO) has released a report: ‘Invisible numbers – the true scale of non-communicable diseases’ on non-Communicable diseases
- WHO has launched a portal, which, for the first time, brings together all WHO data related to NCDs for 194 countries.
- President of the Public Health Foundation of India had described NCDs as a public health emergency in slow motion.
Findings of the report:
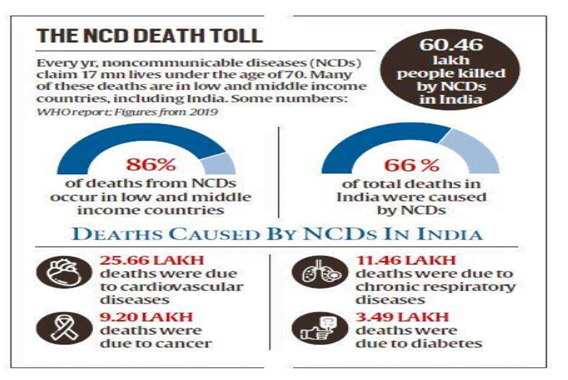
- NCDs led to 66% of deaths in India in 2019
- Further there was a 22 per cent probability of death between the age of 30 and 70
- Over 60.46 lakh people died due to NCDs in India in 2019.
- Every two seconds, one person under the age of 70 dies of a non-communicable disease (NCD) with 86 per cent of those deaths occurring in low- and middle-income countries.
- Non-communicable disease deaths are due to cardiovascular diseases (over 25 lakhs deaths), chronic respiratory disease (over 11 lakhs deaths), diabetes (around 3.5 lakhs deaths), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cancer.
- Diabetes of Type 2 nature accounts for more than 95 per cent of global cases caused due to– tobacco use, unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity, and air pollution.
- Cancer causes one in six deaths – 9.3 million people a year — and 44 per cent of cancer deaths could have been prevented or delayed by eliminating risks to health.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease kills 4.1 million people a year i.e., cause of one in 13 deaths.
- Covid-19 highlighted the links between NCDs and infectious disease, as in the early months of the pandemic, 75 per cent of countries reported disruption to essential NCD services.
About Type 2 diabetes:
- Diabetes is one of the most common NCDs
- Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, or it resists insulin.
- It is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity, lack of exercise, excessive use of alcohol and tobacco and unhealthy lifestyle.
- Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision.
- Treatments include diet, exercise, medication, and insulin therapy.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of egg.
- A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from mother and not from father.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2











