Geography
Gogra-Hotsprings area
In News: India and China announced that their Armies have begun to disengage from Patrolling Point-15 in the Gogra-Hotsprings area of eastern Ladakh, marking a step forward towards ending the stand-off ongoing since May 2020.
Patrolling Point 15 and 17A:
- Along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China, Indian Army has been given certain locations that its troops have access to patrol the area under its control.
- These points are known as patrolling points, or PPs.
- Barring certain areas, like Depsang Plains, these patrolling points are on the LAC, and troops access these points to assert their control over the territory.
- It is an important exercise since the boundary between India and China is not yet officially demarcated.
- PP15 and PP17A are two of the 65 patrolling points in Ladakh along the LAC.
- Both these points are in an area where India and China largely agree on the alignment of the LAC.
- PP15 is located in an area known as the Hot Springs, while PP17A is near an area called the Gogra post.
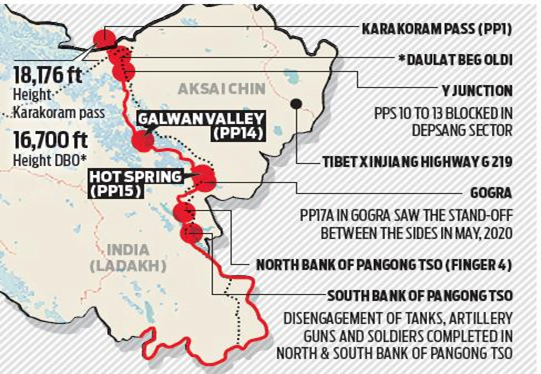
Location of Hot Springs and Gogra Post:
- Hot Springs is just north of the Chang Chenmo river and Gogra Post is east of the point where the river takes a hairpin bend coming southeast from Galwan Valley and turning southwest.
- The area is north of the Karakoram Range of mountains, which lies north of the Pangong Tso lake, and south east of Galwan Valley.
Importance
- The area lies close to Kongka Pass, one of the main passes, which, according to China marks the boundary between India and China.
- India’s claim of the international boundary lies significantly east, as it includes the entire Aksai Chin area as well.
- Hot Springs and Gogra Post are close to the boundary between two of the most historically disturbed provinces (Xinjiang and Tibet) of China.
Galwan Valley
- The valley refers to the land that sits between steep mountains that buffet the Galwan River.
- The river has its source in Aksai Chin, on China’s side of the LAC, and it flows from the east to Ladakh, where it meets the Shyok river on India’s side of the LAC.
- The valley is strategically located between Ladakh in the west and Aksai Chin in the east, which is currently controlled by China as part of its Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region.
Chang Chenmo River
- Chang Chenmo River or Changchenmo River is a tributary of the Shyok River, part of the Indus River system.
- It is at the southern edge of the disputed Aksai Chin region and north of the Pangong Lake basin.
- The source of Chang Chenmo is near the Lanak Pass.
Kongka Pass
- The Kongka Pass or Kongka La is a low mountain pass over a hill that intrudes into the Chang Chenmo Valley. It is in the disputed India-China border area in Ladakh.
Karakoram Range
- A mountain range in Kashmir spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan.
- Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the jurisdiction of Gilgit-Baltistan which is controlled by Pakistan.
- Highest peak (and world’s second highest), K2, is located in Gilgit-Baltistan.
- Begins in the Wakhan Corridor (Afghanistan) in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, and extends into Ladakh (controlled by India) and Aksai Chin (controlled by China).
- One of the world’s most geologically active areas, at the plate boundary between the Indo-Australian plate and the Eurasian plate.
- Maximum development of glaciers occurs in the Karakoram range. This range accounts for about 16,000 sq km or about half of the snow bound area of the Himalayan region.
Location:
- Bounded on the east by the Aksai Chin plateau
- On the northeast by the edge of the Tibetan Plateau
- On the north by the river valleys of the Yarkand and Karakash rivers beyond which lie the Kunlun Mountains.
- At the northwest corner are the Pamir Mountains.
- The southern boundary of the Karakoram is formed, west to east, by the Gilgit, Indus and Shyok rivers, which separate the range from the northwestern end of the Himalaya range proper.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
- East of Aksai Chin
- East of Leh
- North of Gilgit
- North of Nubra Valley











