Environment & Ecology
In news: With winter around the corner, air pollution levels rise at an alarming rate.
Concerns:
- Stubble burning, vehicular emissions, construction activities, fire crackers contribute to degrading air quality.
- These can lead to breathing issues and aggravate diseases and health conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), respiratory infections and cardiovascular diseases.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has declared air pollution as a public health emergency and more than 90 per cent of the global pollution is enduring toxic, polluted outdoor air.
- Smog is a mixture of smoke and air pollution, can damage lungs.
- Smog can comprise airborne particulate matter, mostly PM 2.5 and PM 10, that can have adverse health effects.
About PM2.5:
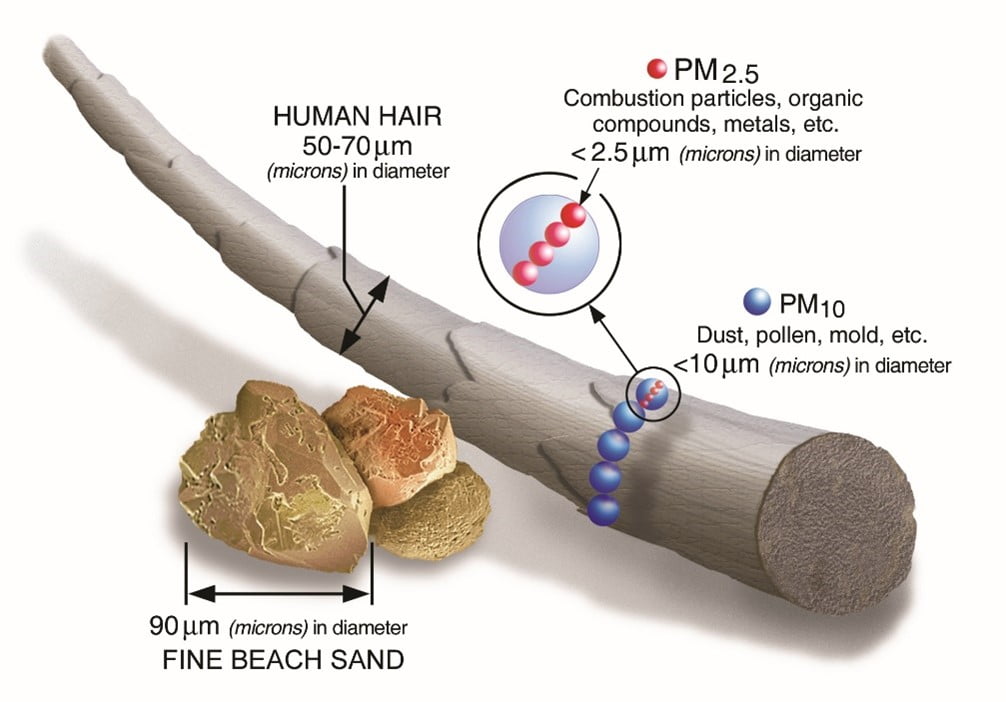
- It is a fine, inhalable particle, generally 2.5 micrometres of diameter or smaller.
- PM 2.5 have small diameters but they can spread over large surface areas.
- Due to its smaller size, the particulate matter can be drawn deep in the lungs and can be more harmful as compared to PM 10.
- It can penetrate the lung deeply, irritate and corrode the epithelial walls and consequently impair lung function.
- The combustion of gasoline, oil, diesel fuel or wood produces much of the PM 2.5.
- They are capable of carrying various toxic stuff, passing through the filtration of nose hair, reaching the end of the respiratory tract with airflow and accumulating there by diffusion, damaging other parts of the body through air exchange in the lungs.
- PM 2.5 was one of the causative factors of human non-accidental death, particularly in the elderly.
About PM10:
- It is an inhalable particle, generally with 10 micrometres of diameter or smaller.
- It includes dust from construction site, landfills, agriculture, waste burning and so on.
- These particles settle and get deposited in the lungs.
- The larger size of particulate matter means it gets trapped mostly in the nose, mouth or throat, causing irritation of mucous membranes.
- The exposure of particulate PM 10 is associated with worsening of respiratory diseases like asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
Impacts of air pollution:
- While it is a common notion that air pollution mostly affects lungs, other body organs too can be damaged due to continuous exposure to polluted air.
- Air pollution can damage skin and cause premature ageing and problems like rashes, wrinkles, discoloration, pigmentation and so on.
- Exposure to polluted outdoor air has been proven to be harmful to the human eye. Common eye problems caused by pollution are watery eyes, soreness, redness, itching sensation, dry eyes and allergy.
- Other than this, air pollution can have adverse effects on the cardiovascular, nervous, digestive and urinary systems.
- Due to air pollution, there have been increasing cases of heart diseases and cancer.
About Air Quality Index (AQI) levels:
- It is a daily measure of the quality of air to calculate or measure how air pollution affects health and help people become more aware, especially those who suffer from serious or chronic illnesses caused by exposure to pollutants.

Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Photochemical smog is a resultant of the reaction among (2013)
- NO2, O3 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
- CO, O2 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
- CO, CO2 and NO2 at low temperature
- High concentration of NO2, O3 and CO in the evening
Q.2) In the context of WHO Air Quality Guidelines, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m3 and annual mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 5 ug/m3.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above are correct ?
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only











