International Relations
In News: The U.S. Congressional amendment to the National Defense Authorization Act states that India faces immediate and serious regional border threats from China, with continued military aggression by the Chinese people along the India-China border.
About India-US relations:
- The U.S.-India strategic partnership is founded on shared values including a commitment to democracy and upholding the rules-based international system.
- There are more than 50 bilateral dialogue mechanisms between the two governments.
- Despite COVID-19 pandemic, India-U.S. cooperation witnessed intense engagement under various bilateral dialogue mechanisms in wide range of areas including defence, security, health, trade, economic, science & technology, energy and people-to-people ties.
Political relations:
- The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue is the premier recurring dialogue mechanism between the countries. U.S. hosted the fourth 2+2 Dialogue in 2022.
- The United States welcomed India joining the UN Security Council in 2021 for a two-year term and supports a reformed UN Security Council that includes India as a permanent member.
- India and the US jointly proposed to list Makki, a top LeT (Lashkar-e-Taiba) Militant, under the UN Security Council’s Al-Qaeda and ISIL (Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant) Sanctions Committee which is also known as the UNSC 1267 Committee.
- Quad is a strategic security dialogue between Australia, India, Japan, and the United States and is viewed as a response to increased Chinese economic and military power.
- There have been regular parliamentary exchanges and high-level visits to strengthen ties of friendship and cooperation – External Affairs Minister’s visit in September 2022, PM Modi’s visit in 2021 and Donald Trump’s visit to India in 2020.
Defence relations:
- India-US defence cooperation is based on “New Framework for India-US Defence Cooperation”, which was renewed for a period of ten years in 2015.
- A strong United States-India defence partnership is rooted in shared democratic values and is critical to advancing United States interests in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Defence procurements from the US have been an area of steady growth in the last decade. India has procured defence items of around US$ 21 billion from the US since 2008.
- India-specific waiver under CAATSA – will allow India to freely purchase Russia’s S-400 missile system without the fear of American sanctions.
- Defence agreements include The Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement, or BECA (2020) on sharing sensitive satellite data and allowing US’s strategic partners to access a range of sensitive geospatial and aeronautical data which is useful for military actions. Other agreements include Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Association (LEMOA 2016) and COMCASA.
- Both countries setup Counter-Narcotics Working Group which met for the first time virtually on 24 November 2020.
- India-US Cyber Framework signed in 2016, provides for expanding cooperation in cyber domain.
- India-US military exercises include Yudh Abhyas, Vajra Prahar, Cope India, MALABAR, Red Flag and RIMPAC.
Economic relations:
- The U.S. is India’s largest trading partner and most important export market.
- In 2021, overall U.S.-India bilateral trade in goods and services reached a record $157 billion. Major export items from India include petroleum, polished diamonds, pharmaceutical products, jewellery, frozen shrimp, whereas major imports from the US include petroleum, rough diamonds, liquified natural gas, gold, coal, waste and scrap, almonds and so on.
- In 2021-22, India had a trade surplus of $32.8 billion with the US.
- During financial year 2020-21, India received the highest ever FDI amounting to $81.72 billion, as per Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- US is one of the top 5 investment destinations for Indian FDI. At 2020, Indian investment in the United States totalled $12.7 billion, supporting over 70,000 American jobs.
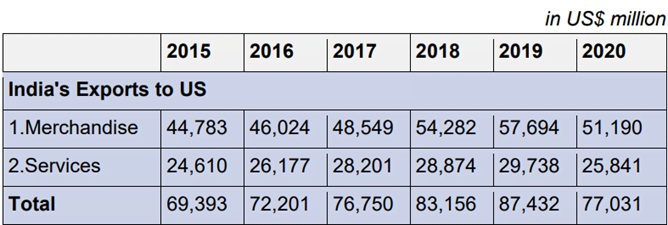
Bilateral dialogues:
- India is one of twelve countries partnering with the United States on the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) to make our economies more connected, resilient, clean, and fair.
- India-U.S. Trade Policy Forum: Established in 2005, it serves as the leading bilateral mechanism. The 11th Meeting was held in 2017.
- India-U.S. Commercial Dialogue: focuses on cooperation in areas such as standards, ease of doing business, travel & tourism. The meeting is chaired by the Minister of Commerce & Industry and the U.S. Secretary of Commerce.
Indian Diaspora:
- About 4.2 million Indian Americans/Indian origin people reside in the US. The Indian Americans constitute the third largest Asian ethnic group in the US.
- There are a number of Indian American community organizations as well as several professional organizations of Indian Americans.
- Indian Americans are one of the most successful immigrant communities in the US and are excelling in diverse fields, including politics.
- The Indian diaspora has been a catalyst in cementing closer ties between India and the U.S.
- The nearly 200,000 Indian students in the United States contribute $7.7 billion annually to the U.S. economy.
- U.S. accounts for 23% of total remittances in 2020-21.
Science & Environment:
- In 2021, U.S. joined the International Solar Alliance headquartered in India, and in 2022 the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) Administrator became Co-chair of the Governing Council of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) where India is a permanent co-chair.
- Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies is a collaboration between engineers, computer scientists, governments, academia, and industry. It is vital to address the latest advances in artificial intelligence, quantum computing, biotechnology, aerospace, and semiconductor manufacturing and to help foster innovation and facilitate technological advances that continue to far outpace the technology of the Russia and China.
- At the Leaders’ Summit on Climate held in 2021, “U.S.- India Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 Partnership,” was launched which envisages bilateral cooperation on strong actions in the current decade to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement.
Challenges:
- US-Pakistan friendship: US decided to provide a $450-million sustenance package for Pakistan’s aging F-16 fleet.
- US sanctions: targeted an India-based petrochemical company for selling Iranian petroleum products to China.
- Russia-Ukraine conflict: Due to India’s neutral stance, the US reiterated India’s position as “unsatisfactory” but “unsurprising” due to its historical relationship with Russia
- Concern of China: China has been opposing the U.S.’ proactive policy specifically in the disputed South China Sea and thus reducing India’s chances of forming a favourable partner in the area.
Way forward:
- Such a partnership between the world’s oldest and largest democracies is critical and should continue to be strengthened in response to increasing threats in the Indo-Pacific region so as to send an unequivocal signal that sovereignty and international law must be respected.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently told President Vladimir Putin that “today’s era is not of war” on account of Russia-Ukraine conflict and the US was pleased with the formulation and its articulation in full public glare.
Source: The Hindu











