Science and Technology
In news: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing a rocket named Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) to replace its ageing workhorse the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- ISRO to develop a ‘Bharat Krishi satellite’ to study the growth pattern of crops, identify irrigation deficiencies and provide information that will help in pest-control and verification of farm insurance claims besides many other applications.
- ISRO is also exploring the possibility of increasing civilian use of the country’s indigenous satellite navigation system NaVIC.
About NGLV:
- NGLV will use ‘semi-cryogenic’ technology which is both efficient and cost-effective.
- The new rocket could also be ‘reusable’. A reusable rocket will have a smaller payload than an expendable one. If it is reusable, the payload will be around five tonnes and if it’s expendable, it will go up 10 tonnes.
- Participation of the industry would ensure that capability is created outside ISRO to build, operate and launch it on a commercial basis.
About PSLV technology:
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- It is a four-staged launch vehicle with first and third stage using solid rocket motors and second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
- The PS4 is the uppermost stage of PSLV, comprising of two Earth storable liquid engines.
- The third stage of PSLV is a solid rocket motor that provides the upper stages high thrust after the atmospheric phase of the launch.
- PSLV uses an Earth storable liquid rocket engine for its second stage, know as the Vikas engine, developed by Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
- PSLV uses the S139 solid rocket motor that is augmented by 6 solid strap-on boosters.
- PSLV uses 6 solid rocket strap-on motors to augment the thrust provided by the first stage in its PSLV-G and PSLV-XL variants. However, strap-ons are not used in the core alone version (PSLV-CA).
- Initially, PSLV had a carrying capacity of 850 kg but has been enhanced to 1.9 tonnes.
- It comes in the category of medium-lift launchers with a reach up to various orbits, including the Geo Synchronous Transfer Orbit, Lower Earth Orbit, and Polar Sun Synchronous Orbit.
- All the operations of PSLV are controlled from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
MUST READ: Indigenisation of PSLV technology
About GSLV technology:
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) is an expendable space launch vehicle designed, developed, and operated by ISRO to launch satellites and other space objects into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits.
- GSLV is 49.13 m tall and tallest among all other vehicles of ISRO.
- It is a three-stage vehicle with a lift-off mass of 420 tonnes.
- Stages in GSLV
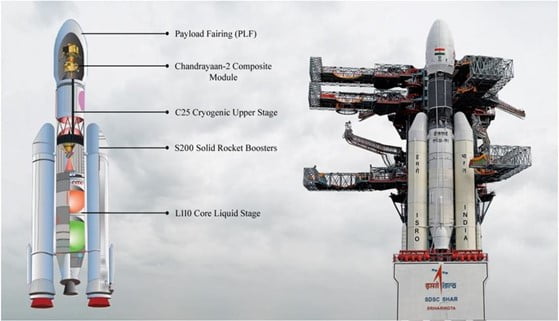
- First stage – comprises S139 solid booster with 138-tonne propellant and four liquid strap-on motors, with 40-tonne propellant.
- Second stage – is a liquid engine carrying 40-tonne of liquid propellant.
- Third stage – is the indigenously built Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) carrying 15-tonne of cryogenic propellants.
- GSLV rockets using the Russian Cryogenic Stage (CS) are designated as the GSLV Mk I while versions using the indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) are designated the GSLV Mk II.
- All GSLV launches have been conducted from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- GSLV has the capability to put a heavier payload than PSLV.
- PSLV can carry satellites up to a total weight of 2000 kg into space and reach up to an altitude of 600-900 km. GSLV can carry weight up to 5,000 kg and reach up to 36,000 km.
- PSLV is designed mainly to deliver earth observation or remote sensing satellites, whereas, GSLV has been designed for launching communication satellites.
- GSLV delivers satellites into a higher elliptical orbit, Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO).
- Mission Chandrayan-2 was launched by GSLV Mk-III
MUST READ: NaVIC
Source: New Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only













