Environment & Ecology
Context: The Uttar Pradesh (UP) cabinet recently approved the notification of the state’s fourth tiger reserve in the Ranipur Wildlife Sanctuary (RWS) in Chitrakoot district.
About Ranipur Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Ranipur Wildlife Sanctuary, was founded in 1977.
- This will be the fourth tiger reserve in the state to be developed, after Dudhwa, Pilibhit, and Amangarh.
- RWS has no tigers of its own. But it is an important corridor for the movement of tigers.
- The Ranipur Tiger Reserve has tropical dry deciduous forests and is home to fauna such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, spotted deer, sambhar, chinkara and a number of birds and reptiles.
- It will also be the first in the state’s portion of the Bundelkhand region, which it shares with neighbouring Madhya Pradesh.
- There are 53 Tiger Reserves in India spread across India.
- There were 2,967 tigers in India according to the National Tiger Conservation Authority estimation in 2018.
About National Tiger Conservation Authority:
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change constituted under enabling provisions of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as amended in 2006, for strengthening tiger conservation.
- The authority consists of the Minister in charge of the Ministry of Environment and Forests ( as Chairperson), the Minister of State in the Ministry of Environment and Forests (as Vice-Chairperson), three members of Parliament, Secretary, Ministry of Environment and Forests and other members.
- The ‘Project Tiger’ is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, providing funding support to tiger range States for in-situ conservation of tigers in designated tiger reserves.
- The objectives of NTCA are:
- Providing statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance of its directives become legal.
- Fostering accountability of Centre-State in management of Tiger Reserves, by providing a basis for MoU with States within our federal structure.
- Providing for an oversight by Parliament.
- Addressing livelihood interests of local people in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
Map showing locations of Tiger Reserves in India
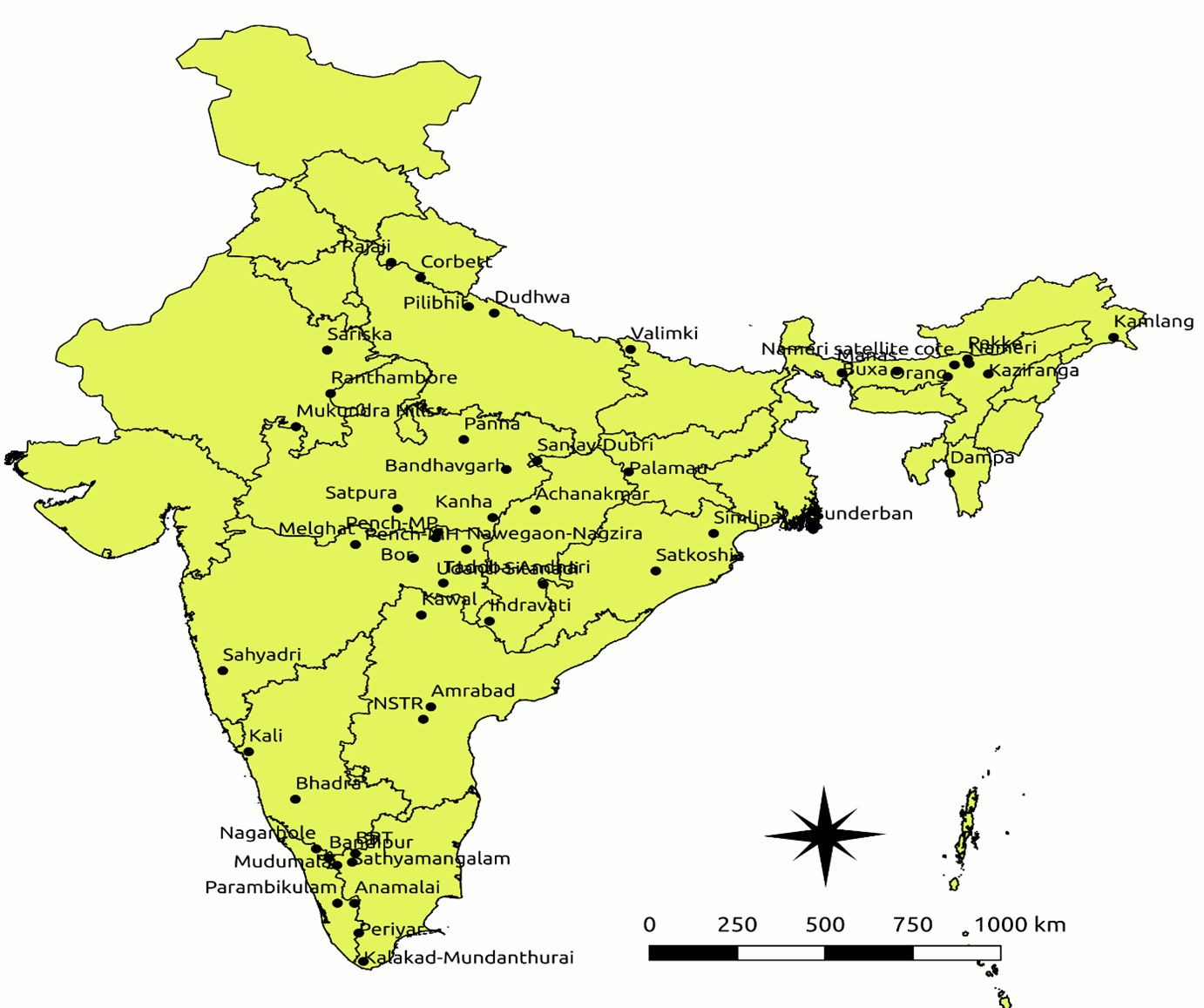
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
- Corbett
- Ranthambore
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
- Sundarbans
Q.2) The term M-STrIPES’ is sometimes seen in news in the context of (2017)
- Captive breeding of Wild Fauna
- Maintenance of Tiger Reservoirs
- Indigenous Satellite Navigation System
- Security of National Highways
Q.3) Consider the following statements :
- Animal Welfare Board of India is established under the Environments (Protection) Act, 1986
- National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body
- National Ganga River Basin Authority is chaired by the Prime Minister
Which if the statements given above is/are correct? (2014)
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3











