Geography
Context: Recently residents across western and northern New York are bracing for historic “lake-effect snow,” a storm set to engulf most of the region in a crippling white cloak.
How does lake-effect snow form?
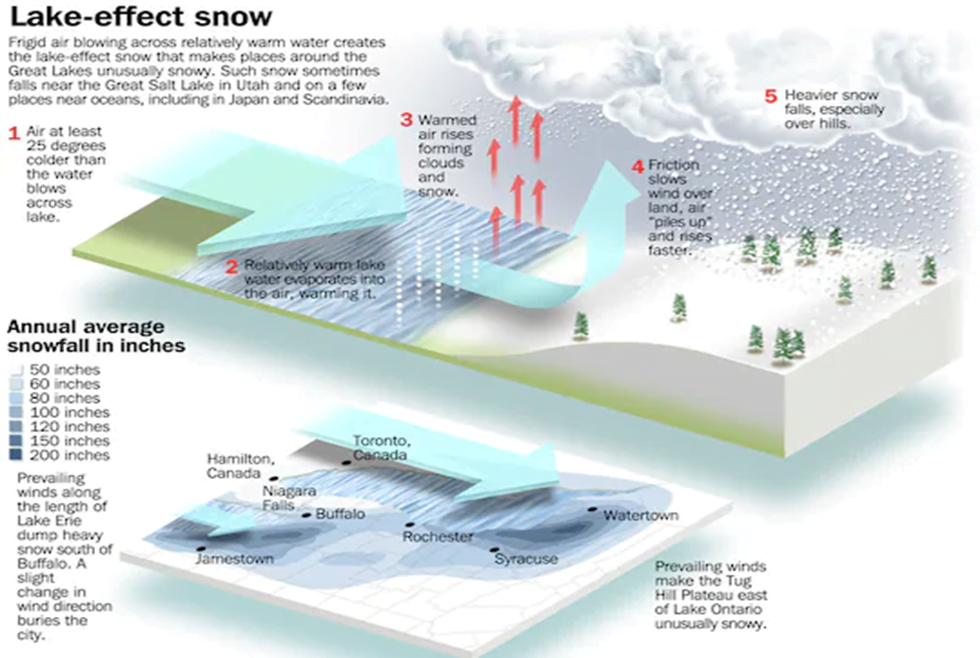
- Lake-effect snow forms when dry, freezing air picks up moisture and heat as it moves along warmer lake water.
- This causes some of the lake water to evaporate into the air, causing the air to be warmer and wetter.
- As the air cools and moves from the lake, it dumps all the moisture on the ground. When it’s cold enough, it results in a massive dumping of snow.
- The perfect recipe for lake-effect storms occurs during the late fall and early winter, when there is the largest difference between the warm lake water and the colder air moving over it.
- The bigger the temperature difference, the heavier the storm.
Will climate change affect lake-effect snow?
- Human-caused climate change has the potential to intensify lake-effect snow events, at least in the short term, according to the NOAA’s U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit.
- “Ice cover extent and lake water temperatures are the main controls on lake-effect snow that falls downwind of the Great Lakes,”.
- The predictions change once lake temperatures rise to a point when much of what now falls as snow will instead fall as rain.”
- Lake-effect snow frequently pummels the Great Lakes with feet of wet snow that can trap people in their homes and covers cars.


Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert? (2022)
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Faguibine
- Lake Oguta
- Lake Volta











