Science and Technology
Context: In 1922. On December 8th, the International Anthrax Commission has passed a resolution requiring the hairs and wools used in brush-making, upholstering and textile industries be disinfected before they are handled industrially.
About Anthrax:
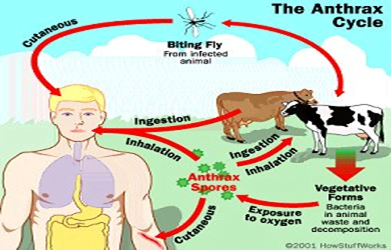
- Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could be transferred from animals to humans) caused by the spore-producing bacterium Bacillus anthracis.
- Reservoirs are grass-eating animals, and the spores can survive in the environment for decades.
- It is usually a disease of wild and domestic animals, including cattle, sheep, and goats.
- Human infection, while rare, does occur.
- Human infection usually results from contact with infected animals or their products.
Types of Anthrax:
- cutaneous (through the skin),
- gastrointestinal, and
- There have been no confirmed cases of person-to-person transmission of cutaneous, gastrointestinal, or inhalational anthrax.
- Anthrax is most common in developing countries.
- The largest reported agricultural outbreak occurred in Zimbabwe, with more than 10,000 cases reported between 1979 and 1985.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics, such as penicillin, are used to treat all forms of anthrax.
- An antibiotic known as ciprofloxacin (Cipro) was approved in August 2000 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating people who have been exposed to inhalational anthrax.
Source: The Hindu











